J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jul;62(4):382-388. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0130.
Biomechanical Properties of the Cranial Dura Mater with Puncture Defects: An In Vitro Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kutahya Health Science University, Kutahya, Turkey.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Dokuz Eylul University School of Medicine, Izmir, Turkey. ceren.kizmazoglu@gmail.com
- 3Department of Biomechanics, Dokuz Eylul University School of Medicine Health Science Institute, Izmir, Turkey.
- 4Department of Pathology, Forensic Medicine Institution , Izmir, Turkey.
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, EskiÅŸehir Osmangazi University School of Medicine, Eskisehir, Turkey.
- KMID: 2463668
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0130
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The primary aim of this investigation was to explore the nature of dura mater biomechanics following the introduction of puncture defect(s).
METHODS
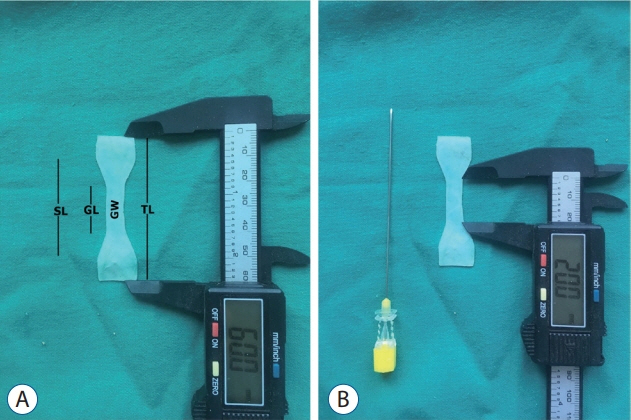
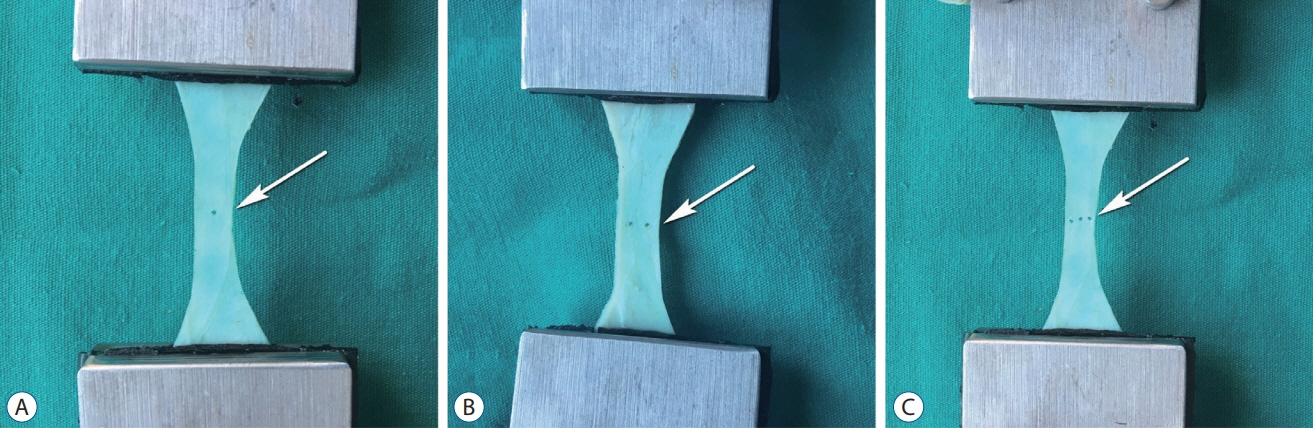
Twenty-eight dura mater specimens were collected during autopsy from the department of forensic medicine of the authors' institution. Specimens were divided randomly into one of four groups : group I (cranial dura mater; n=7), group II (cranial dura mater with one puncture defect; n=7); group III (cranial dura mater with two puncture defects; n=7), and group IV (cranial dura mater with three puncture defects; n=7).
RESULTS
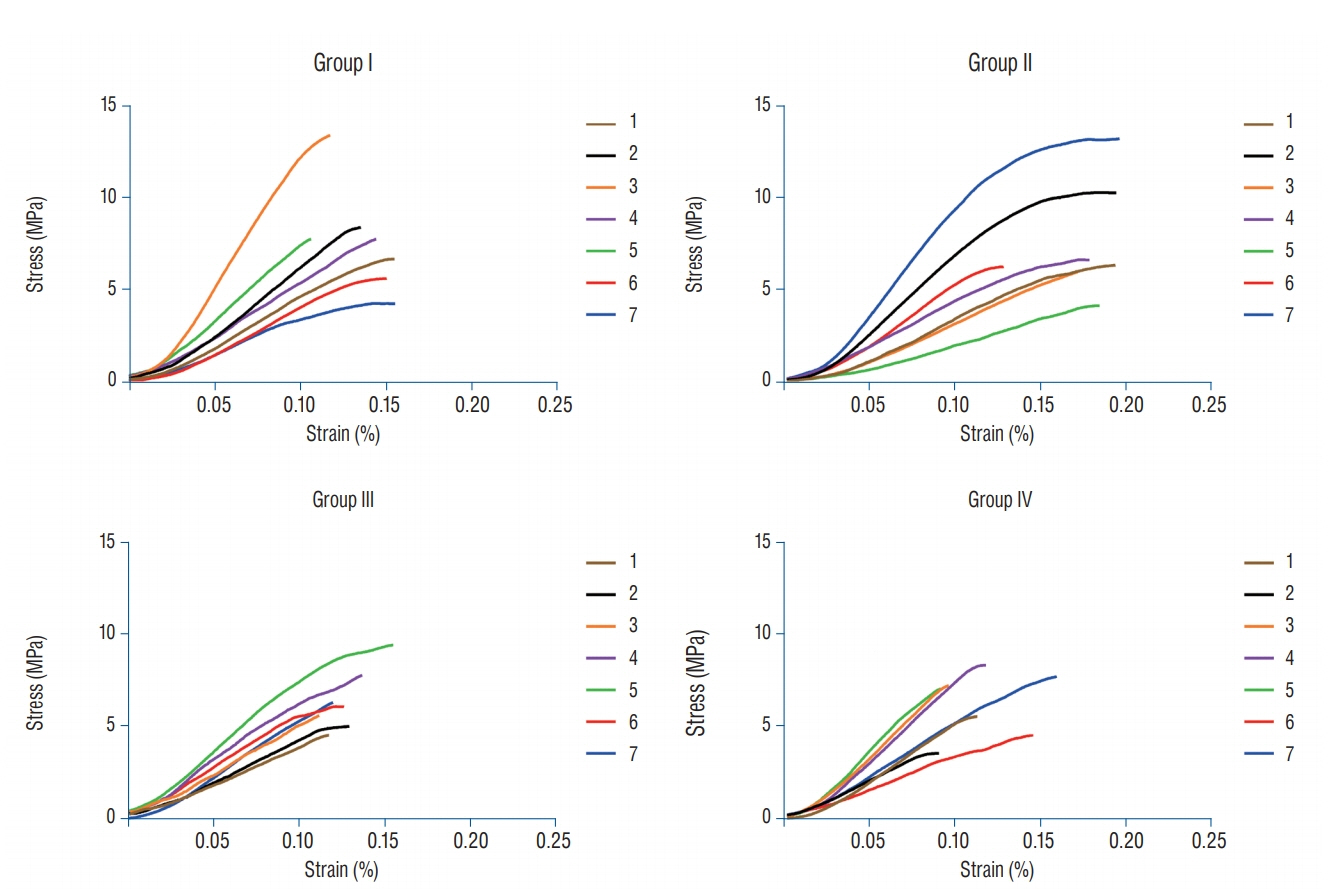
The mean±standard deviation tensile strengths of the dura mater were 8.35±3.16, 8.22±3.32, 7.13±1.77, and 6.94±1.93 MPa for groups I, II, III, and IV, respectively. There was no statistical difference between all groups. A single, two or more punctures of the dura mater using a 20-gauge Quincke needle did not affect cranial dura tensile strength.
CONCLUSION
This biomechanical study may contribute to the future development of artificial dura mater substitutes and medical needles that have a lower negative impact on the biomechanical properties of dura mater.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Davignon KR, Dennehy KC. Update on postdural puncture headache. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 40:89–102. 2002.
Article2. Dufrane D, Marchal C, Cornu O, Raftopoulos C, Delloye C. Clinical application of a physically and chemically processed human substitute for dura mater. J Neurosurg. 98:1198–1202. 2003.
Article3. Famaey N, Verhoeven J, Jacobs S, Pettinari M, Meyns B. In situ evolution of the mechanical properties of stretchable and non-stretchable ePTFE vascular grafts and adjacent native vessels. Int J Artif Organs. 37:900–910. 2014.
Article4. Flaatten H, Felthaus J, Kuwelker M, Wisborg T. Postural post-dural puncture headache. A prospective randomised study and a meta-analysis comparing two different 0.40 mm O.D. (27 g) spinal needles. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 44:643–647. 2000.
Article5. Flaatten H, Thorsen T, Askeland B, Finne M, Rosland J, Hansen T, et al. Puncture technique and postural postdural puncture headache. A randomised, double-blind study comparing transverse and parallel puncture. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 42:1209–1214. 1998.
Article6. Kim M, Yoon H. Comparison of post-dural puncture headache and low back pain between 23 and 25 gauge Quincke spinal needles in patients over 60 years: randomized, double-blind controlled trial. Int J Nurs Stud. 48:1315–1322. 2011.
Article7. Lewis MC, Lafferty JP, Sacks MS, Pallares VS, TerRiet M. How much work is required to puncture dura with Tuohy needles? Br J Anaesth. 85:238–241. 2000.
Article8. Liu SS, McDonald SB. Current issues in spinal anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 94:888–906. 2001.
Article9. Longo S. Postdural puncture: implications and complications. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 12:271–275. 1999.
Article10. Lux EA, Althaus A. Is there a difference in postdural puncture headache after continuous spinal anesthesia with 28G microcatheters compared with punctures with 22G Quincke or Sprotte spinal needles? Local Reg Anesth. 7:63–67. 2014.
Article11. Lybecker H, Møller JT, May O, Nielsen HK. Incidence and prediction of postdural puncture headache. A prospective study of 1021 spinal anesthesias. Anesth Analg. 70:389–394. 1990.
Article12. Mahvash M, Dupont PE. Fast needle insertion to minimize tissue deformation and damage. IEEE Int Conf Robot Autom. 2009:3097–3102. 2009.
Article13. Matas SL. Why should we use atraumatic needles in lumbar puncture? Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 71:681–684. 2013.
Article14. McGarvey KA, Lee JM, Boughner DR. Mechanical suitability of glycerolpreserved human dura mater for construction of prosthetic cardiac valves. Biomaterials. 5:109–117. 1984.
Article15. Mihic DN. Postspinal headaches, needle surfaces and longitudinal orientation of the dural fibers. Results of a survey. Reg Anaesth. 9:54–56. 1986.16. Oh J, Liu K, Medina T, Kralick F, Noh HM. A novel microneedle array for the treatment of hydrocephalus. Microsyst Technol. 20:1169–1179. 2014.
Article17. Protasoni M, Sangiorgi S, Cividini A, Culuvaris GT, Tomei G, Dell’Orbo C, et al. The collagenic architecture of human dura mater. J Neurosurg. 114:1723–1730. 2011.
Article18. Reina MA, De Leon Casasola O, López A, De Andrés JA, Mora M, Fernández A. The origin of the spinal subdural space: ultrastructure findings. Anesth Analg. 94:991–995. table of contents. 2002.
Article19. Reina MA, López-García A, Dittmann M, de Andrés JA. Analysis of the external and internal surface of human dura mater with scanning electron microscopy. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 43:130–134. 1996.20. Schmittner MD, Urban N, Janke A, Weiss C, Bussen DG, Burmeister MA, et al. Influence of the pre-operative time in upright sitting position and the needle type on the incidence of post-dural puncture headache (PDPH) in patients receiving a spinal saddle block for anorectal surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 26:97–102. 2011.
Article21. Seeberger MD, Kaufmann M, Staender S, Schneider M, Scheidegger D. Repeated dural punctures increase the incidence of postdural puncture headache. Anesth Analg. 82:302–305. 1996.
Article22. van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, van den Dobbelsteen JJ. Needle-tissue interaction forces--a survey of experimental data. Med Eng Phys. 34:665–680. 2012.23. van Noort R, Black MM, Martin TR, Meanley S. A study of the uniaxial mechanical properties of human dura mater preserved in glycerol. Biomaterials. 2:41–45. 1981.
Article24. Wolfinbarger L Jr, Zhang YX, Adam BLT, Homsi D, Gates K, Sutherland V. Biomechanical aspects on rehydrated freeze-dried human allograft dura-mater tissues. J Appl Biomater. 5:265–270. 1994.
Article25. Yamada K, Miyamoto S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Ikada Y, Iwata H, et al. Development of a dural substitute from synthetic bioabsorbable polymers. J Neurosurg. 86:1012–1017. 1997.
Article26. Yamada K, Miyamoto S, Takayama M, Nagata I, Hashimoto N, Ikada Y, et al. Clinical application of a new bioabsorbable artificial dura mater. J Neurosurg. 96:731–735. 2002.
Article27. Zerris VA, James KS, Roberts JB, Bell E, Heilman CB. Repair of the dura mater with processed collagen devices. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 83:580–588. 2007.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Biomechanical Properties of Dura Mater Substitutes and Cranial Human Dura Mater : An In Vitro Study
- In vitro Fusion of the Posterior Frontal Calvarial Suture in the Mouse
- Dural Puncture by Introducer when Performing Spinal Anesthesia -A case report-
- Idiopathic Hypertrophic Cranial Pachymeningitis: Case Report
- Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis in the Craniocervical Junction