Cancer Res Treat.
2019 Apr;51(2):769-776. 10.4143/crt.2018.366.
Salvage Concurrent Chemo-radiation Therapy for Loco-regional Recurrence Following Curative Surgery of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ahnyc@skku.edu
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Changwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Hematology-Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2464422
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2018.366
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study is to report clinical outcomes of salvage concurrent chemo-radiation therapy (CCRT) in treating patients with loco-regional recurrence (LRR) following initial complete resection of non-small cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between February 2004 and December 2016, 127 patients underwent salvage CCRT for LRR. The median radiation therapy (RT) dose was 66 Gy and clinical target volume was to cover recurrent lesion with margin without elective inclusion of regional lymphatics. Majority of patients (94.5%) received weekly platinum-based doublet chemotherapy during RT course.
RESULTS
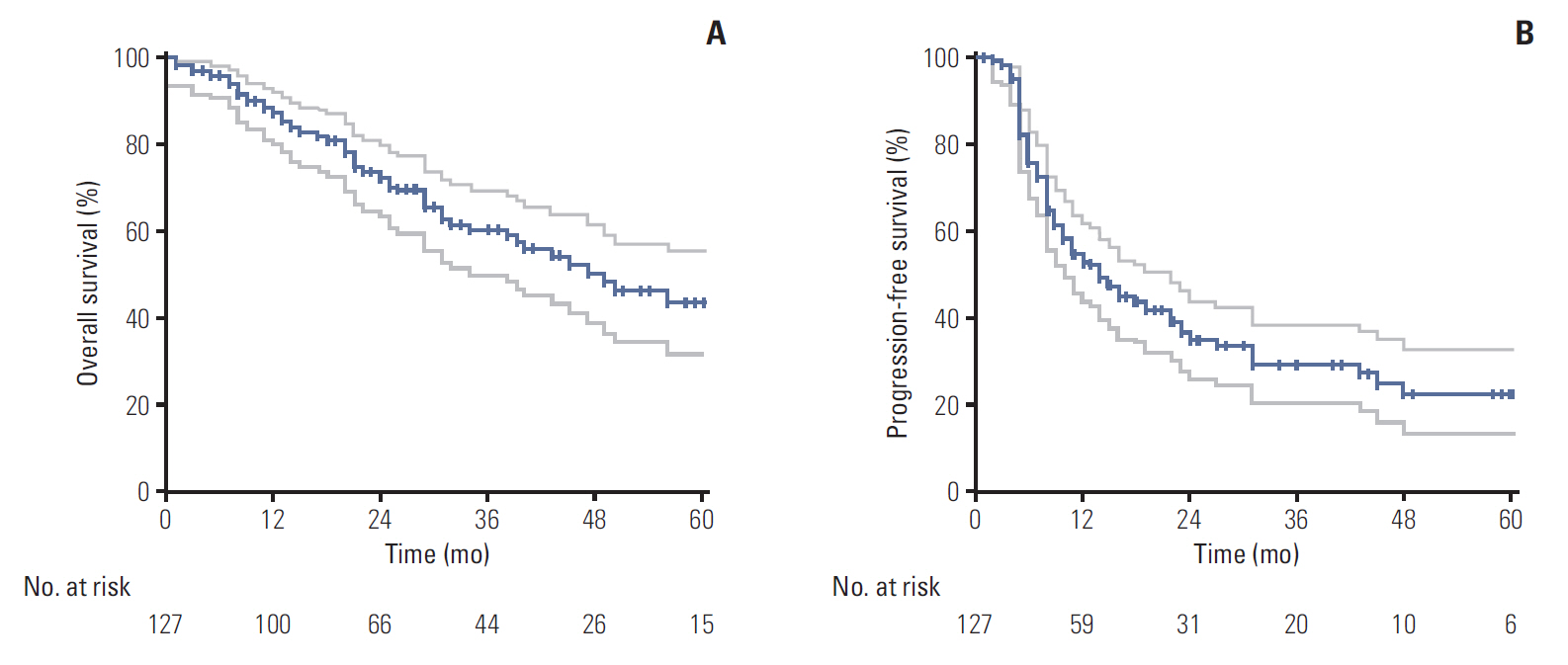
The median follow-up time from the start of CCRT was 25 months. The median survival duration was 49 months, and overall survival (OS) rates at 2 and 5 years were 72.9% and 43.9%. The 2- and 5-year rates of in-field failure-free survival, distant metastasis free survival, and progression free survival were 82.4% and 73.8%, 50.4% and 39.9%, and 34.6% and 22.3%, respectively. Grade ≥ 3 radiation-related esophagitis and pneumonitis occurred in 14 (11.0%) and six patients (4.7%), respectively. On both univariate and multivariate analysis, higher biologically equivalent dose (BEDâ‚â‚€) (≥ 79.2 Gyâ‚â‚€ vs. < 79.2 Gyâ‚â‚€; hazard ratio [HR], 0.431), smaller CTV (≤ 80 cm³ vs. > 80 cm³; HR, 0.403), and longer disease-free interval (> 1 year vs. ≤ 1 year; HR, 0.489) were significantly favorable factors for OS.
CONCLUSION
The current study has demonstrated that high dose salvage CCRT focused to the involved lesion only was highly effective and safe. In particular, higher BEDâ‚â‚€, smaller CTV, and longer disease-free interval were favorable factors for improved survival.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015; 136:E359–86.
Article2. Jung KW, Won YJ, Oh CM, Kong HJ, Lee DH, Lee KH, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2014. Cancer Res Treat. 2017; 49:292–305.
Article3. al-Kattan K, Sepsas E, Fountain SW, Townsend ER. Disease recurrence after resection for stage I lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1997; 12:380–4.
Article4. Williams BA, Sugimura H, Endo C, Nichols FC, Cassivi SD, Allen MS, et al. Predicting postrecurrence survival among completely resected nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006; 81:1021–7.
Article5. Sugimura H, Nichols FC, Yang P, Allen MS, Cassivi SD, Deschamps C, et al. Survival after recurrent nonsmall-cell lung cancer after complete pulmonary resection. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007; 83:409–17.
Article6. Saisho S, Yasuda K, Maeda A, Yukawa T, Okita R, Hirami Y, et al. Post-recurrence survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer after curative resection with or without induction /adjuvant chemotherapy. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013; 16:166–72.7. Lee J, Kim HK, Park BJ, Cho JH, Choi YS, Zo JI, et al. Recurrence dynamics after trimodality therapy (Neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy and surgery) in patients with stage IIIA (N2) lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2018; 115:89–96.
Article8. Sonobe M, Yamada T, Sato M, Menju T, Aoyama A, Sato T, et al. Identification of subsets of patients with favorable prognosis after recurrence in completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:2546–54.
Article9. Yano T, Okamoto T, Fukuyama S, Maehara Y. Therapeutic strategy for postoperative recurrence in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2014; 5:1048–54.
Article10. Terzi A, Lonardoni A, Falezza G, Scanagatta P, Santo A, Furlan G, et al. Completion pneumonectomy for non-small cell lung cancer: experience with 59 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002; 22:30–4.
Article11. Kim HS, I H, Choi YS, Kim K, Shim YM, Kim J. Surgical resection of recurrent lung cancer in patients following curative resection. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:224–8.
Article12. Kelsey CR, Clough RW, Marks LB. Local recurrence following initial resection of NSCLC: salvage is possible with radiation therapy. Cancer J. 2006; 12:283–8.13. Tada T, Fukuda H, Nakagawa K, Matsui K, Hosono M, Takada Y, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: radiation therapy for locoregional recurrence after complete resection. Int J Clin Oncol. 2005; 10:425–8.
Article14. Cai XW, Xu LY, Wang L, Hayman JA, Chang AC, Pickens A, et al. Comparative survival in patients with postresection recurrent versus newly diagnosed non-small-cell lung cancer treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010; 76:1100–5.
Article15. Bae SH, Ahn YC, Nam H, Park HC, Pyo HR, Shim YM, et al. High dose involved field radiation therapy as salvage for locoregional recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:1120–7.
Article16. Bar J, Ng D, Moretto P, Goss GD, Sun A, Macrae R, et al. Chemoradiotherapy for locoregional recurrence of non-small-cell lung cancer after surgical resection: a retrospective analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 2013; 14:200–4.
Article17. Lee NK, Moon SH, Kim TH, Han JY, Yun T, Kim HT, et al. Prognostic value of gross tumor volume for definitive radiation therapy in patients with locoregionally recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer after surgical resection. Clin Lung Cancer. 2013; 14:399–406.
Article18. Kim E, Song C, Kim MY, Kim JS. Long-term outcomes after salvage radiotherapy for postoperative locoregionally recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol J. 2017; 35:55–64.
Article19. Seol KH, Lee JE, Cho JY, Lee DH, Seok Y, Kang MK. Salvage radiotherapy for regional lymph node oligo-recurrence after radical surgery of non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer. 2017; 8:620–9.
Article20. Okawara G, Mackay JA, Evans WK, Ung YC; Lung Cancer Disease Site Group of Cancer Care Ontario's Program in Evidence-based Care. Management of unresected stage III non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol. 2006; 1:377–93.
Article21. O'Rourke N, Roqué I Figuls M, Farre Bernado N, Macbeth F. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; (6):CD002140.22. van Tinteren H, Hoekstra OS, Smit EF, van den Bergh JH, Schreurs AJ, Stallaert RA, et al. Effectiveness of positron emission tomography in the preoperative assessment of patients with suspected non-small-cell lung cancer: the PLUS multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2002; 359:1388–93.
Article23. Bar-Shalom R, Yefremov N, Guralnik L, Gaitini D, Frenkel A, Kuten A, et al. Clinical performance of PET/CT in evaluation of cancer: additional value for diagnostic imaging and patient management. J Nucl Med. 2003; 44:1200–9.24. Berghmans T, Dusart M, Paesmans M, Hossein-Foucher C, Buvat I, Castaigne C, et al. Primary tumor standardized uptake value (SUVmax) measured on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) is of prognostic value for survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a systematic review and meta-analysis (MA) by the European Lung Cancer Working Party for the IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2008; 3:6–12.
Article25. Paesmans M, Berghmans T, Dusart M, Garcia C, Hossein-Foucher C, Lafitte JJ, et al. Primary tumor standardized uptake value measured on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is of prognostic value for survival in non-small cell lung cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis by the European Lung Cancer Working Party for the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Staging Project. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:612–9.
Article26. Jimenez-Bonilla JF, Quirce R, Martinez-Rodriguez I, Banzo I, Rubio-Vassallo AS, Del Castillo-Matos R, et al. Diagnosis of recurrence and assessment of post-recurrence survival in patients with extracranial non-small cell lung cancer evaluated by 18F-FDG PET/CT. Lung Cancer. 2013; 81:71–6.
Article27. Dosoretz DE, Galmarini D, Rubenstein JH, Katin MJ, Blitzer PH, Salenius SA, et al. Local control in medically inoperable lung cancer: an analysis of its importance in outcome and factors determining the probability of tumor eradication. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993; 27:507–16.
Article28. Kong FM, Ten Haken RK, Schipper MJ, Sullivan MA, Chen M, Lopez C, et al. High-dose radiation improved local tumor control and overall survival in patients with inoperable/unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a radiation dose escalation study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 63:324–33.
Article29. Bradley JD, Paulus R, Komaki R, Masters G, Blumenschein G, Schild S, et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): a randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:187–99.
Article30. Jegadeesh N, Liu Y, Gillespie T, Fernandez F, Ramalingam S, Mikell J, et al. Evaluating intensity-modulated radiation therapy in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the national cancer data base. Clin Lung Cancer. 2016; 17:398–405.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High Dose Involved Field Radiation Therapy as Salvage for Loco-Regional Recurrence of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chemo-radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Salvage radiation therapy for postoperative locoregionally recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: a single-center experience
- Postoperative Radiation Therapy in Resected N2 Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Management of Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer