J Clin Neurol.
2019 Oct;15(4):583-584. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.583.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy in a Patient with Pantothenate-Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. koodaelim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2467774
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.4.583
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
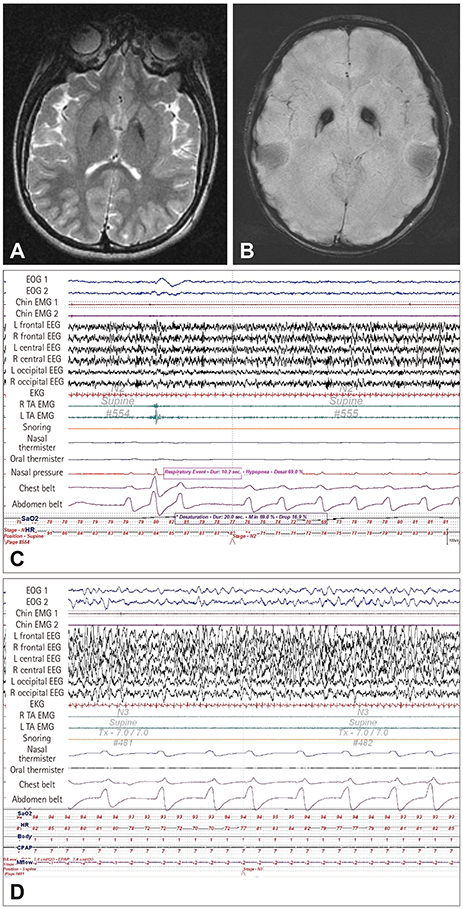
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gregory A, Hayflick SJ. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. In : Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K, editors. GeneReviews. Seattle: University of Washington;1993.2. McCarty SF, Gaebler-Spira D, Harvey RL. Improvement of sleep apnea in a patient with cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 80:540–542.
Article3. Marchese-Ragona R, Vianello A, Restivo DA, Pittoni G, Lionello M, Martini A, et al. Sleep-related adductor laryngeal dystonia causing sleep apnea: a sleep-related breathing disorder diagnosed with sleep endoscopy and treated with botulinum toxin. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:1560–1563.4. Koo DL, Nam H, Thomas RJ, Yun CH. Sleep disturbances as a risk factor for stroke. J Stroke. 2018; 20:12–32.
Article5. Fantini ML, Cossu G, Molari A, Cabinio M, Uyanik O, Cilia R, et al. Sleep in genetically confirmed pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration: a video-polysomnographic study. Parkinsons Dis. 2010; 2010:342834.
Article6. Hogarth P, Kurian MA, Gregory A, Csányi B, Zagustin T, Kmiec T, et al. Consensus clinical management guideline for pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN). Mol Genet Metab. 2017; 120:278–287.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel PANK2 Mutation in a Patient with Atypical Pantothenate-Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration Presenting with Adult-Onset Parkinsonism
- Treatment of Pantothenate-Kinase Neurodegeneration With Baclofen, Botulinum Toxin, and Deferiprone: A Case Report
- Botulinum Toxin-A Injection in the Treatment of Spasticity in a Infantile-Onset Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation: A Case Report
- Three Patients With Classic and Atypical Neurodegeneration With Brain Iron Accumulation
- The Case of a Patient with Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration Presenting with a Prolonged History of Stuttering Speech and a Misdiagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease