Infect Chemother.
2019 Dec;51(4):337-344. 10.3947/ic.2019.51.4.337.
Seroprevalence of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in the Agricultural Population of Jeju Island, Korea, 2015–2017
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University, College of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, Jeju National University, College of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Jeju National University, College of Medicine and Graduate School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. yomust7@gmail.com
- KMID: 2466466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2019.51.4.337
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a tick-borne zoonotic disease that is caused by the SFTS virus (SFTSV), and exhibits an overall mortality rate of approximately 20.0% in Korea. Most cases of this disease have been reported in Korea, East China, and Japan, and it mostly affects outdoor workers and farmers. This study aimed to investigate the seroprevalence of SFTSV among healthy farmers on Jeju Island, Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
In this prospective cross-sectional study, we analyzed 421 blood samples obtained from 254 farmers (mean age, 59.9 years; 68.9% male) to determine the seroprevalence of SFTSV in 16 rural areas of the Jeju Special Self-Governing Province over a period of 3 years (January 2015-December 2017). We used an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect immunoglobulin (Ig) G antibodies against SFTSV in the collected samples.
RESULTS
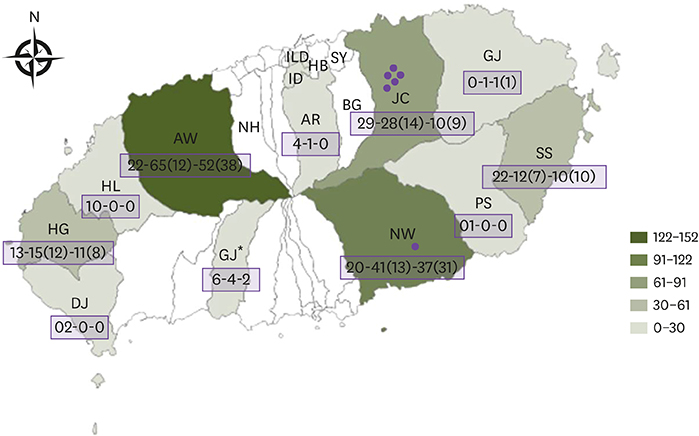
The seroprevalence of the SFTSV IgG among farmers on Jeju Island was observed to be 2.4%. One subject showed seropositivity over the entire 3-year study period. The areas with the highest SFTSV IgG seropositivity rates were Seonheul-ri in Jocheon-eup, followed by Namwon-eup. Fruit farmers were at a higher risk of exposure to SFTSV than other farmers.
CONCLUSION
The seroprevalence of SFTSV in the healthy agricultural population of Jeju Island was not high. However, personal hygiene management should be implemented for the agricultural population in the endemic areas. Surveillance of mild or asymptomatic infections is required in the endemic regions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies
Asymptomatic Infections
China
Cross-Sectional Studies
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Epidemiology
Farmers
Fever*
Fruit
Humans
Hygiene
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins
Japan
Korea*
Mortality
Phlebovirus
Prospective Studies
Seroepidemiologic Studies*
Thrombocytopenia*
Zoonoses
Antibodies
Immunoglobulin G
Immunoglobulins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Status and Infection Control of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Korea
Hyunjoo Oh, Jeong Rae Yoo, Misun Kim, Sang Taek Heo
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2022;27(1):18-27. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.18.
Reference
-
1. Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:763–772.
Article2. Park SW, Ryou J, Choi WY, Han MG, Lee WJ. Epidemiological and clinical features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome during an outbreak in South Korea, 2013-2015. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016; 95:1358–1361.
Article3. Li Z, Hu J, Cui L, Hong Y, Liu J, Li P, Guo X, Liu W, Wang X, Qi X, Wu B, Feng Z, Shen A, Liu X, Zhao H, Tan W, Zhou J, Xing Z, Bao C. Increased prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Eastern China clustered with multiple genotypes and reasserted virus during 2010-2015. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:6503.
Article4. Park SW, Song BG, Shin EH, Yun SM, Han MG, Park MY, Park C, Ryou J. Prevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in South Korea. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014; 5:975–977.
Article5. Kato H, Yamagishi T, Shimada T, Matsui T, Shimojima M, Saijo M, Oishi K. SFTS epidemiological research group-Japan. Epidemiological and clinical features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Japan, 2013-2014. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0165207.6. Yoo JR, Kim SH, Kim YR, Lee KH, Oh WS, Heo ST. Application of therapeutic plasma exchange in patients having severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Korean J Intern Med. 2019; 34:902–909.
Article7. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Infectious Disease Surveillance 2017, Public Health Weekly Report. 2017. Accessed February 21 2019. Available at:https://is.cdc.go.kr.8. Kim WY, Choi W, Park SW, Wang EB, Lee WJ, Jee Y, Lim KS, Lee HJ, Kim SM, Lee SO, Choi SH, Kim YS, Woo JH, Kim SH. Nosocomial transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Korea. Clin Infect Dis. 2015; 60:1681–1683.
Article9. Yoo JR, Heo ST, Park D, Kim H, Fukuma A, Fukushi S, Shimojima M, Lee KH. Family cluster analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection in Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016; 95:1351–1357.
Article10. Yoo JR, Lee KH, Heo ST. Surveillance results for family members of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Zoonoses Public Health. 2018; 65:903–907.
Article11. Ni H, Yang F, Li Y, Liu W, Jiao S, Li Z, Yi B, Chen Y, Hou X, Hu F, Ding Y, Bian G, Du Y, Xu G, Cao G. Apodemus agrarius is a potential natural host of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS)-causing novel bunyavirus. J Clin Virol. 2015; 71:82–88.
Article12. Hayasaka D, Fuxun Y, Yoshikawa A, Posadas-Herrera G, Shimada S, Tun MM, Agoh M, Morita K. Seroepidemiological evidence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infections in wild boars in Nagasaki, Japan. Trop Med Health. 2016; 44:6.
Article13. Li P, Tong ZD, Li KF, Tang A, Dai YX, Yan JB. Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0175592.
Article14. Liu K, Cui N, Fang LQ, Wang BJ, Lu QB, Peng W, Li H, Wang LY, Liang S, Wang HY, Zhang YY, Zhuang L, Yang H, Gray GC, de Vlas SJ, Liu W, Cao WC. Epidemiologic features and environmental risk factors of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Xinyang, China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014; 8:e2820.
Article15. Gokuden M, Fukushi S, Saijo M, Nakadouzono F, Iwamoto Y, Yamamoto M, Hozumi N, Nakayama K, Ishitani K, Nishi N, Ootsubo M. Low seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus antibodies in individuals living in an endemic area in Japan. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2018; 24:225–228.
Article16. Han MA, Kim CM, Kim DM, Yun NR, Park SW, Han MG, Lee WJ. Seroprevalence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus antibodies in rural areas, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018; 24:872–874.
Article17. Li Z, Hu J, Bao C, Li P, Qi X, Qin Y, Wang S, Tan Z, Zhu Y, Tang F, Zhou M. Seroprevalence of antibodies against SFTS virus infection in farmers and animals, Jiangsu, China. J Clin Virol. 2014; 60:185–189.
Article18. Qi R, Huang YT, Yu XJ. Persistence and gender differences in protection against severe fever with thrombocytopaenia syndrome virus with natural infection: a 4-year follow-up and mathematical prediction study. Epidemiol Infect. 2019; 147:e78.
Article19. Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhao L, Li B, Yu H, Wen H, Yu XJ. An emerging hemorrhagic fever in China caused by a novel bunyavirus SFTSV. Sci China Life Sci. 2013; 56:697–700.
Article20. Shin J, Kwon D, Youn SK, Park JH. Characteristics and factors associated with death among patients hospitalized for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015; 21:1704–1710.
Article21. Huang YT, Zhao L, Wen HI, Yang Y, Yu H, Yu XJ. Neutralizing antibodies to severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus 4 years after hospitalization, China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016; 22:1985–1987.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The First Case of Non-retrospective Clinical Identification of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Patient in 2013 in South Korea
- Case of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome in Jeju Island
- Four Cases of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Occurring in Jeju
- Phylogenetic Analysis for the Origin of Typhoid Fever Outbreak on Jeju Island, Korea, in 2017
- Differences of clinical manifestation of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome between Korean and Chinese patients