Electrolyte Blood Press.
2019 Dec;17(2):36-44. 10.5049/EBP.2019.17.2.36.
Association of Blood Pressure at Specific Time-Points with 1-Year Renal Outcomes in Patients with Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Cheju, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. imsejoong@hanmail.net
- 7Kidney Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2467959
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2019.17.2.36
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
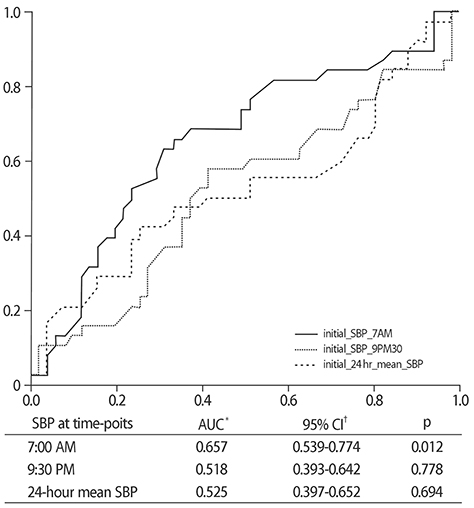
The 24-hour mean blood pressure (mBP) is the best predictor of organ damage; however, it is not easily applicable in clinical practice. The APrODiTe study suggested that systolic blood pressure (SBP) values at 7:00 AM and 9:30 PM were associated with the 24-hour mSBP in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). We investigated the association of the SBP values at these time-points with the renal outcomes in patients with diabetic CKD during 1-year follow-up.
METHODS
Ninety-six patients with diabetic CKD were included at 1-year follow-up. The renal outcomes were an increase in the random urine protein/creatinine ratio or estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) deterioration, which means a decrease in eGFR ≥5 mL/min/1.73 m² compared to the baseline values.
RESULTS
The baseline SBP values at 7:00 AM, and 9:30 PM, and the 24-hour mSBP were 135.6±24.9 mmHg, 141.7±25.6 mmHg, and 136.4±20.7 mmHg, respectively. The SBP values measured at the same time-points after 1 year were similar to those at baseline. The SBP at 7:00 AM was significantly associated with eGFR deterioration in the univariate and multivariate analyses (odds ratio [OR]: 1.032; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.006-1.059; p=0.016). The SBP at 7:00AM and 24-hour mSBP did not show a concordant association with sustained proteinuria in the linear and logistic analyses. In the subgroup analysis, the association between the SBP at 7:00 AM and eGFR deterioration persisted in patients with CKD stage 3-5 (OR: 1.041; 95% CI: 1.010-1.073; p=0.010).
CONCLUSION
The SBP at 7:00 AM, in addition to the 24-hour mSBP, is also associated with eGFR deterioration in patients with diabetic CKD, particularly in those with CKD stage 3-5.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schrier RW, Estacio RO, Mehler PS, Hiatt WR. Appropriate blood pressure control in hypertensive and normotensive type 2 diabetes mellitus: a summary of the ABCD trial. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007; 3:428.
Article2. Mogensen CE, Christensen CK. Blood pressure changes and renal function in incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension. 1985; 7:Ii64–Ii73.
Article3. Bakris GL, Williams M, Dworkin L, et al. Preserving renal function in adults with hypertension and diabetes: a consensus approach. National Kidney Foundation Hypertension and Diabetes Executive Committees Working Group. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000; 36:646–661.
Article4. Parving HH, Andersen AR, Smidt UM, Svendsen PA. Early aggressive antihypertensive treatment reduces rate of decline in kidney function in diabetic nephropathy. Lancet. 1983; 1:1175–1179.
Article5. Wright JT Jr, Bakris G, Greene T, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease: results from the AASK trial. JAMA. 2002; 288:2421–2231.
Article6. Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL. Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004; 15:1983–1992.
Article7. Dhaun N, Macintyre IM, Melville V, et al. Blood pressure-independent reduction in proteinuria and arterial stiffness after acute endothelin-a receptor antagonism in chronic kidney disease. Hypertension. 2009; 54:113–119.
Article8. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004; 43:S1–S290.9. Parati G, Stergiou G, O'Brien E, et al. European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J Hypertens. 2014; 32:1359–1366.10. Minutolo R, Borrelli S, Scigliano R, et al. Prevalence and clinical correlates of white coat hypertension in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007; 22:2217–2223.
Article11. Bangash F, Agarwal R. Masked hypertension and white-coat hypertension in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 4:656–664.
Article12. Mancia G, Parati G. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and organ damage. Hypertension. 2000; 36:894–900.
Article13. Minutolo R, Agarwal R, Borrelli S, et al. Prognostic role of ambulatory blood pressure measurement in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease. Arch Intern Med. 2011; 171:1090–1098.
Article14. Kim IY, Song SH. Blood pressure measurement in patients with chronic kidney disease: from clinical trial to clinical practice. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2019; 38:138–140.
Article15. Ryu J, Cha RH, Kim DK, et al. Time points for obtaining representative values of 24-hour blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med. 2015; 30:665–674.
Article16. Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, et al. KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014; 63:713–735.
Article17. Lee CS, Cha R-h, Lim Y-H, et al. Ethnic coefficients for glomerular filtration rate estimation by the modification of diet in renal disease study equations in the Korean population. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1616–1625.
Article18. Andersen MJ, Khawandi W, Agarwal R. Home blood pressure monitoring in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005; 45:994–1001.
Article19. Agarwal R, Andersen MJ. Correlates of systolic hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease. Hypertension. 2005; 46:514–520.
Article20. O'Brien E, Asmar R, Beilin L, et al. European Society of Hypertension recommendations for conventional, ambulatory and home blood pressure measurement. J Hypertens. 2003; 21:821–848.21. Alborzi P, Patel N, Agarwal R. Home blood pressures are of greater prognostic value than hemodialysis unit recordings. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 2:1228–1234.
Article22. Fagard RH, Van Den Broeke C, De Cort P. Prognostic significance of blood pressure measured in the office, at home and during ambulatory monitoring in older patients in general practice. J Hum Hypertens. 2005; 19:801–807.
Article23. Elliot WJ. Cyclic and circadian variations in cardiovascular events. Am J Hypertens. 2001; 14:291s–295s.24. Kamoi K, Miyakoshi M, Soda S, Kaneko S, Nakagawa O. Usefulness of home blood pressure measurement in the morning in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:2218–2223.
Article25. Kario K, Pickering TG, Hoshide S, et al. Morning blood pressure surge and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease: role of the alpha adrenergic sympathetic nervous system. Am J Hypertens. 2004; 17:668–675.
Article26. Kuriyama S, Otsuka Y, Iida R, Matsumoto K, Tokudome G, Hosoya T. Morning blood pressure predicts hypertensive organ damage in patients with renal diseases: effect of intensive antihypertensive therapy in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Intern Med. 2005; 44:1239–1246.
Article27. Spallone V, Bernardi L, Ricordi L, et al. Relationship between the circadian rhythms of blood pressure and sympathovagal balance in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1993; 42:1745–1752.
Article28. Sturrock ND, George E, Pound N, Stevenson J, Peck GM, Sowter H. Non-dipping circadian blood pressure and renal impairment are associated with increased mortality in diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2000; 17:360–364.
Article29. White WB. Cardiovascular risk and therapeutic intervention for the early morning surge in blood pressure and heart rate. Blood Press Monit. 2001; 6:63–72.
Article30. Turin TC, Coresh J, Tonelli M, et al. Change in the estimated glomerular filtration rate over time and risk of all-cause mortality. Kidney Int. 2013; 83:684–691.
Article31. Turin TC, Coresh J, Tonelli M, et al. One-year change in kidney function is associated with an increased mortality risk. Am J Nephrol. 2012; 36:41–49.
Article32. Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I, et al. Home blood pressure measurement has a stronger predictive power for mortality than does screening blood pressure measurement: a population-based observation in Ohasama, Japan. J Hypertens. 1998; 16:971–975.
Article