Imaging Sci Dent.
2019 Dec;49(4):301-306. 10.5624/isd.2019.49.4.301.
Power Doppler ultrasound-guided sialography using the phenomenon of increased blood flow: A technical report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. omrcys@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2466553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2019.49.4.301
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This report presents a procedure for performing power Doppler ultrasound-guided sialography using the phenomenon of increased blood flow and illustrates its application to practical patient cases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
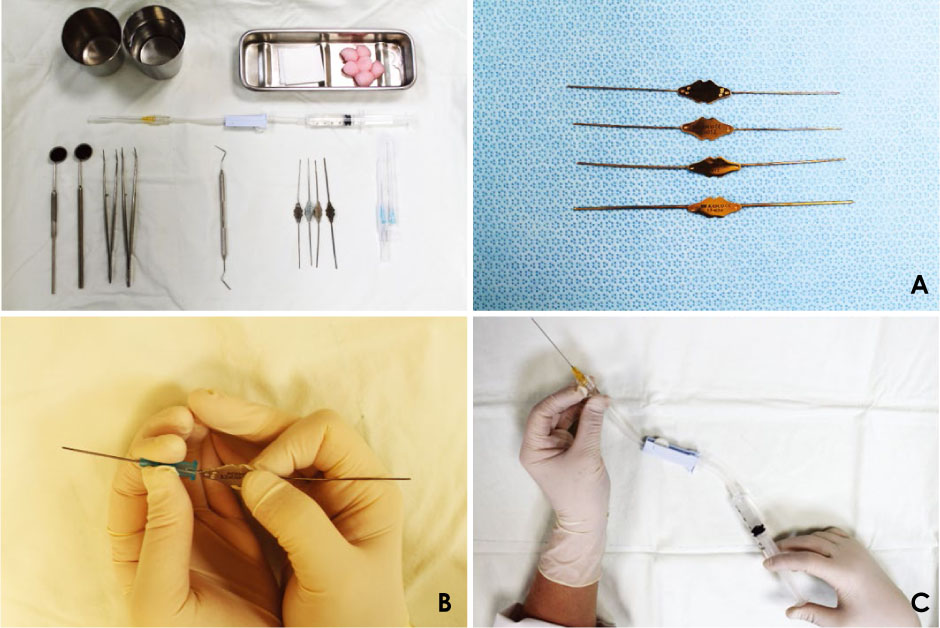
The salivary gland was scanned using ultrasound equipment (GE LOGIQ5 Expert® device; GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI, USA) to identify pathological findings related to the patient's chief complaint. To identify the orifice of the main duct, it should be cannulated using a lacrimal dilator. After inserting the catheter into the cannulated main duct, the position of the catheter within the duct was confirmed by ultrasound. A contrast agent was injected until the patient felt fullness, and ultrasound (B-mode) was used to confirm whether the contrast agent filled the main canal and secondary and tertiary ducts. Then, power Doppler ultrasound was performed to determine whether the salivary gland had increased blood flow.
RESULTS
In 2 cases in this report, a power Doppler ultrasound scan showed a significant increase in blood flow after contrast medium injection, which was not observed on a preoperative scan.
CONCLUSION
Power Doppler ultrasound was found to be a simple, safe, and effective tool for real-time sialography monitoring.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abdel Razek AA, Mukherji SK. State-of-the-art imaging of salivary gland tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2018; 28:303–317.
Article2. Som PM, Brandwein-Gensler MS. Anatomy and pathology of the salivary glands. In : Som PM, Curtin HD, editors. Head and neck imaging. 5th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier;2011. p. 2468–2474.3. Capaccio P, Torretta S, Ottavian F, Sambataro G, Pignataro L. Modern management of obstructive salivary diseases. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2007; 27:161–172.4. Kalk WW, Vissink A, Spijkervet FK, Möller JM, Roodenburg JL. Morbidity from parotid sialography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92:572–575.
Article5. Oh SH, Kang JH, Choi YJ, Kim BY, Lee SR, Lee SH, et al. Ultrasound-guided sialo-irrigation with a saline-air mixture as the contrast medium. Oral Radiol. 2019; 35:84–89.
Article6. Babcock DS, Patriquin H, LaFortune M, Dauzat M. Power Doppler sonography: basic principles and clinical applications in children. Pediatr Radiol. 1996; 26:109–115.
Article7. Shimizu M, Tokumori K, Okamura K, Chikui T, Yoshiura K, Kanda S. Possibility of sialographic sonography: a Doppler phantom study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 91:719–727.
Article8. Funakoshi M, Hamada T, Kawamura Y. The effect of pressure within the submandibular gland on the glandular blood circulation. Jpn J Physiol. 1967; 17:21–29.
Article9. Reed RK, Rubin K. Transcapillary exchange: role and importance of the interstitial fluid pressure and the extracellular matrix. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 87:211–217.
Article10. Levick JR, Michel CC. Microvascular fluid exchange and the revised Starling principle. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 87:198–210.
Article11. Rubin JM, Bude RO, Carson PL, Bree RL, Adler RS. Power Doppler US: a potentially useful alternative to mean frequency-based color Doppler US. Radiology. 1994; 190:853–856.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasonography in the Detection of Intratesticular Blood Flow of Normal Infants
- Three-Dimensional Power Doppler Imaging
- Doppler ultrasound investigation of female infertility
- Power Versus Color Doppler Sonography of Focal Hepatic Lesions
- Sonographic Evaluation of Recurrent Parotitis in Childhood