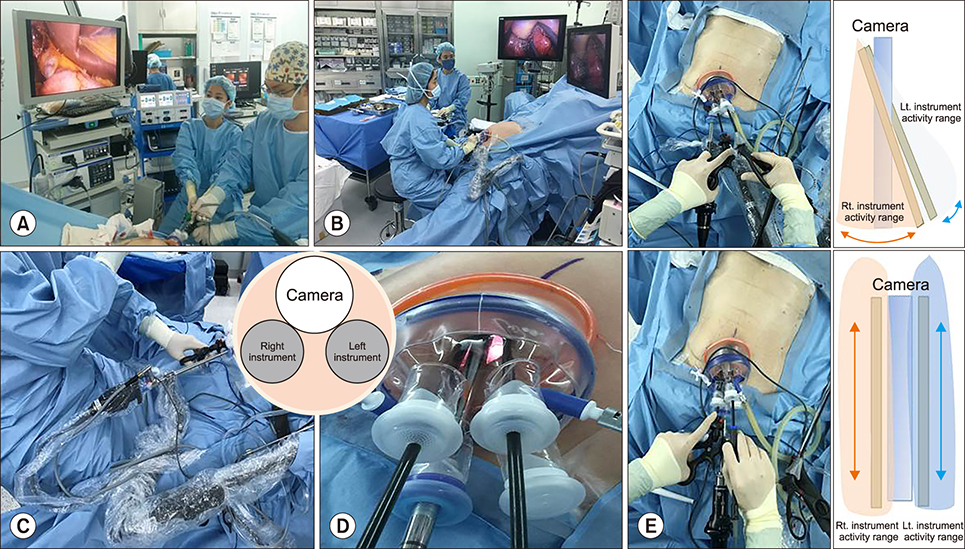
Solo single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy using the parallel method; Surgical technique reducing a steep learning curve
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University, College of Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. choiyoungrok@gmail.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Chung-Ang University, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2464323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2019.23.4.344
Abstract
- BACKGROUNDS/AIMS
To describe the techniques, short-term outcomes, and learning curve of solo single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Solo-SILC) using a laparoscopic scope holder.
METHODS
A total of 591 patients who underwent Solo-SILC from July 2014 to December 2016 performed by four experienced hepatobiliary surgeons were retrospectively assessed. Solo-SILC was performed using the parallel method using a scope holder. The moving average method was used to investigate the learning curve in terms of operative time.
RESULTS
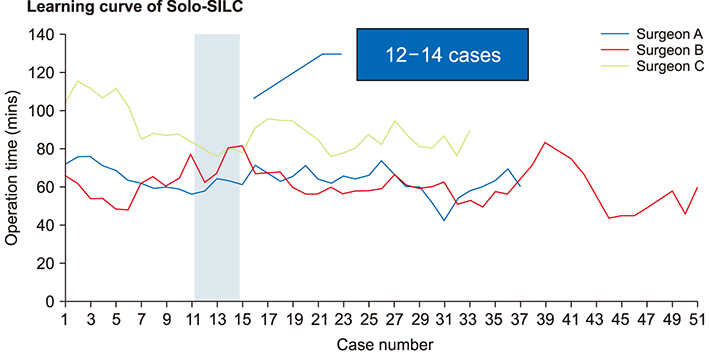
In total, 590 Solo-SILC procedures were performed. Very few procedures were converted to multi-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy. There was one case of bile duct injury. The mean operative time (59.93±25.77 min) was shorter than that in other studies of SILC. Three postoperative complications, delaying bile leakage, occurred in the patients treated by one surgeon. These cases were resolved by ultrasound-guided puncture and drainage. The learning curve for surgeons A, B, and C was overcome after 14, 12, and 12 cases. Surgeon D, who had the most experience with SILC, had no obvious learning curve.
CONCLUSIONS
Hepatobiliary surgeons experienced in LC can perform Solo-SILC almost immediately. Solo-SILC using the parallel technique represents a more stable option and is a promising treatment for gallbladder disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Use of a ring retractor to facilitate specimen removal in laparoscopic surgery
Deok Ho Hong, Miseon Kim, Kidong Kim, Dong Hoon Suh, Jae Hong No, Yong Beom Kim
Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2020;63(4):548-549. doi: 10.5468/ogs.20025.Comparison of outcomes of single incision robotic cholecystectomy and single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Sun Min Lee, Jin Hong Lim
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(1):78-83. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.1.78.Outcome of single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy compared to three-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis
Sanggyun Suh, Soyeon Choi, YoungRok Choi, Boram Lee, Jai Young Cho, Yoo-Seok Yoon, Ho-Seong Han
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2023;27(4):372-379. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.23-058.
Reference
-
1. Litynski GS. Highlights in the history of laparoscopy: the development of laparoscopic techniques--a cumulative effort of internists, gynecologists, and surgeons. Frankfurt: Barbara Bernert Verlag;1996. p. 165–168.2. Navarra G, Pozza E, Occhionorelli S, Carcoforo P, Donini I. One-wound laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg. 1997; 84:695.3. Aprea G, Coppola Bottazzi E, Guida F, Masone S, Persico G. Laparoendoscopic single site (LESS) versus classic video-laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized prospective study. J Surg Res. 2011; 166:e109–e112.4. Lai EC, Yang GP, Tang CN, Yih PC, Chan OC, Li MK. Prospective randomized comparative study of single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy versus conventional four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am J Surg. 2011; 202:254–258.5. Lee SK, You YK, Park JH, Kim HJ, Lee KK, Kim DG. Single-port transumbilical laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a preliminary study in 37 patients with gallbladder disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2009; 19:495–499.6. Asakuma M, Hayashi M, Komeda K, Shimizu T, Hirokawa F, Miyamoto Y, et al. Impact of single-port cholecystectomy on postoperative pain. Br J Surg. 2011; 98:991–995.7. Khambaty F, Brody F, Vaziri K, Edwards C. Laparoscopic versus single-incision cholecystectomy. World J Surg. 2011; 35:967–972.8. Tsimoyiannis EC, Tsimogiannis KE, Pappas-Gogos G, Farantos C, Benetatos N, Mavridou P, et al. Different pain scores in single transumbilical incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy versus classic laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled trial. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1842–1848.9. Ma J, Cassera MA, Spaun GO, Hammill CW, Hansen PD, Aliabadi-Wahle S. Randomized controlled trial comparing single-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy and four-port laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:22–27.10. Edwards C, Bradshaw A, Ahearne P, Dematos P, Humble T, Johnson R, et al. Single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy is feasible: initial experience with 80 cases. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:2241–2247.11. Fronza JS, Linn JG, Nagle AP, Soper NJ. A single institution's experience with single incision cholecystectomy compared to standard laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surgery. 2010; 148:731–734. discussion 734–736.12. Gangl O, Hofer W, Tomaselli F, Sautner T, Függer R. Single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy (SILC) versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC)-a matched pair analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2011; 396:819–824.13. Greaves N, Nicholson J. Single incision laparoscopic surgery in general surgery: a review. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2011; 93:437–440.14. Ishikawa N, Arano Y, Shimizu S, Morishita M, Kawaguchi M, Matsunoki A, et al. Single incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) using cross hand technique. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2009; 18:322–324.15. Jaspers JE, Breedveld P, Herder JL, Grimbergen CA. Camera and instrument holders and their clinical value in minimally invasive surgery. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2004; 14:145–152.16. Singh M, Mehta KS, Yasir M, Kaur A, Aiman A, Sharma A, et al. Single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy using conventional laparoscopic instruments and comparison with three-port cholecystectomy. Indian J Surg. 2015; 77:Suppl 2. 546–550.17. Choi Y, Han HS, Yoon YS, Cho JY, Jang JY, Choi HL, et al. Single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy without a camera operator. J Minim Invasive Surg. 2017; 20:63–68.18. Daabiss M. American Society of Anaesthesiologists physical status classification. Indian J Anaesth. 2011; 55:111–115.19. Philipp SR, Miedema BW, Thaler K. Single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy using conventional instruments: early experience in comparison with the gold standard. J Am Coll Surg. 2009; 209:632–637.20. Podolsky ER, Rottman SJ, Curcillo PG 2nd. Single port access (SPA) cholecystectomy: two year follow-up. JSLS. 2009; 13:528–535.21. Hall TC, Dennison AR, Bilku DK, Metcalfe MS, Garcea G. Single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a systematic review. Arch Surg. 2012; 147:657–666.22. Hodgett SE, Hernandez JM, Morton CA, Ross SB, Albrink M, Rosemurgy AS. Laparoendoscopic single site (LESS) cholecystectomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009; 13:188–192.23. Pan MX, Liang ZW, Cheng Y, Jiang ZS, Xu XP, Wang KH, et al. Learning curve of transumbilical suture-suspension single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:4786–4790.24. Mutter D, Leroy J, Cahill R, Marescaux J. A simple technical option for single-port cholecystectomy. Surg Innov. 2008; 15:332–333.25. Choi YR, Han HS, Yoon YS, Cho JY, Jang JS, Kwon SU, et al. Solo single incision laparoscopic left hemihepatectomy using a laparoscopic scope holder. Videoscopy. 2018; 28:DOI: 10.1089/vor.2017.0473.26. Jin SH, Kim DY, Kim H, Jeong IH, Kim MW, Cho YK, et al. Multidimensional learning curve in laparoscopy-assisted gastrectomy for early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:28–33.27. Ramsay CR, Grant AM, Wallace SA, Garthwaite PH, Monk AF, Russell IT. Statistical assessment of the learning curves of health technologies. Health Technol Assess. 2001; 5:1–79.28. Kravetz AJ, Iddings D, Basson MD, Kia MA. The learning curve with single-port cholecystectomy. JSLS. 2009; 13:332–336.29. Carr A, Bhavaraju A, Goza J, Wilson R. Initial experience with single-incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am Surg. 2010; 76:703–707.30. Han HJ, Choi SB, Park MS, Lee JS, Kim WB, Song TJ, et al. Learning curve of single port laparoscopic cholecystectomy determined using the non-linear ordinary least squares method based on a non-linear regression model: an analysis of 150 consecutive patients. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011; 18:510–515.31. Qiu Z, Sun J, Pu Y, Jiang T, Cao J, Wu W. Learning curve of transumbilical single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy (SILS): a preliminary study of 80 selected patients with benign gallbladder diseases. World J Surg. 2011; 35:2092–2101.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy for patients with Mirizzi syndrome
- The Learning Curve for Single-Port Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy by Experienced Laparoscopic Surgeon
- Single-Port Laparoscopic Solo Surgery: Technical Aspects and Personal Experience
- Comparison of Single-Incision Robotic Cholecystectomy, Single-Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy and 3-Port Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy -Postoperative Pain, Cosmetic Outcome and Surgeon's Workload
- Single Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy without a Camera Operator