Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Oct;43(5):544-554. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.5.544.
Reliability and Validity of the Comprehensive Limb and Oral Apraxia Test: Standardization and Clinical Application in Korean Patients With Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rmpyun@korea.ac.kr
- 2Brain Convergence Research Center, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Speech Pathology, Daegu University, Gyeongsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2463702
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.5.544
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To develop and standardize the Limb and Oral Apraxia Test (LOAT) for Korean patients and investigate its reliability, validity, and clinical usefulness for patients with stroke.
METHODS
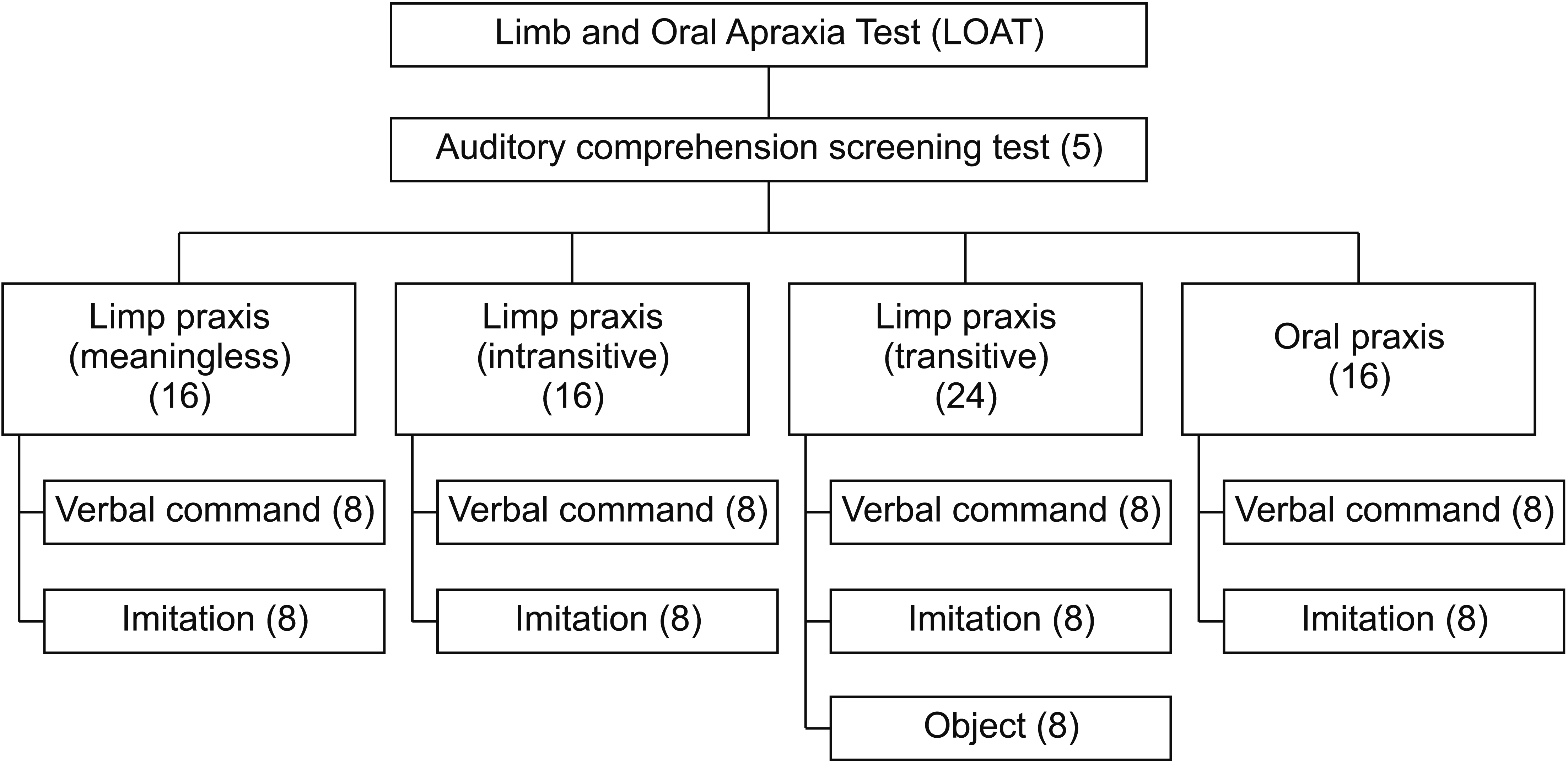
We developed the LOAT according to a cognitive neuropsychological model of limb and oral praxis. The test included meaningless, intransitive, transitive, and oral praxis composed of 72 items (56 items on limb praxis and 16 items on oral praxis; maximum score 216). We standardized the LOAT in a nationwide sample of 324 healthy adults. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability and concurrent validity tests were performed in patients with stroke. We prospectively applied the LOAT in 80 patients and analyzed the incidence of apraxia. We also compared the clinical characteristics between the apraxia and non-apraxia groups.
RESULTS
The internal consistency was high (Cronbach's alpha=0.952). The inter-rater and intra-rater reliability and concurrent validity were also high (r=0.924-0.992, 0.961-0.999, and 0.830, respectively; p<0.001). The mean total, limb, and oral scores were not significantly different according to age and education (p>0.05). Among the 80 patients with stroke, 19 (23.8%) had limb apraxia and 21 (26.3%) had oral apraxia. Left hemispheric lesions and aphasia were significantly more frequently observed in the limb/oral apraxia group than in the non-apraxia group (p<0.001).
CONCLUSION
The LOAT is a newly developed comprehensive test for limb and oral apraxia for Korean patients with stroke. It has high internal consistency, reliability, and validity and is a useful apraxia test for patients with stroke.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rothi LJ, Heilman KM, Watson RT. Pantomime comprehension and ideomotor apraxia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985; 48:207–10.
Article2. Gonzalez Rothi LJ, Ochipa C, Heilman KM. A cognitive neuropsychological model of limb praxis. Cogn Neuropsychol. 1991; 8:443–58.
Article3. Foundas AL, Henchey R, Gilmore RL, Fennell EB, Heilman KM. Apraxia during Wada testing. Neurology. 1995; 45:1379–83.
Article4. Foundas AL, Macauley BL, Raymer AM, Maher LM, Heilman KM, Gonzalez Rothi LJ. Ecological implications of limb apraxia: evidence from mealtime behavior. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 1995; 1:62–6.
Article5. De Renzi E, Faglioni P, Sorgato P. Modality-specific and supramodal mechanisms of apraxia. Brain. 1982; 105(Pt 2):301–12.
Article6. Goldenberg G, Hermsdorfer J, Spatt J. Ideomotor apraxia and cerebral dominance for motor control. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res. 1996; 3:95–100.
Article7. Koski L, Iacoboni M, Mazziotta JC. Deconstructing apraxia: understanding disorders of intentional movement after stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 2002; 15:71–7.
Article8. Finney GR. Perceptual-motor dysfunction. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2015; 21:678–89.
Article9. Chang SE, Kenney MK, Loucks TM, Poletto CJ, Ludlow CL. Common neural substrates support speech and non-speech vocal tract gestures. Neuroimage. 2009; 47:314–25.
Article10. Dovern A, Fink GR, Weiss PH. Diagnosis and treatment of upper limb apraxia. J Neurol. 2012; 259:1269–83.
Article11. Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:3186–91.
Article12. Guillemin F, Bombardier C, Beaton D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993; 46:1417–32.
Article13. Lee JS, Suh KT, Kim JI, Lee HS, Goh TS. Validation of the korean version of the neck pain and disability scale. Asian Spine J. 2013; 7:178–83.
Article14. Ha JW, Pyun SB, Lee HY, Hwang YM, Nam K. Reliability and validity analyses of the Korean version of Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test in brain-damaged patients. Korean J Commun Disord. 2009; 14:46–57.15. Kim SJ, Shin JC, Kim DY, Kim H. Korean version of Stroke and Aphasia Quality of Life Scale-39 (KSAQOL-39): its validity and reliability. J Rehabil Res. 2012; 16:245–65.16. Kim DY, Pyun SB, Kim EJ, Ryu BJ, Choi TW, Pulvermuller F. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Communicative Activity Log (CAL). Aphasiology. 2016; 30:96–105.
Article17. Helm-Estabrooks N. TOLA: Test of Oral and Limb Apraxia. Chicago, IL: Riverside Publishing Company;1992.18. Enderby P, Crow E. Frenchay aphasia screening test: validity and comparability. Disabil Rehabil. 1996; 18:238–40.
Article19. Dabul B. Apraxia battery for adults. Austin, TX: Pro-ED;2000.20. Vanbellingen T, Kersten B, Van de Winckel A, Bellion M, Baronti F, Muri R, et al. A new bedside test of gestures in stroke: the apraxia screen of TULIA (AST). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011; 82:389–92.
Article21. Kertesz A. Western aphasia battery test manual. New York, NY: Grune & Stratton;1982.22. Mutha PK, Sainburg RL, Haaland KY. Coordination deficits in ideomotor apraxia during visually targeted reaching reflect impaired visuomotor transformations. Neuropsychologia. 2010; 48:3855–67.
Article23. Papagno C, Della Sala S, Basso A. Ideomotor apraxia without aphasia and aphasia without apraxia: the anatomical support for a double dissociation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993; 56:286–9.
Article24. Vry MS, Tritschler LC, Hamzei F, Rijntjes M, Kaller CP, Hoeren M, et al. The ventral fiber pathway for pantomime of object use. Neuroimage. 2015; 106:252–63.
Article25. Weiss PH, Ubben SD, Kaesberg S, Kalbe E, Kessler J, Liebig T, et al. Where language meets meaningful action: a combined behavior and lesion analysis of aphasia and apraxia. Brain Struct Funct. 2016; 221:563–76.
Article26. Kertesz A, Hooper P. Praxis and language: the extent and variety of apraxia in aphasia. Neuropsychologia. 1982; 20:275–86.
Article27. Zwinkels A, Geusgens C, van de Sande P, Van Heugten C. Assessment of apraxia: inter-rater reliability of a new apraxia test, association between apraxia and other cognitive deficits and prevalence of apraxia in a rehabilitation setting. Clin Rehabil. 2004; 18:819–27.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Apraxia: Review and Update
- Neuroanatomical Basis of Apraxia
- Korean Version of the Stroke Rehabilitation Motivation Scale: Reliability and Validity Evaluation
- Reliability and Validity of Korean Version of Apraxia Screen of TULIA (K-AST)
- Psychometric Analysis of Comprehensive Basic Medical Sciences Examination