J Liver Cancer.
2019 Sep;19(2):154-158. 10.17998/jlc.19.2.154.
Sorafenib-induced Pancreatic Pseudocyst in a Patient with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Rare Adverse Event
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea. gudwns21@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2463617
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.154
Abstract
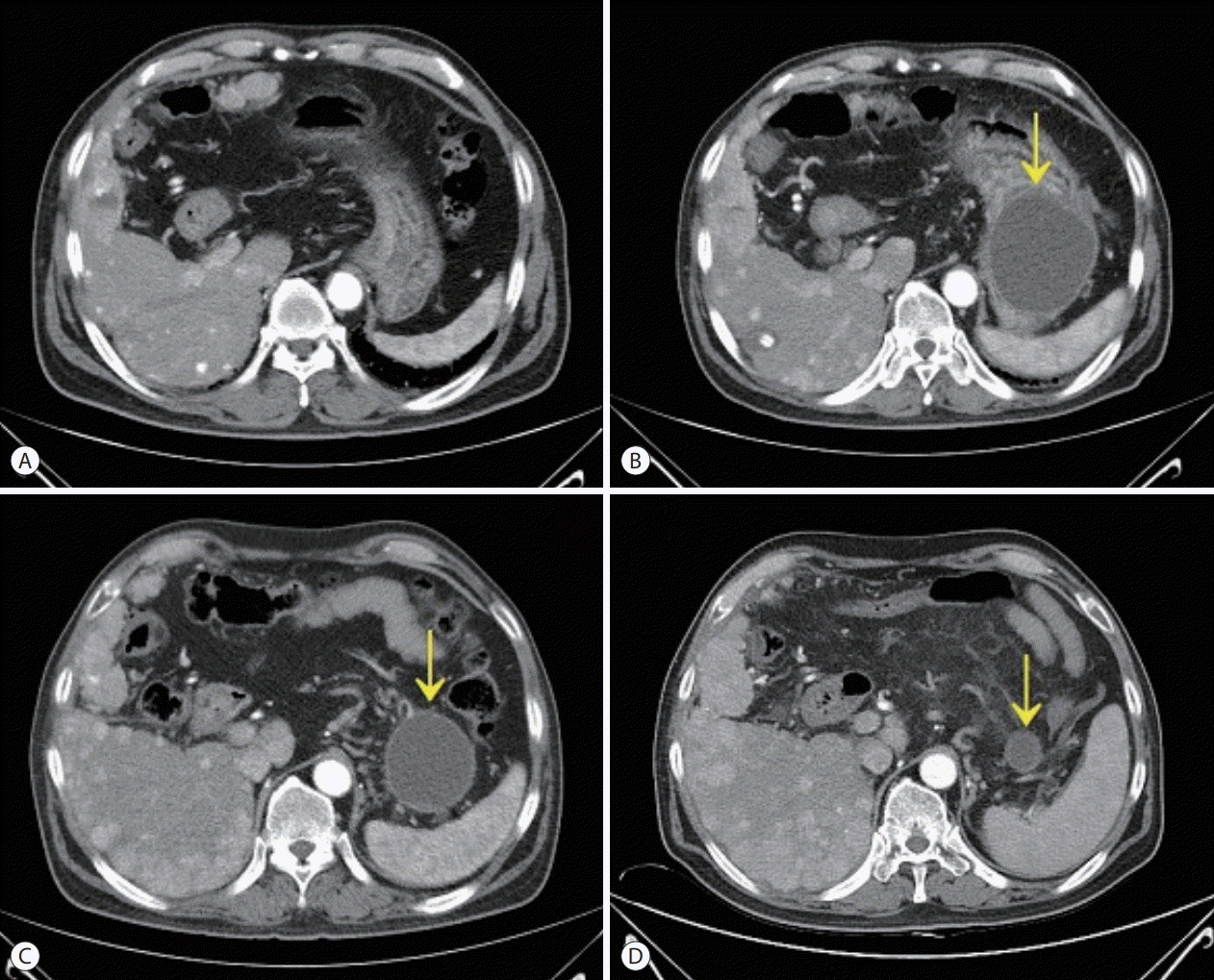
- A 54-year old man diagnosed with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma began treatment with sorafenib. After 3 weeks of treatment, he complained of abdominal pain and nausea. Abdominal sonography showed multiple hepatic lesions only. Serum amylase and lipase levels were 35 U/L and 191 U/L, respectively. The patient was diagnosed with sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis. After 10 days of discontinuing sorafenib he still complained of nausea and loss of appetite. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed a large bulging lesion, which was suspected to cause extrinsic compression on the high body of the gastric anterior wall. Computed tomography scan revealed a cystic lesion, 8.3 cm in size, in the pancreatic tail, suggesting a pancreatic pseudocyst. After the withdrawal of sorafenib, systemic chemotherapy with Adriamycin and cisplatin was administered. Four months after the discontinuation of sorafenib, the size of the pancreatic pseudocyst decreased from 8.3 cm to 3 cm. The patient's symptoms were also relieved.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A, Wilkie D, et al. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:11851–11858.2. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:378–390.3. Li M, Srinivas S. Acute pancreatitis associated with sorafenib. South Med J. 2007; 100:909–911.4. Pezzilli R, Corinaldesi R, Morselli-Labate AM. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors and acute pancreatitis. JOP. 2010; 11:291–293.5. Amar S, Wu KJ, Tan WW. Sorafenib-induced pancreatitis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007; 82:521.6. Kobayashi Y, Kanemitu T, Kamoto A, Satoh M, Mori N, Sekii K, et al. Painless acute pancreatitis associated with sorafenib treatment: a case report. Med Oncol. 2011; 28:463–465.7. Chou JW, Cheng KS, Huang CW. Sorafenib-induced acute pancreatitis: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med. 2016; 55:623–627.8. Ratain MJ, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Flaherty KT, Kaye SB, Rosner GL, et al. Phase II placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation trial of sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2505–2512.9. Ishida H, Ichikawa W, Sasaki Y. Crizotinib-induced pancreatic pseudocyst: a novel adverse event. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015.10. Kawakubo K, Hata H, Kawakami H, Kuwatani M, Kawahata S, Kubo K, et al. Pazopanib-induced severe acute pancreatitis. Case Rep Oncol. 2015; 8:356–358.11. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102–111.12. Foley WD, Stewart ET, Lawson TL, Geenan J, Loguidice J, Maher L, et al. Computed tomography, ultrasonography, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the diagnosis of pancreatic disease: a comparative study. Gastrointest Radiol. 1980; 5:29–35.13. Kressel HY, Margulis AR, Gooding GW, Filly RA, Moss A, Korobkin M. CT scanning and ultrasound in the evaluation of pancreatic pseudocysts: a preliminary comparison. Radiology. 1978; 126:153–157.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatments Other than Sorafenib for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sorafenib-Induced Interstitial Pneumonitis in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Case Report
- Complete Response of Single Nodular Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Pulmonary Metastasis by Sequential Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib: A Case Report
- The Genomic Landscape and Its Clinical Implications in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The Efficacy of Sorafenib for Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma