J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2018 Dec;44(6):293-297. 10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.6.293.
Palatal rhinosporidiosis: an unusual case report and review of the literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Institute of Dental Sciences, Rohilkhand University, Bareilly, India.
- 2Department of Oral Biology, Faculty of Dentistry, Taif University, Taif, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. drmanju26@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2467177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2018.44.6.293
Abstract
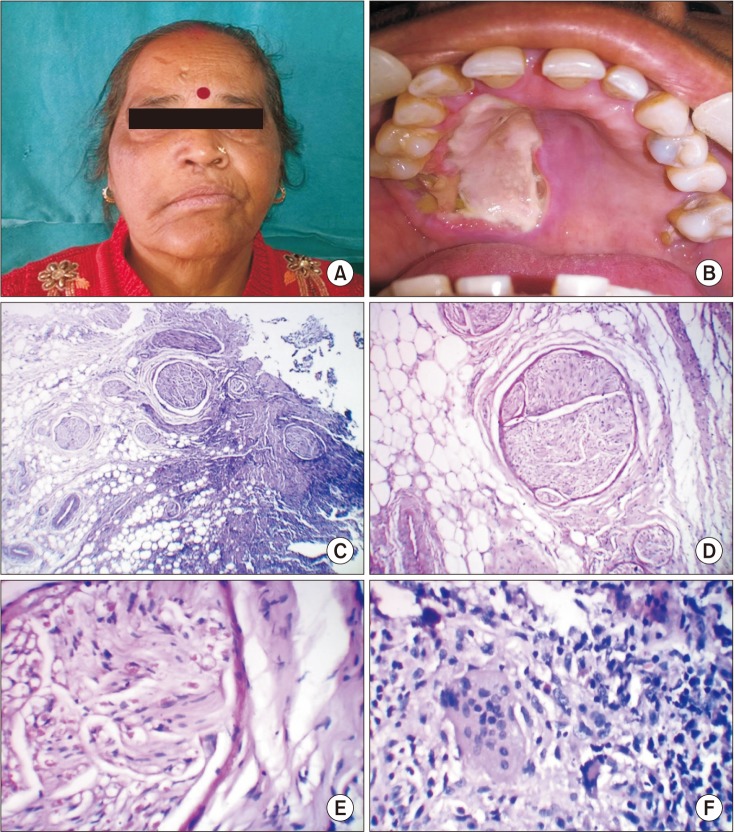
- Rhinosporidiosis is a chronic, granulomatous, mucocutaneous infection caused by Rhinosporidium seeberi . The infection is non-contagious and sporadic in humans. The site most commonly affected is the mucous membrane of the nose and nasopharynx, followed by the oropharynx, trachea, bronchi, ear, eye, and genitourinary tract. It can also spread to other areas through blood and lymph. Here, we report a case of rhinosporidiosis affecting the palate in a 60-year-old female patient.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sefu U, Fauzia A. Human nasal rhinosporidiosis: a case report from Malawi. Pan Afr Med J. 2011; 9:27. PMID: 22355433.
Article2. Tiwari R, Karthik K, Dhama K, Shabbir MZ, Khurana SK. Rhinosporidiosis: a riddled disease of man and animals. Adv Anim Vet Sci. 2015; 3(2S):54–63.
Article3. Morelli L, Polce M, Piscioli F, Del Nonno F, Covello R, Brenna A, et al. Human nasal rhinosporidiosis: an Italian case report. Diag Pathol. 2006; 1:25.
Article4. Das S, Kashyap B, Barua M, Gupta N, Saha R, Vaid L, et al. Nasal rhinosporidiosis in humans: new interpretations and a review of the literature of this enigmatic disease. Med Mycol. 2011; 49:311–315. PMID: 20954821.
Article5. Babu S, Anuradha A, Chandra S, Kashyap B. Rhinosporidiosis: a case report with review of literature. Ann Trop Med Public Health. 2012; 5:127–129.
Article6. Nambiar SS, Radhakrishnan S, Vijayan A. Rhinosporidiosis: report of an extra-ductal facial lesion. IDCases. 2017; 7:40–43. PMID: 28070493.
Article7. Kindo AJ, Kalyani J, Sundaram S, Kannan S, Kumar AR. Unusual presentation of rhinosporidiosis: a case report. Sri Ramchandra J Med. 2007; 1:60–61.8. Bhumbla U, Mathur DR. Nasal rhinosporidiosis: a case report. Int J Innov Res Dev. 2014; 3:149–151.9. Kumari R, Laxmisha C, Thappa DM. Disseminated cutaneous rhinosporidiosis. Dermatol Online J. 2005; 11:19.
Article10. Vilela R, Mendoza L. The taxonomy and phylogenetics of the human and animal pathogen Rhinosporidium seeberi: a critical review. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2012; 29:185–199. PMID: 22504725.
Article11. Monnaf MH. Rhinosporidiosis: definition, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigation, treatment [Internet]. EasyMBBS;updated 2013 Jun 13. cited 2017 Sep 13. Available from: http://www.easymbbs.org/rhinosporidiosis-definition-pathogenesis-clinical-features-investigation-treatment/.12. Nayak S, Acharjya B, Devi B, Sahoo A, Singh N. Disseminated cutaneous rhinosporidiosis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007; 73:185–187. PMID: 17558053.
Article13. Arseculeratne SN. Recent advances in rhinosporidiosis and Rhinosporidium seeberi. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002; 20:119–131. PMID: 17657050.
Article14. Herr RA, Ajello L, Taylor JW, Arseculeratne SN, Mendoza L. Phylogenetic analysis of Rhinosporidium seeberi's 18S small-subunit ribosomal DNA groups this pathogen among members of the protoctistan Mesomycetozoa clade. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:2750–2754. PMID: 10449446.15. von Haacke NP, Mugliston TA. Rhinosporidiosis. J Laryngol Otol. 1982; 96:743–750. PMID: 7108362.
Article16. Hussein MR, Rashad UM. Rhinosporidiosis in Egypt: a case report and review of literature. Mycopathologia. 2005; 159:205–207. PMID: 15770444.
Article17. Ngamdu YB, Ngadda HA, Kodiya AM, Sandabe MB, Isa A, Garandawa HI. Nasal rhinosporidiosis: a case report and review of literature. J Case Rep. 2014; 4:26–28.
Article18. Sivapathasundharam B, Saraswathi TR, Manjunath K, Sriram G. Rhinosporidiosis of parotid duct. Indian J Dent Res. 2009; 20:388–389. PMID: 19884731.
Article19. Rajeshwari A, Gangadhara S, Deviprasad S, Manohar S. Rhinosporidiosis—a report of two cases. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 62:322–325. PMID: 23120734.20. Burgess HJ, Lockerbie BP, Czerwinski S, Scott M. Equine laryngeal rhinosporidiosis in western Canada. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012; 24:777–780. PMID: 22604769.
Article21. Yadav SK, Shrestha S. Rhinosporidiosis of the parotid duct. Case Rep Dent. 2014; 2014:131794. PMID: 24592336.
Article22. Fouzia B, Ali SI, Gyaneshwari S. Nasal rhinosporidiosis: a case study. J Med Microbiol Diagn. 2015; 4:1–2.
Article23. Maruf Raza AKM, Bordhon A, Roy P. Rhinosporidiosis of parotid duct. Middle East J Case Rep. 2016; 1:1–3.24. John D, Selvin SST, Irodi A, Jacob P. Disseminated rhinosporidiosis with conjunctival involvement in an immunocompromised patient. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2017; 24:51–53. PMID: 28546693.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Rhinosporidiosis of the Nasal Cavity
- Detection of maxillary second molar with two palatal roots using cone beam computed tomography: a case report
- Congenital Palatal Fistula with Submucous Cleft Palate
- Radix mesiolingualis and radix distolingualis: a case report of a tooth with an unusual morphology
- A Case of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor