J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2019 Jun;21(2):101-106. 10.7461/jcen.2019.21.2.101.
Transvenous Embolization of Dural Carotid Cavernous Fistula through the Supraorbital Vein
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Eulji University Eulji Hospital, Seoul, Korea. grimi2@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2465203
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2019.21.2.101
Abstract
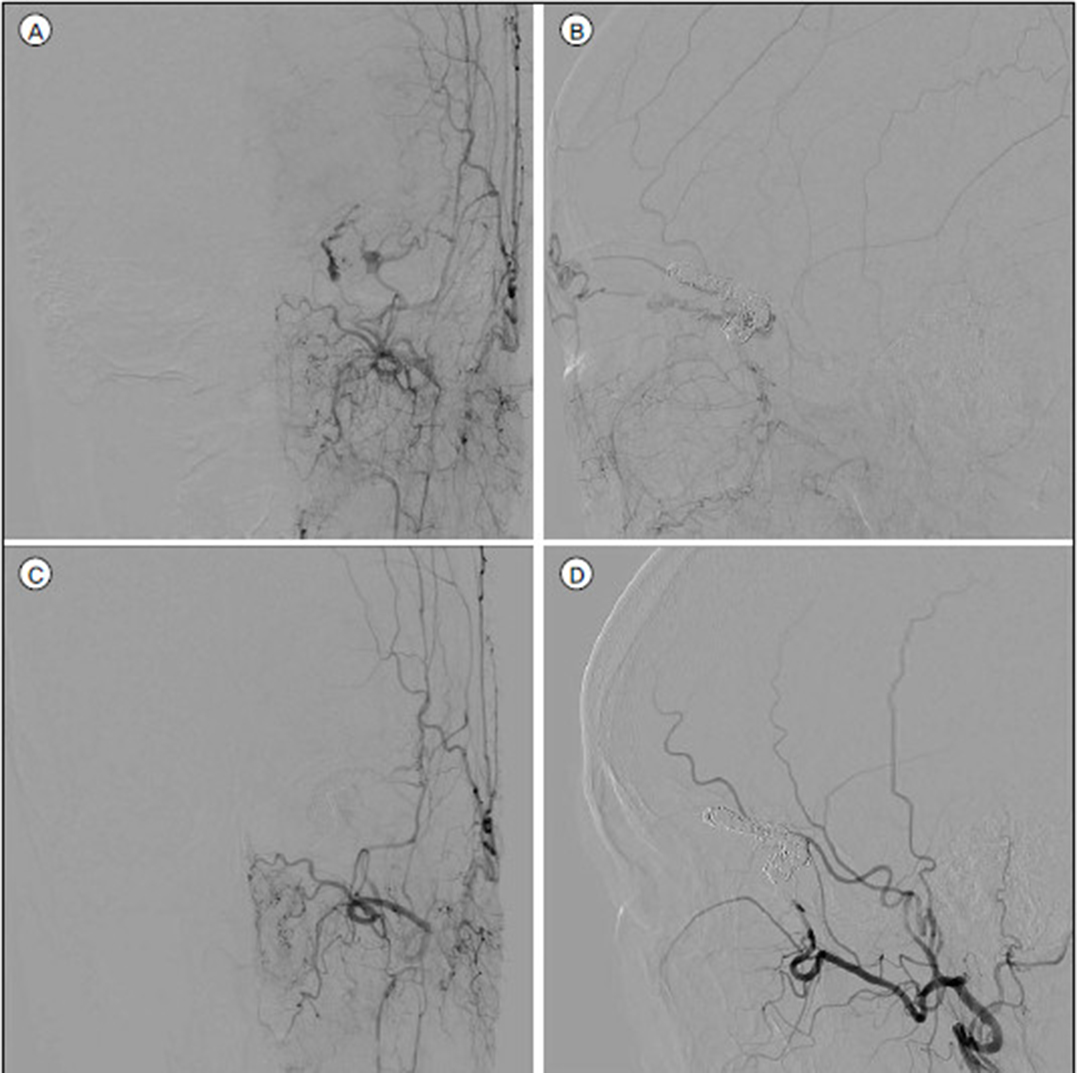
- We describe a case of transvenous embolization through the dilated supraorbital vein to treat a dural carotid cavernous fistula. The approach through the common facial vein or direct access of the superior ophthalmic vein is a commonly used route to the superior ophthalmic vein when the approach via the inferior petrosal sinus is unavailable. In rare cases, the dilated supraorbital vein provides an alternative route and we discuss the technical details.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Middle temporal vein access for transvenous embolization of Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula: A case report and review of literature
Su-Chel Kim, Jae-Hyun Kim, Chang-Hyun Kim, Chang-Young Lee
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2022;24(1):44-50. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.06.008.
Reference
-
1. Aboian MS, Daniels DJ, Rammos SK, Pozzati E, Lanzino G. The putative role of the venous system in the genesis of vascular malformations. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 11. 27(5):E9.
Article2. Agid R, Willinsky RA, Haw C, Souza MP, Vanek IJ, TerBrugge KG. Targeted compartmental embolization of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae using transfemoral medial and lateral facial vein approaches. Neuroradiology. 2004; 02. 46(2):156–160.
Article3. Barber SM, Rangel-Castilla L, Zhang YJ, Klucznik R, Diaz O. Mid- and long-term outcomes of carotid-cavernous fistula endovascular management with Onyx and n-BCA: experience of a single tertiary center. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 10. 7(10):762–769.
Article4. Chalouhi N, Dumont AS, Tjoumakaris S, Gonzalez LF, Bilyk JR, Randazzo C, et al. The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: a novel technique using Onyx. Neurosurg Focus. 2012; 05. 32(5):E13.
Article5. Cheng KM, Chan CM, Cheung YL. Transvenous embolisation of dural carotid-cavernous fistulas by multiple venous routes: a series of 27 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2003; 01. 145(1):17–29.
Article6. Cheung N, McNab AA. Venous anatomy of the orbit. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 03. 44(3):988–995.
Article7. de Castro-Afonso LH, Trivelato FP, Rezende MT, Ulhoa AC, Nakiri GS, Monsiqnore LM, et al. Transvenous embolization of dural carotid cavernous fistulas: the role of liquid embolic agents in association with coils on patient outcomes. J Neurointerv Surg. 2018; 05. 10(5):461–462.
Article8. Elhammady MS, Wolfe SQ, Farhat H, Moftakhar R, Aziz-Sultan MA. Onyx embolization of carotid-cavernous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2010; 03. 112(3):589–594.
Article9. Gemmete JJ, Ansari SA, Gandhi DM. Endovascular techniques for treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula. J Neuroophthalmol. 2009; 03. 29(1):62–71.
Article10. Jahan R, Gobin YP, Glenn B, Duckwiler GR, Viñuela F. Transvenous embolization of a dural arteriovenous fistula of the cavernous sinus through the contralateral pterygoid plexus. Neuroradiology. 1998; 03. 40(3):189–193.
Article11. Komiyama M, Morikawa K, Fu Y, Yagura H, Yasui T, Baba M. Indirect carotid-cavernous fistula: transvenous embolization from the external jugular vein using a superior ophthalmic vein approach. A case report. Surg Neurol. 1990; 01. 33(1):57–63.12. Luo CB, Chang FC, Teng MM, Ting TW. Anatomic variation of facial vein in carotid-cavernous fistula and trans-facial vein embolization. World Neurosurg. 2015; 07. 84(1):90–96.
Article13. Mounayer C, Piotin M, Spelle L, Moret J. Superior petrosal sinus catheterization for transvenous embolization of a dural carotid cavernous sinus fistula. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 08. 23(7):1153–1155.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Using the Direct Superior Ophthalmic Vein Approach: A Case Report
- Intraoperative Embolization of Dural Carotid-Cavernous Fistula: Case Report
- Transvenous injection of n-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate to obliterate the pathologic cavernous sinus as a salvage technique for incompletely obliterated complex cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula after transvenous coil embolization
- Transvenous Coil Embolization for Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas of the Ophthalmic Sheath: Report of Two Cases and Review of the Literature
- Facilitated Retrograde Access via the Facial Vein for Transvenous Embolization of the Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Isolated Ophthalmic Venous Drainage