J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jul;62(4):458-466. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0211.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Involving the Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus: A Single Center Experience and Review of the Literatures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea. nsdoctor@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2463677
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0211
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We retrospectively assessed the efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) involving the transverse-sigmoid sinus and analyzed the angiographic and clinical results with our 8-year experience.
METHODS
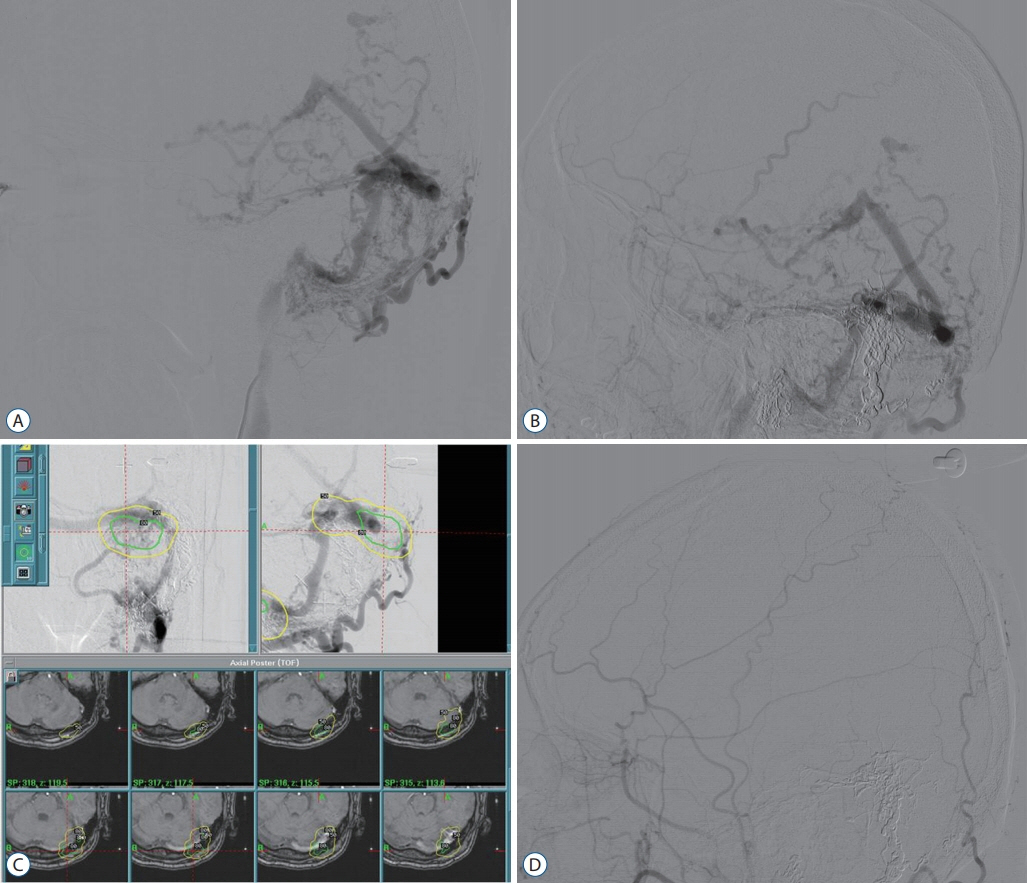
Nine patients with intracranial DAVFs involving the transverse-sigmoid sinus underwent SRS using a Gamma Knife® (Elekta Inc., Atlanta, GA, USA) between 2009 and 2016. Five patients underwent SRS for residual DAVFs after embolization and four patients were treated with SRS alone. The median target volume was 1.9 cm3 (range, 0.8-14.2) and the median radiation dose of the target was 17 Gy (range, 16-20). The median follow-up period was 37 months (range, 7-81).
RESULTS
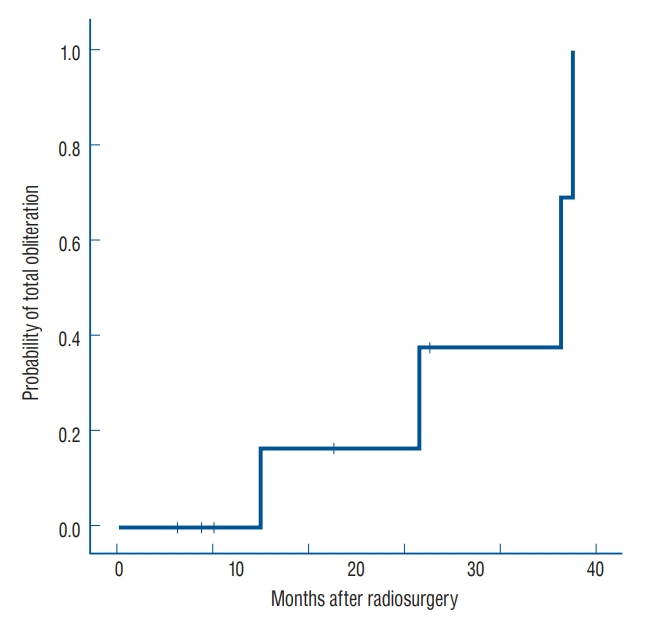
Pulsating tinnitus (33%) was the most common symptom. DAVFs were completely obliterated in four patients (44%) and subtotally obliterated in five (56%). Six patients (67%) showed complete recovery of symptoms or signs, and three (33%) showed incomplete recovery. One patient experienced a recurrent seizure. Adverse radiation effects after SRS occurred in one patient (11%). The total obliteration rates after SRS were 16.7%, 37.5%, and 68.7% at 1, 2, and 3 years, respectively. The median interval from SRS to total obliteration of the fistula was 31 months (range, 12-38). The rates at which the symptoms started to improve were 40% at 1 month and 80% at 2 months after SRS. Symptoms started to improve at a median of 5 weeks after SRS (range, 3-21).
CONCLUSION
SRS with or without embolization is a safe and effective treatment to relieve symptoms and obliterate DAVFs on the transverse-sigmoid sinus.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 82:166–179. 1995.
Article2. Chen CJ, Lee CC, Ding D, Starke RM, Chivukula S, Yen CP, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: a systematic review. J Neurosurg. 122:353–362. 2015.
Article3. Chung SJ, Kim JS, Kim JC, Lee SK, Kwon SU, Lee MC, et al. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: analysis of 60 patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 13:79–88. 2002.
Article4. Cifarelli CP, Kaptain G, Yen CP, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP. Gamma knife radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 67:1230–1235. discussion 1235. 2010.
Article5. Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 194:671–680. 1995.
Article6. Friedman JA, Pollock BE, Nichols DA, Gorman DA, Foote RL, Stafford SL. Results of combined stereotactic radiosurgery and transarterial embolization for dural arteriovenous fistulas of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses. J Neurosurg. 94:886–891. 2001.
Article7. Hanakita S, Koga T, Shin M, Shojima M, Igaki H, Saito N. Role of gamma knife surgery in the treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 117 Suppl:158–163. 2012.
Article8. Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Yang HC, Flannery TJ, Awan NR, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations, part 3: outcome predictors and risks after repeat radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 116:21–32. 2012.
Article9. Kwon BJ, Han MH, Kang HS, Chang KH. MR imaging findings of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: relations with venous drainage patterns. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 26:2500–2507. 2005.10. Macdonald JHM, Millar JS, Barker CS. Endovascular treatment of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: a single-centre, 14-year experience and the impact of Onyx on local practise. Neuroradiology. 52:387–395. 2010.
Article11. Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Britz GW, Sekhar LN. Multimodality treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in the Onyx era: a single center experience. World Neurosurg. 73:365–379. 2010.
Article12. Pan DH, Chung WY, Guo WY, Wu HM, Liu KD, Shiau CY, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of dural arteriovenous fistulas involving the transverse-sigmoid sinus. J Neurosurg. 96:823–829. 2002.
Article13. Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Patel AK, Bissonette DJ, Lunsford LD. Magnetic resonance imaging: an accurate method to evaluate arteriovenous malformations after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 85:1044–1049. 1996.
Article14. Pollock BE, Nichols DA, Garrity JA, Gorman DA, Stafford SL. Stereotactic radiosurgery and particulate embolization for cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurgery. 45:459–466. discussion 466- 467. 1999.
Article15. van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M. Curative embolization with Onyx of dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous drainage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 31:1516–1520. 2010.
Article16. Yang HC, Kano H, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Horowitz MB, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with or without embolization for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurgery. 67:1276–1283. discussion 1284-1285. 2010.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Contralateral Transverse Sinus Occlusion After Treatment of Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
- Infantile Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Transverse Sinus Presenting with Ocular Symptoms, Case Reports and Review of Literature
- Endovascular management of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: Overall review and considerations
- Navigation guided small craniectomy and direct cannulation of pure isolated sigmoid sinus for treatment of dural arteriovenous fistula
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for dural arteriovenous fistula