Korean J Radiol.
2016 Dec;17(6):961-964. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.6.961.
Computed Tomography Findings of Community-Acquired Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia Pneumonia in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang 10326, Korea. jeungkim@dumc.or.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang 10326, Korea.
- KMID: 2466293
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.6.961
Abstract
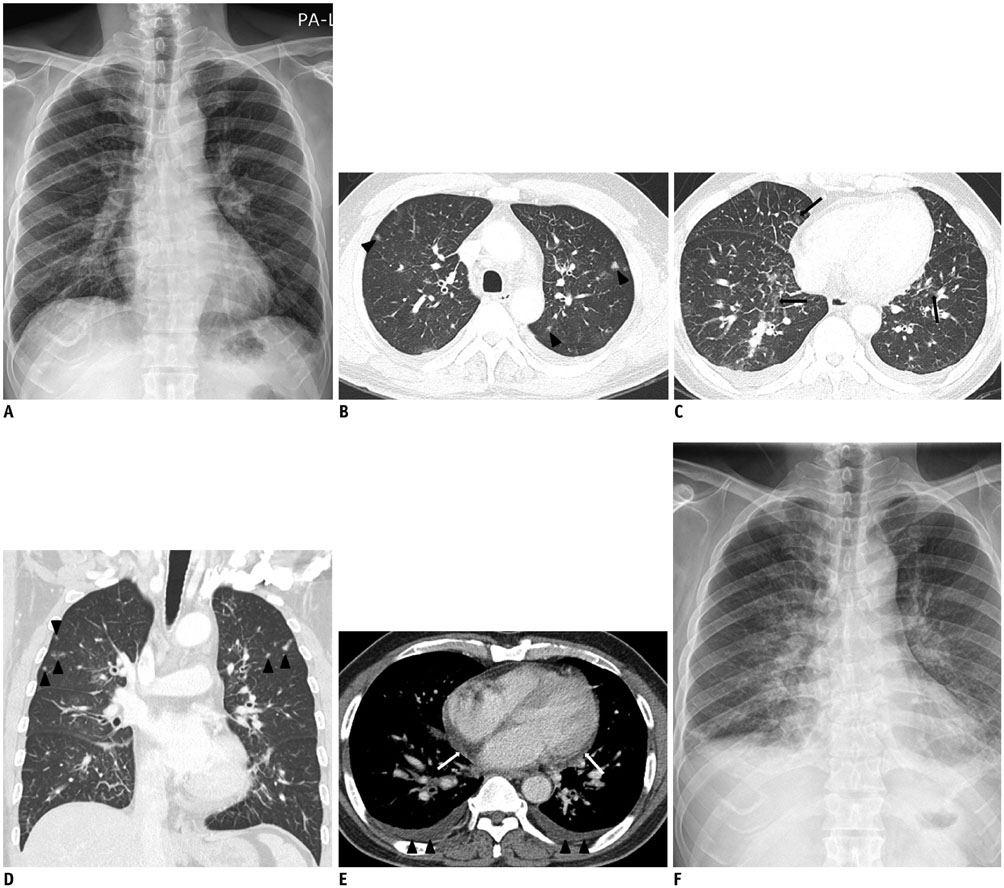
- Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (S. maltophilia) is a rare, but globally emerging gram-negative multiple-drug-resistant organism usually found in a nosocomial setting in immunocompromised patients. To our best knowledge, computed tomography (CT) features of community-acquired S. maltophilia pneumonia have not been previously reported in an immunocompetent patient. Herein, we presented the CT findings of a previous healthy 56-year-old male with S. maltophilia pneumonia.
MeSH Terms
-
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid/microbiology
Bronchoscopy
Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections/*diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology
Humans
Immunocompromised Host
Levofloxacin/therapeutic use
Male
Middle Aged
Pleural Effusion/etiology
Pneumonia/*diagnosis/microbiology
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia/*isolation & purification
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Levofloxacin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brooke JS. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25:2–41.2. Falagas ME, Kastoris AC, Vouloumanou EK, Dimopoulos G. Community-acquired Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 28:719–730.3. Lai CH, Chi CY, Chen HP, Chen TL, Lai CJ, Fung CP, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of patients with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia bacteremia. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2004; 37:350–358.4. Jang TN, Wang FD, Wang LS, Liu CY, Liu IM. Xanthomonas maltophilia bacteremia: an analysis of 32 cases. J Formos Med Assoc. 1992; 91:1170–1176.5. Victor MA, Arpi M, Bruun B, Jønsson V, Hansen MM. Xanthomonas maltophilia bacteremia in immunocompromised hematological patients. Scand J Infect Dis. 1994; 26:163–170.6. Denton M, Todd NJ, Littlewood JM. Role of anti-pseudomonal antibiotics in the emergence of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in cystic fibrosis patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1996; 15:402–405.7. Burns JL, Emerson J, Stapp JR, Yim DL, Krzewinski J, Louden L, et al. Microbiology of sputum from patients at cystic fibrosis centers in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 27:158–163.8. Goss CH, Otto K, Aitken ML, Rubenfeld GD. Detecting Stenotrophomonas maltophilia does not reduce survival of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:356–361.9. Sakhnini E, Weissmann A, Oren I. Fulminant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia soft tissue infection in immunocompromised patients: an outbreak transmitted via tap water. Am J Med Sci. 2002; 323:269–272.10. Denton M, Todd NJ, Kerr KG, Hawkey PM, Littlewood JM. Molecular epidemiology of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolated from clinical specimens from patients with cystic fibrosis and associated environmental samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:1953–1958.11. Gasparetto EL, Bertholdo DB, Davaus T, Marchiori E, Escuissato DL. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia pneumonia after bone marrow transplantation: case report with emphasis on the high-resolution CT findings. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:e19–e20.12. Kassel TW, Ryan LK, Li A. Computed tomography features of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia pneumonia in patients with neutropenic fever: report of two cases. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2013; 8:14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Localized Cutaneous Infection due to Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in Immunocompetent Patient
- A Case of Metastatic Cellulitis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- A case of soft tissue infection by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia manifesting as subcutaneous nodules in a patient with leukemia
- A Case of Indophenol Oxidase-positive Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolated from Urine in a Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- A Case of Acute Cholecystitis Caused by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Bacteremia