J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jul;62(4):476-486. 10.3340/jkns.2019.0104.
Quantitative Feasibility Evaluation of ¹¹C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography Images in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery : Phantom-Based Study and Clinical Application
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea. breadot@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Hwasun, Korea.
- KMID: 2463679
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2019.0104
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The functional information of ¹¹C-methionine positron emission tomography (MET-PET) images can be applied for Gamma knife radiosurgery (GKR) and its image quality may affect defining the tumor. This study conducted the phantom-based evaluation for geometric accuracy and functional characteristic of diagnostic MET-PET image co-registered with stereotactic image in Leksell GammaPlan® (LGP) and also investigated clinical application of these images in metastatic brain tumors.
METHODS
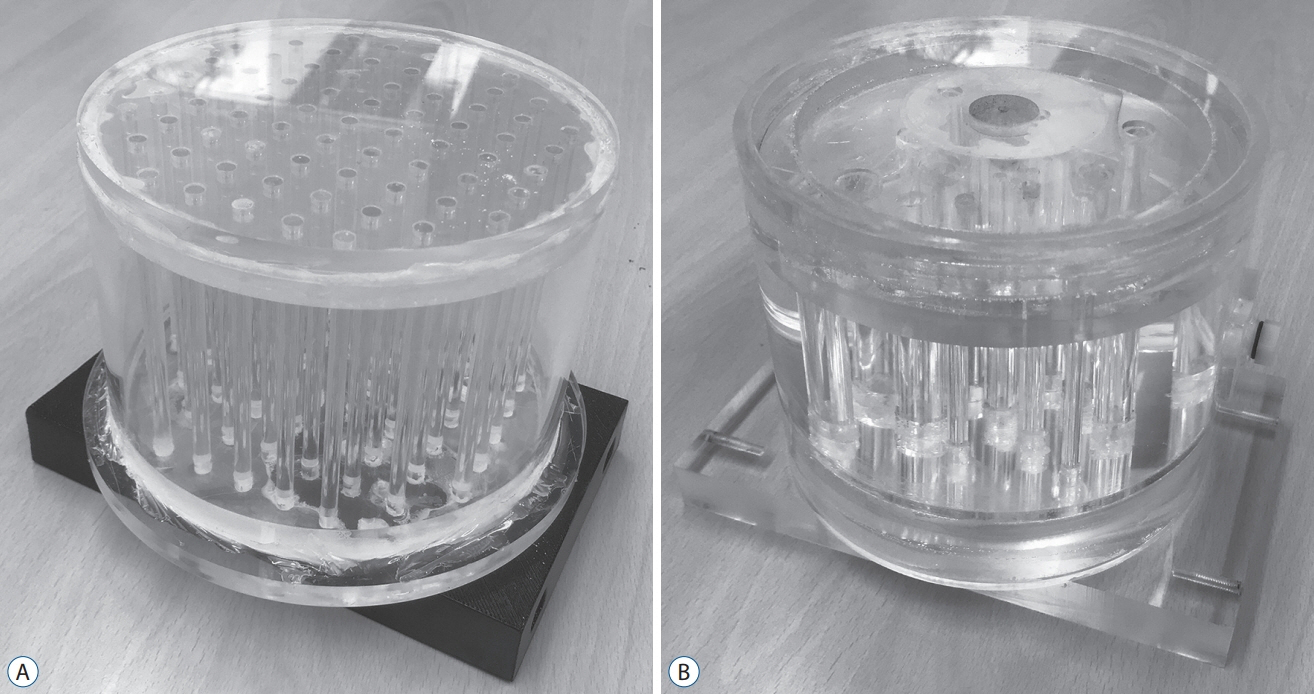
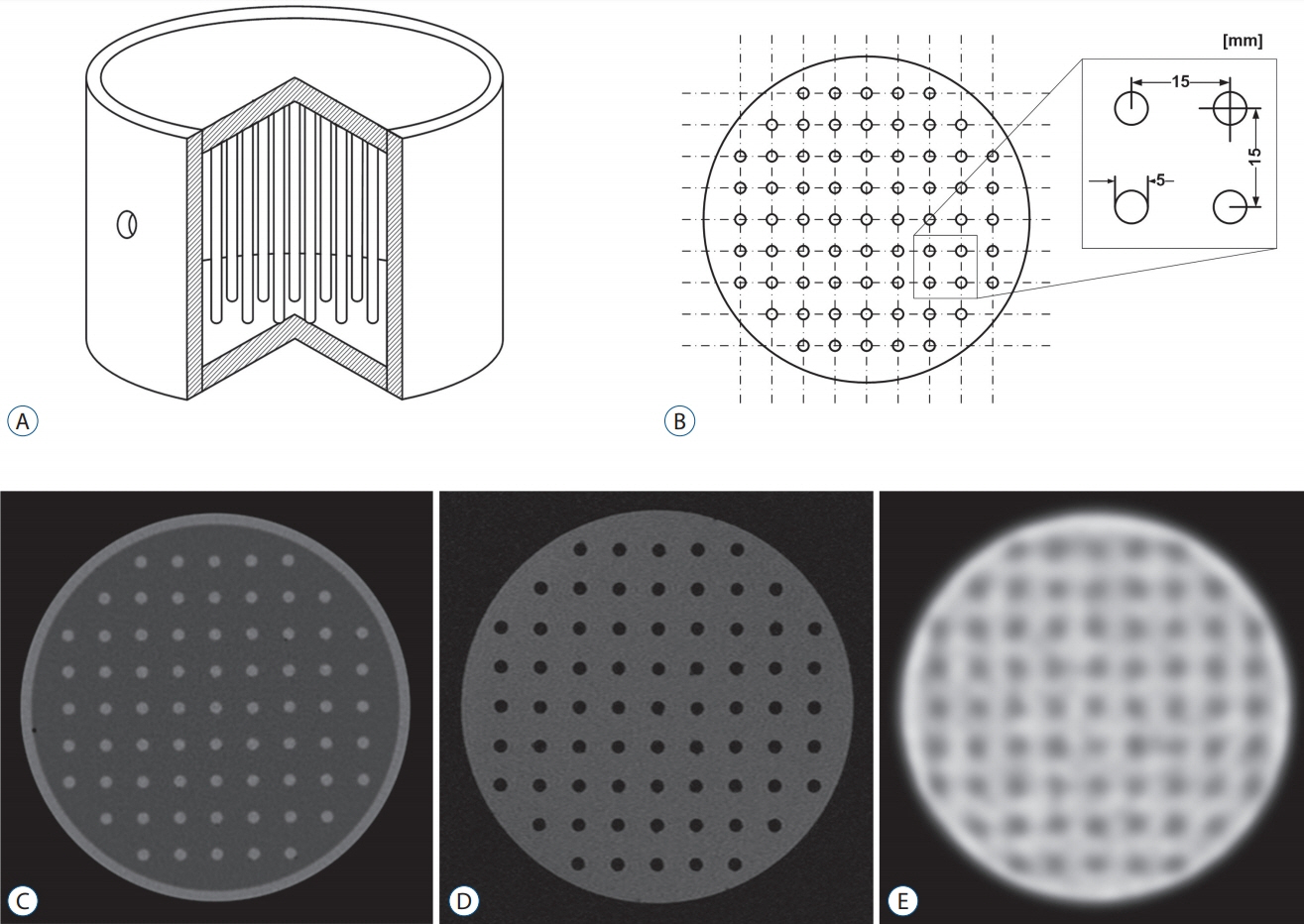
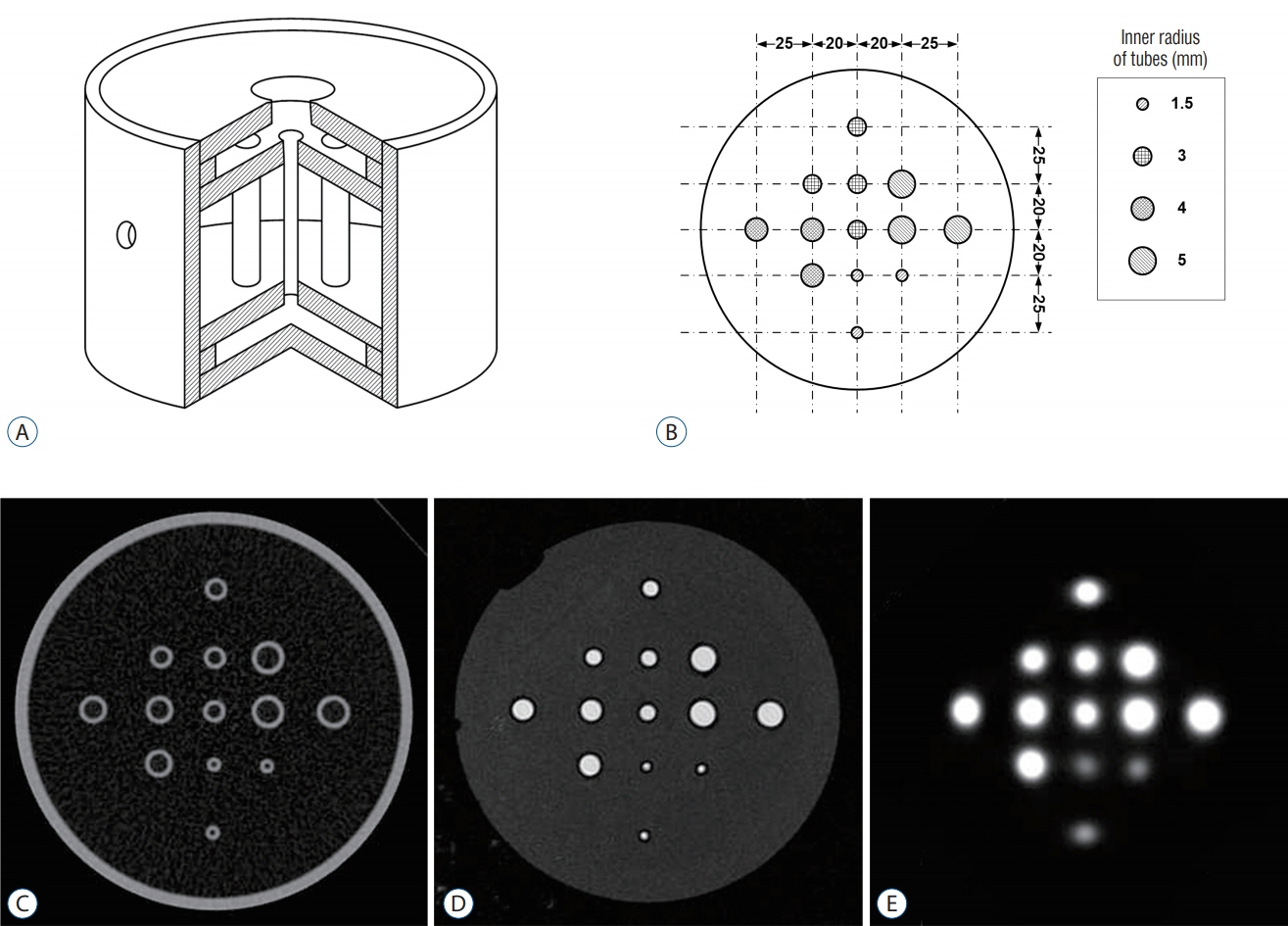
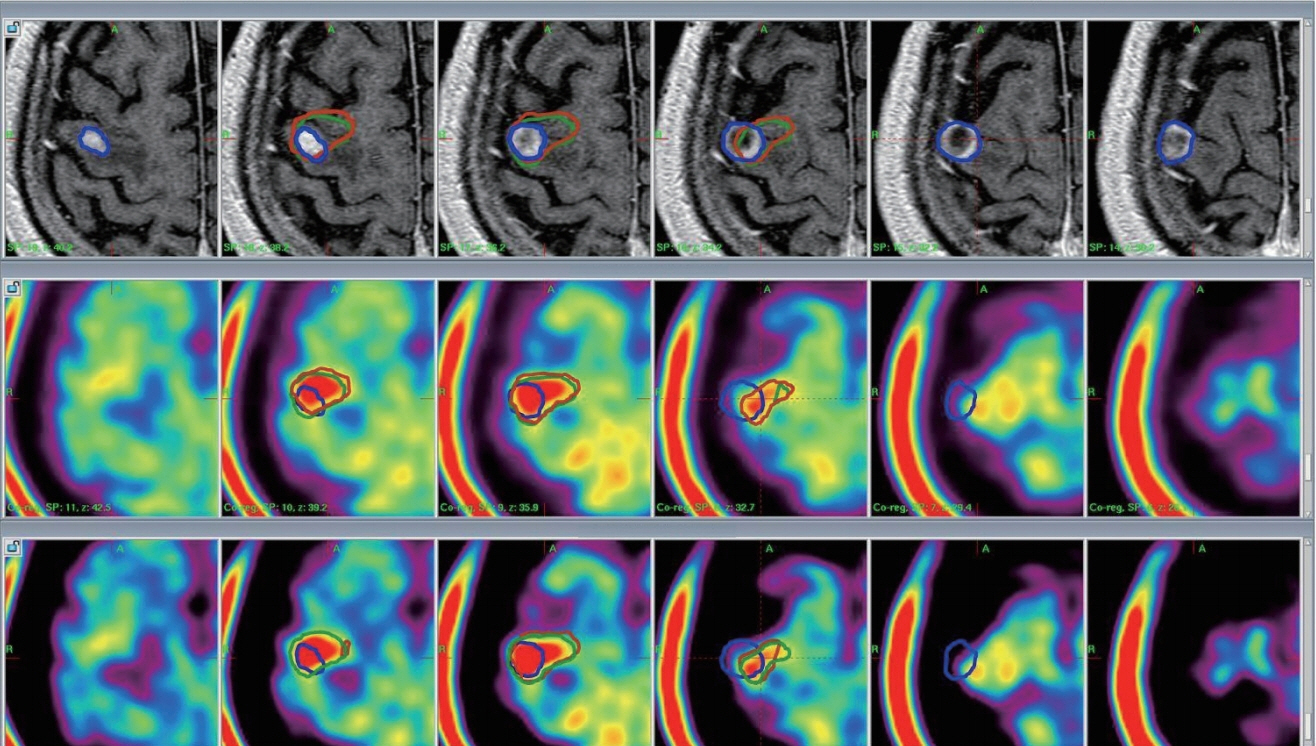
Two types of cylindrical acrylic phantoms fabricated in-house were used for this study : the phantom with an array-shaped axial rod insert and the phantom with different sized tube indicators. The phantoms were mounted on the stereotactic frame and scanned using computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and PET system. Three-dimensional coordinate values on co-registered MET-PET images were compared with those on stereotactic CT image in LGP. MET uptake values of different sized indicators inside phantom were evaluated. We also evaluated the CT and MRI co-registered stereotactic MET-PET images with MR-enhancing volume and PET-metabolic tumor volume (MTV) in 14 metastatic brain tumors.
RESULTS
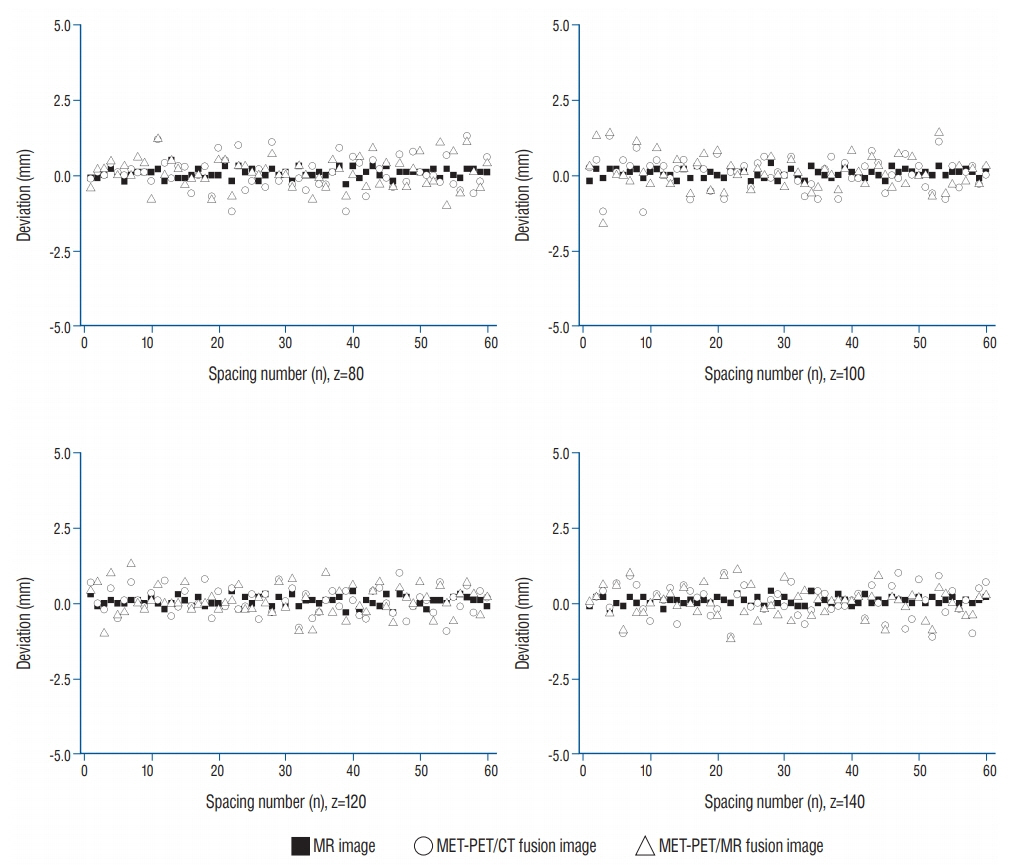
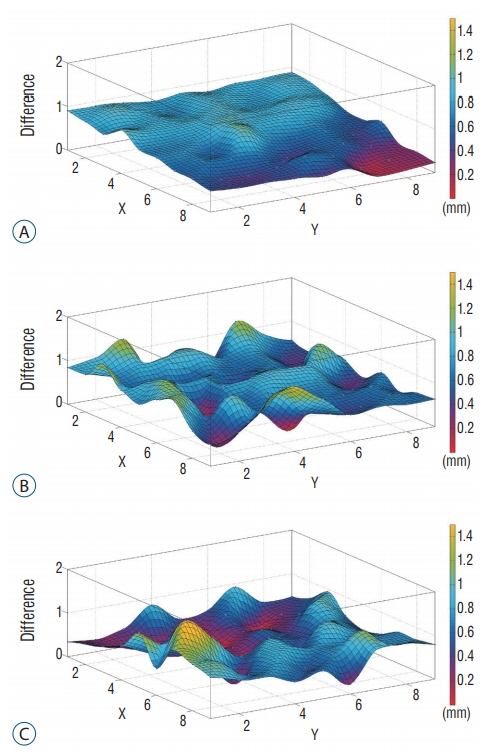
Imaging distortion of MET-PET was maintained stable at less than approximately 3% on mean value. There was no statistical difference in the geometric accuracy according to co-registered reference stereotactic images. In functional characteristic study for MET-PET image, the indicator on the lateral side of the phantom exhibited higher uptake than that on the medial side. This effect decreased as the size of the object increased. In 14 metastatic tumors, the median matching percentage between MR-enhancing volume and PET-MTV was 36.8% on PET/MR fusion images and 39.9% on PET/CT fusion images.
CONCLUSION
The geometric accuracy of the diagnostic MET-PET co-registered with stereotactic MR in LGP is acceptable on phantom-based study. However, the MET-PET images could the limitations in providing exact stereotactic information in clinical study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Carney JP, Townsend DW, Rappoport V, Bendriem B. Method for transforming CT images for attenuation correction in PET/CT imaging. Medical physics. 33:976–983. 2006.
Article2. Chung HT, Kim DG. Distortion correction for digital subtraction angiography imaging: PC based system for radiosurgery planning. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 71:165–173. 2003.
Article3. Isambert A, Bonniaud G, Lavielle F, Malandain G, Lefkopoulos D. A phantom study of the accuracy of CT, MR and PET image registrations with a block matching-based algorithm. Cancer Radiother. 12:800–808. 2008.
Article4. Jin SG, Ryu HH, Li SY, Li CH, Lim SH, Jang WY, et al. Nogo-A inhibits the migration and invasion of human malignant glioma U87MG cells. Oncol Rep. 35:3395–3402. 2016.
Article5. Kaneko K, Kuwabara Y, Sasaki M, Koga H, Abe K, Baba S, et al. Validation of quantitative accuracy of the post-injection transmission-based and transmissionless attenuation correction techniques in neurological FDG-PET. Nucl Med Commun. 25:1095–1102. 2004.
Article6. Levivier M, Massager N, Wikler D, Lorenzoni J, Ruiz S, Devriendt D, et al. Use of stereotactic PET images in dosimetry planning of radiosurgery for brain tumors: clinical experience and proposed classification. J Nucl Med. 45:1146–1154. 2004.7. Nakazawa H, Komori M, Shibamoto Y, Takikawa Y, Mori Y, Tsugawa T. Geometric accuracy in three-dimensional coordinates of Leksell stereotactic skull frame with wide-bore 1.5-T MRI compared with conventional 1.5-T MRI. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 58:595–600. 2014.
Article8. Nakazawa H, Mori Y, Komori M, Shibamoto Y, Tsugawa T, Kobayashi T, et al. Validation of accuracy in image co-registration with computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in Gamma knife radiosurgery. J Radiat Res. 55:924–933. 2014.
Article9. Nakazawa H, Mori Y, Yamamuro O, Komori M, Shibamoto Y, Uchiyama Y, et al. Geometric accuracy of 3D coordinates of the Leksell stereotactic skull frame in 1.5 Tesla- and 3.0 Tesla-magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison of three different fixation screw materials. J Radiat Res. 55:1184–1191. 2014.
Article10. Neumann JO, Giese H, Biller A, Nagel AM, Kiening K. Spatial distortion in MRI-guided stereotactic procedures: evaluation in 1.5-, 3- and 7-Tesla MRI Scanners. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 93:380–386. 2015.
Article11. Okamoto S, Shiga T, Hattori N, Kubo N, Takei T, Katoh N, et al. Semiquantitative analysis of C-11 methionine PET may distinguish brain tumor recurrence from radiation necrosis even in small lesions. Ann Nucl Med. 25:213–220. 2011.
Article12. Price RR, Axel L, Morgan T, Newman R, Perman W, Schneiders N, et al. Quality assurance methods and phantoms for magnetic resonance imaging: report of AAPM nuclear magnetic resonance Task Group No. 1. Med Phys. 17:287–295. 1990.
Article13. Rousseau J, Clarysse P, Blond S, Gibon D, Vasseur C, Marchandise X. Validation of a new method for stereotactic localization using MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 15:291–296. 1991.
Article14. Scarfone C, Lavely WC, Cmelak AJ, Delbeke D, Martin WH, Billheimer D, et al. Prospective feasibility trial of radiotherapy target definition for head and neck cancer using 3-dimensional PET and CT imaging. J Nucl Med. 45:543–552. 2004.15. Soret M, Bacharach SL, Buvat I. Partial-volume effect in PET tumor imaging. J Nucl Med. 48:932–945. 2007.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of IAEA TRS-398 Protocol to Gamma Knife Model C
- Clinical Application of 7.0 T Magnetic Resonance Images in Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Patient with Brain Metastases
- Clinical Applications of Technetium-99m Quantitative Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography
- Characteristics of Magnetic Resonance-Based Attenuation Correction Map on Phantom Study in Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging System
- Differences in Target Volume Delineation Using Typical Radiosurgery Planning System