J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Jul;62(4):376-381. 10.3340/jkns.2018.0176.
Three Dimensional Measurement of Ideal Trajectory of Pedicle Screws of Subaxial Cervical Spine Using the Algorithm Could Be Applied for Robotic Screw Insertion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- 2Department of Computer Engineering, Jeju National University College of Engineering, Jeju, Korea. hykwak@gmail.com
- KMID: 2463667
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0176
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To define optimal method that calculate the safe direction of cervical pedicle screw placement using computed tomography (CT) image based three dimensional (3D) cortical shell model of human cervical spine.
METHODS
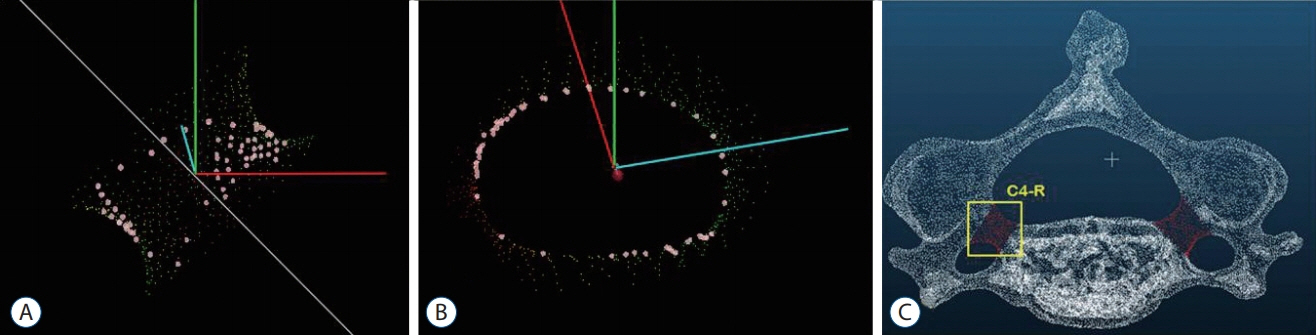
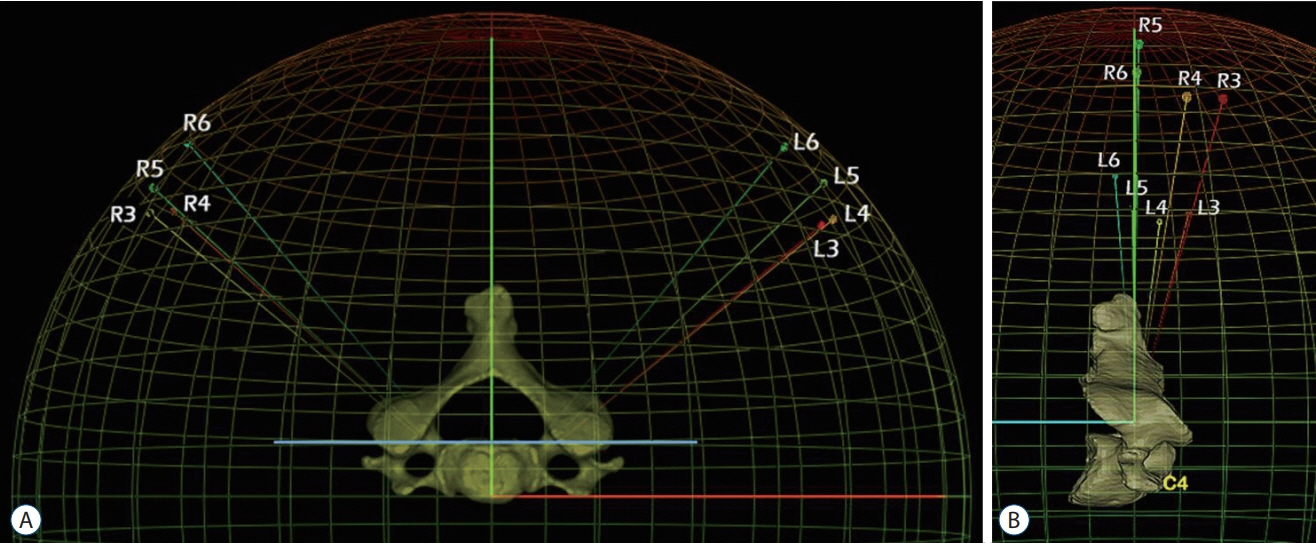
Cortical shell model of cervical spine from C3 to C6 was made after segmentation of in vivo CT image data of 44 volunteers. Three dimensional Cartesian coordinate of all points constituting surface of whole vertebra, bilateral pedicle and posterior wall were acquired. The ideal trajectory of pedicle screw insertion was defined as viewing direction at which the inner area of pedicle become largest when we see through the biconcave tubular pedicle. The ideal trajectory of 352 pedicles (eight pedicles for each of 44 subjects) were calculated using custom made program and were changed from global coordinate to local coordinate according to the three dimensional position of posterior wall of each vertebral body. The transverse and sagittal angle of trajectory were defined as the angle between ideal trajectory line and perpendicular line of posterior wall in the horizontal and sagittal plane. The averages and standard deviations of all measurements were calculated.
RESULTS
The average transverse angles were 50.60º±6.22º at C3, 51.42º±7.44º at C4, 47.79º±7.61º at C5, and 41.24º±7.76º at C6. The transverse angle becomes more steep from C3 to C6. The mean sagittal angles were 9.72º±6.73º downward at C3, 5.09º±6.39º downward at C4, 0.08º±6.06º downward at C5, and 1.67º±6.06º upward at C6. The sagittal angle changes from caudad to cephalad from C3 to C6.
CONCLUSION
The absolute values of transverse and sagittal angle in our study were not same but the trend of changes were similar to previous studies. Because we know 3D address of all points constituting cortical shell of cervical vertebrae. we can easily reconstruct 3D model and manage it freely using computer program. More creative measurement of morphological characteristics could be carried out than direct inspection of raw bone. Furthermore this concept of measurement could be used for the computing program of automated robotic screw insertion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cha SH, Kim C, Choi BK, Kim HJ, Baek SY. C-arm assessment of cervical pedicle screw: screw coaxial fluoroscopy and oblique view. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:1721–1727. 2007.2. Chanplakorn P, Kraiwattanapong C, Aroonjarattham K, Leelapattana P, Keorochana G, Jaovisidha S, et al. Morphometric evaluation of subaxial cervical spine using multi-detector computerized tomography (MD-CT) scan: the consideration for cervical pedicle screws fixation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 15:125. 2014.
Article3. Hojo Y, Ito M, Suda K, Oda I, Yoshimoto H, Abumi K. A multicenter study on accuracy and complications of freehand placement of cervical pedicle screws under lateral fluoroscopy in different pathological conditions: CT-based evaluation of more than 1,000 screws. Eur Spine J. 23:2166–2174. 2014.
Article4. Ito Z, Higashino K, Kato S, Kim SS, Wong E, Yoshioka K, et al. Pedicle screws can be 4 times stronger than lateral mass screws for insertion in the midcervical spine: a biomechanical study on strength of fixation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 27:80–85. 2014.
Article5. Jo DJ, Seo EM, Kim KT, Kim SM, Lee SH. Cervical pedicle screw insertion using the technique with direct exposure of the pedicle by laminoforaminotomy. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 52:459–465. 2012.
Article6. Johnston TL, Karaikovic EE, Lautenschlager EP, Marcu D. Cervical pedicle screws vs. lateral mass screws: uniplanar fatigue analysis and residual pullout strengths. Spine J. 6:667–672. 2006.
Article7. Karaikovic EE, Daubs MD, Madsen RW, Gaines RW Jr. Morphologic characteristics of human cervical pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:493–500. 1997.
Article8. Karaikovic EE, Kunakornsawat S, Daubs MD, Madsen TW, Gaines RW Jr. Surgical anatomy of the cervical pedicles: landmarks for posterior cervical pedicle entrance localization. J Spinal Disord. 13:63–72. 2000.
Article9. Lee DH, Lee SW, Kang SJ, Hwang CJ, Kim NH, Bae JY, et al. Optimal entry points and trajectories for cervical pedicle screw placement into subaxial cervical vertebrae. Eur Spine J. 20:905–911. 2011.
Article10. Liu J, Li Y, Wu Y, Zhu Q. A novel method of cervical pedicle screw placement from C3 to C5 and its clinical applications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:E504–E512. 2013.
Article11. Ludwig SC, Kramer DL, Balderston RA, Vaccaro AR, Foley KF, Albert TJ. Placement of pedicle screws in the human cadaveric cervical spine: comparative accuracy of three techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1655–1667. 2000.12. Panjabi MM, Duranceau J, Goel V, Oxland T, Takata K. Cervical human vertebrae. Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy of the middle and lower regions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 16:861–869. 1991.
Article13. Panjabi MM, Shin EK, Chen NC, Wang JL. Internal morphology of human cervical pedicles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1197–1205. 2000.
Article14. Ruofu Z, Huilin Y, Xiaoyun H, Xishun H, Tiansi T, Liang C, et al. CT evaluation of cervical pedicle in a Chinese population for surgical application of transpedicular screw placement. Surg Radiol Anat. 30:389–396. 2008.
Article15. Tan SH, Teo EC, Chua HC. Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy of cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae of Chinese Singaporeans. Eur Spine J. 13:137–146. 2004.
Article16. Uğur HC, Attar A, Uz A, Tekdemir I, Egemen N, Cağlar S, et al. Surgical anatomic evaluation of the cervical pedicle and adjacent neural structures. Neurosurgery. 47:1162–1168. discussion 1168-1169. 2000.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insertion Angle of Pedicle Screws in the Subaxial Cervical Spine: The Analysis of Computed Tomography-Navigated Insertion of Pedicle Screws
- The Feasibility of Translaminar Screws in the Subaxial Cervical Spine: Computed Tomography and Cadaveric Validation
- Quantitative Anatomy of C7 Vertebra in Southern Chinese for Insertion of Lateral Mass Screws and Pedicle Screws
- A Novel Patient-Specific Drill Guide Template for Pedicle Screw Insertion into the Subaxial Cervical Spine Utilizing Stereolithographic Modelling: An In Vitro Study
- Cervical Pedicle Screw Insertion Using the Technique with Direct Exposure of the Pedicle by Laminoforaminotomy