Ann Clin Microbiol.
2019 Dec;22(4):96-104. 10.5145/ACM.2019.22.4.96.
Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Nursing Hospitals between 2014 and 2017
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul Clinical Laboratory, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Clnical Pathology, Sangji University College of Science, Wonju, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine and Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ejyoon@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2466396
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2019.22.4.96
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an issue not only with regard to public health, but also in terms of economic impact. AMR surveillance has mainly been carried out in general hospitals, and not in nursing hospitals. This study was conducted to investigate the AMR rate for bacterial strains isolated from nursing hospital samples.
METHODS
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) results from a total of 23,518 bacterial isolates recovered from clinical specimens taken in 61 nursing hosals were analyzed. AST was conducted using Vitek 2 with AST cards specific for the bacterial strains.
RESULTS
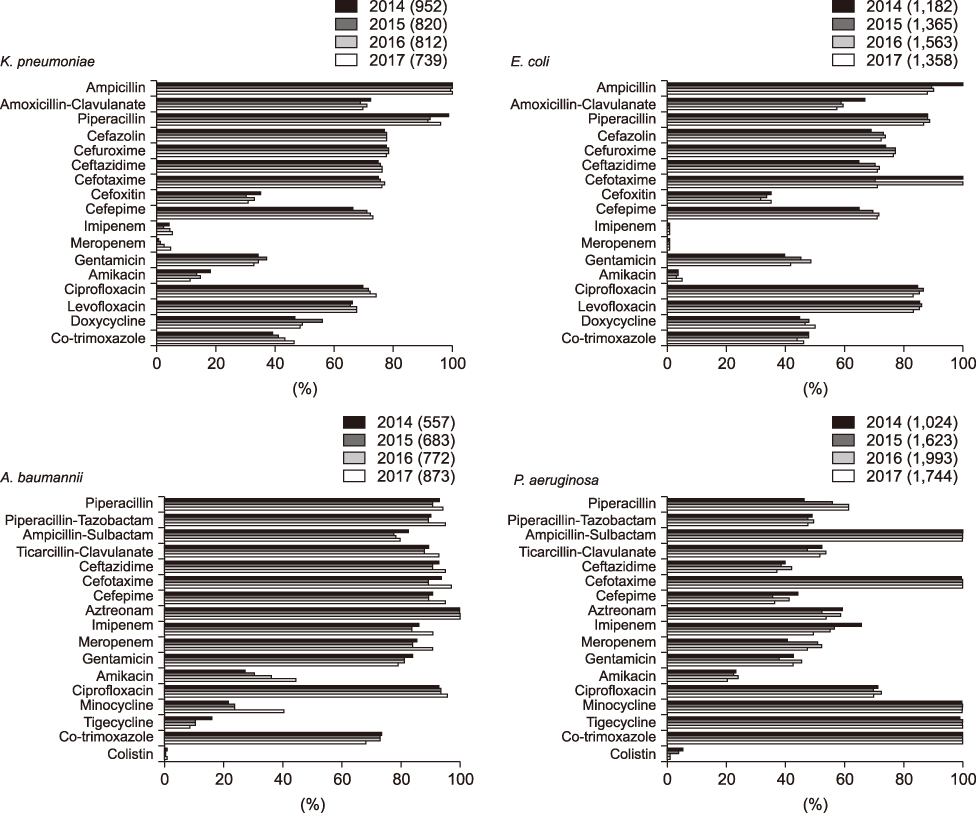
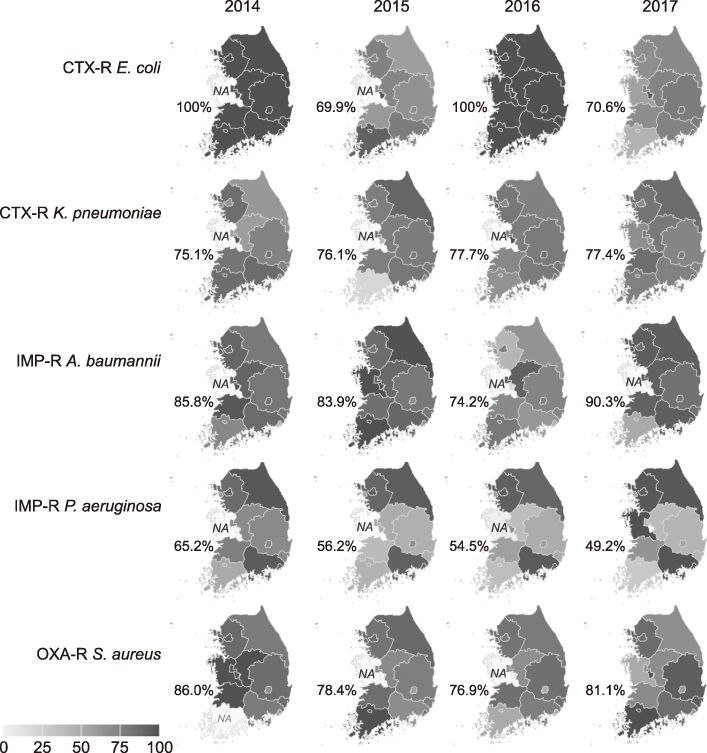
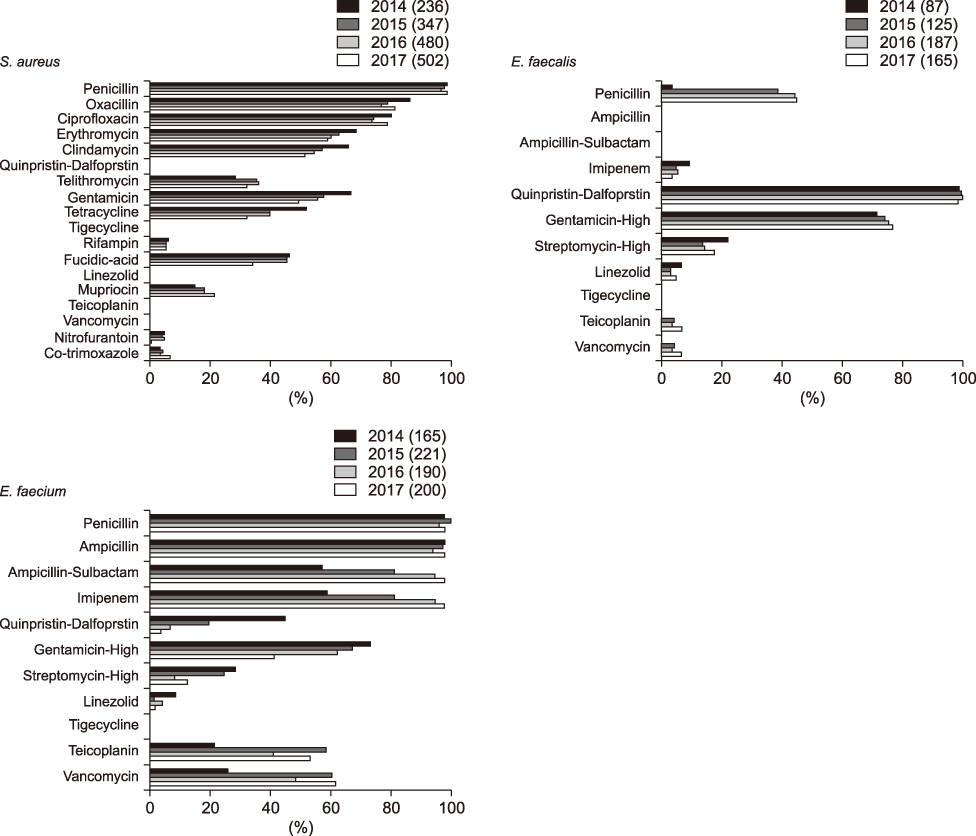
A total of 19,357 Gram-negative and 4,161 Gram-positive bacterial strains were isolated. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n=6,384) and Escherichia coli (n=5,468) were the most prevalent bacterial species and, among Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus (n=1,565) was common. The AMR rate was high for the following strains: cefotaxime-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, 77.4%; cefotaxime-resistant E. coli, 70.6%; imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, 90.3%; imipenem-resistant P. aeruginosa, 49.3%; oxacillin-resistant S. aureus, 81.1%, penicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis, 44.8%, and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, 53.5%. AMR rate change varied by bacterial species and antimicrobial drug.
CONCLUSION
AMR rates of major pathogens from nursing hospitals were higher than those from general hospitals with the exception of imipenem-resistant A. baumannii. Continuous monitoring and infection control strategies are needed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Microorganisms Isolated from Urine Cultures and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns at a Commercial Laboratory during 2018-2020
Byeonghak Kwak, Jungmi Hong, Hye Gyung Bae, Yoon Soo Park, Mi Kyeong Lee, Kyungwon Lee, Kyoung Ryul Lee
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2022;27(1):51-58. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2022.27.1.51.
Reference
-
1. Founou RC, Founou LL, Essack SY. Clinical and economic impact of antibiotic resistance in developing countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0189621.2. Ryu S. The new Korean action plan for containment of antimicrobial resistance. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017; 8:70–73.3. Organization, WH. Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. Geneva: WHO;2015.4. Kim D, Ahn JY, Lee CH, Jang SJ, Lee H, Yong D, et al. Increasing resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins, fluoroquinolone, and carbapenem in gram-negative bacilli and the emergence of carbapenem non-susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae: analysis of Korean Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (KARMS) data from 2013 to 2015. Ann Lab Med. 2017; 37:231–239.5. Lee H, Yoon EJ, Kim D, Jeong SH, Shin JH, Shin JH, et al. Establishment of the South Korean national antimicrobial resistance surveillance system, Kor-GLASS, in 2016. Euro Surveill. 2018; 23.6. Richards CL, Steele L. Antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in long- term care facilities: infection control considerations. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2003; 4(3 Suppl):S110–S114.7. Wiener J, Quinn JP, Bradford PA, Goering RV, Nathan C, Bush K, et al. Multiple antibiotic-resistant Klebsiella and Escherichia coli in nursing homes. JAMA. 1999; 281:517–523.8. Lee BY, Bartsch SM, Wong KF, Singh A, Avery TR, Kim DS, et al. The importance of nursing homes in the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) among hospitals. Med Care. 2013; 51:205–215.9. McBryde ES, Bradley LC, Whitby M, McElwain DL. An investigation of contact transmission of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Hosp Infect. 2004; 58:104–108.10. van den Dool C, Haenen A, Leenstra T, Wallinga J. The role of nursing homes in the spread of antimicrobial resistance over the healthcare network. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016; 37:761–767.11. VAN Gaalen RD, Hopman HA, Haenen A, VAN DEN Dool C. Staff exchange within and between nursing homes in the Netherlands and potential implications for MRSA transmission. Epidemiol Infect. 2017; 145:739–745.12. Jones CD, Cumbler E, Honigman B, Burke RE, Boxer RS, Levy C, et al. Hospital to post-acute care facility transfers: identifying targets for information exchange quality improvement. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017; 18:70–73.13. Lee SC, Wu MS, Shih HJ, Huang SH, Chiou MJ, See LC, et al. Identification of vancomycin-resistant enterococci clones and inter-hospital spread during an outbreak in Taiwan. BMC Infect Dis. 2013; 13:163.14. Donker T, Wallinga J, Slack R, Grundmann H. Hospital networks and the dispersal of hospital-acquired pathogens by patient transfer. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e35002.15. Ruiz de Gopegui E, Oliver A, Ramírez A, Gutiérrez O, Andreu C, Pérez JL. Epidemiological relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a tertiary hospital and a geriatric institution in Spain. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2004; 10:339–342.16. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Korea Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention. Standard guidelines of the control and prevention for healthcare-associated infections. Sejong: KCDC;2017. 07. Report No.: 11-1352159-000840-01. 292 p.17. Ministry of Health and Welfare. General measures of the control and prevention for health care-associated infections ('18~'22). . Sejong: MOHW;2018. 06. p. 34.18. Korean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). The existing state of hospitals in South Korea by district and by type. last visited on 1 May 2019. http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=354&tblId=DT_MIRE01&vw_cd=MT_ZTITLE&list_id=354_MT_DTITLE&seqNo=&lang_mode=ko&language=kor&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=MT_ZTITLE[Online].19. Lee H, Yoon EJ, Kim D, Jeong SH, Won EJ, Shin JH, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of major clinical pathogens in South Korea, May 2016 to April 2017: first one-year report from Kor-GLASS. Euro Surveill. 2018; 23.20. Kim D, Lee H, Yoon EJ, Hong JS, Shin JH, Uh Y, et al. Prospective observational study of the clinical prognoses of patients with bloodstream infections caused by ampicillin-susceptible but penicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019; 63:e00291–e00219.21. Ministry of the Interior and Safety. Gugga hangsaengje naeseong gwanlidaechaeg [National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance (2016–2020)]. last visited on 1 May 2019. https://www.gov.kr/portal/gvrnPolicy/view/156146703[Online].
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance among Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Non-tertiary Care Hospitals in Korea, 2002-2004
- Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance in
Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Fishery Workers - The Prevalence, Genotype and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of High- and Low-Level Mupirocin Resistant Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- Genetic Determinants of Carbapenem and Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates of Clinical Origin
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Clonal Distribution of the Blood Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Two Korean Hospitals