J Dent Anesth Pain Med.
2019 Oct;19(5):295-300. 10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.5.295.
Treatment of severe pain in a patient with complex regional pain syndrome undergoing dental treatment under general anesthesia: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Dental Anesthesiology and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. stone90@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2461246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.5.295
Abstract
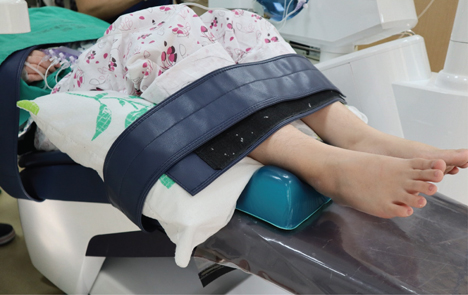
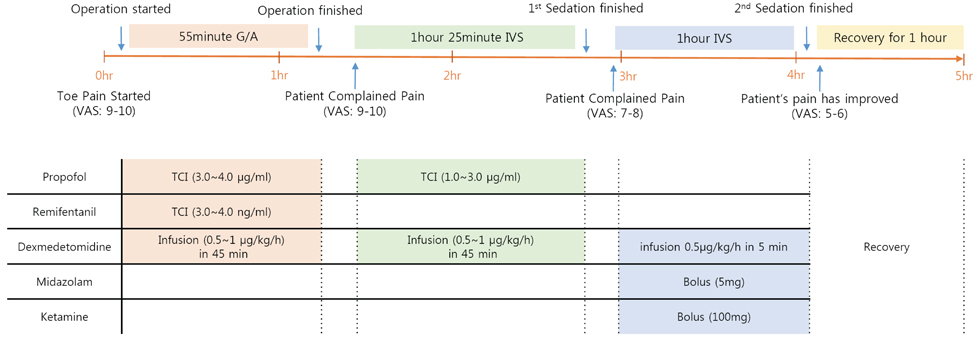
- Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is rare, characterized by pain from diverse causes, and presents as extreme pain even with minor irritation. General anesthesia may be required for dental treatment because the pain may not be controlled with local anesthesia. However, treatment under general anesthesia is also challenging. A 38-year-old woman with CRPS arrived for outpatient dental treatment under general anesthesia. At the fourth general anesthesia induction, she experienced severe pain resulting from her right toe touching the dental chair. Anesthesia was induced to calm her and continue the treatment. After 55 minutes of general anesthesia, the patient still complained of extreme toe pain. Subsequently, two administrations for intravenous sedation were performed, and discharge was possible in the recovery room approximately 5 h after the pain onset. The pain was not located at the dental treatment site. Although the major factor causing pain relief was unknown, ketamine may have played a role.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marinus J, Moseley GL, Birklein F, Baron R, Maihöfner C, Kingery WS, et al. Clinical features and pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:637–648.
Article2. Boas RA. Complex regional pain syndromes: Symptoms, signs, and differential diagnosis. Seattle, WA: IASP Press;1996. p. 79–92.3. Merskey H. Classification of chronic pain; description of chronic pain syndromes and definitions of pain terms. IASP Task Force on Taxonomy;1994. p. 41–43.4. Urits I, Shen AH, Jones MR, Viswanath O, Kaye AD. Complex regional pain syndrome, current concepts and treatment options. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018; 22:10.
Article5. Harden RN, Bruehl S, Perez RS, Birklein F, Marinus J, Maihofner C, et al. Validation of proposed diagnostic criteria (the “budapest criteria”) for complex regional pain syndrome. Pain. 2010; 150:268–274.
Article6. De Mos M, De Bruijn A, Huygen F, Dieleman J, Stricker BC, Sturkenboom M. The incidence of complex regional pain syndrome: A population-based study. Pain. 2007; 129:12–20.
Article7. Mackey S, Feinberg S. Pharmacologic therapies for complex regional pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2007; 11:38–43.
Article8. Okada M, Suzuki K, Hidaka T, Shinohara T, Kataharada K, Takada K, et al. Complex regional pain syndrome type I induced by pacemaker implantation, with a good response to steroids and neurotropin. Intern Med. 2002; 41:498–501.
Article9. Klega A, Eberle T, Buchholz H-G, Maus S, Maihöfner C, Schreckenberger M, et al. Central opioidergic neurotransmission in complex regional pain syndrome. Neurology. 2010; 75:129–136.
Article10. Goebel A. Complex regional pain syndrome in adults. Rheumatology. 2011; 50:1739–1750.
Article11. Turner-Stokes L, Goebel A. Complex regional pain syndrome in adults: Concise guidance. Clin Med (Lond). 2011; 11:596–600.
Article12. Schwartzman RJ, Grothusen J, Kiefer TR, Rohr P. Neuropathic central pain: Epidemiology, etiology, and treatment options. Arch Neurol. 2001; 58:1547–1550.13. Sigtermans MJ, Van Hilten JJ, Bauer MC, Arbous MS, Marinus J, Sarton EY, et al. Ketamine produces effective and long-term pain relief in patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type 1. Pain. 2009; 145:304–311.
Article14. Massad IM, Mohsen WA, Basha AS, Al-Zaben KR, Al-Mustafa MM, Alghanem SM. A balanced anesthesia with dexmedetomidine decreases postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic surgery. Saudi Med J. 2009; 30:1537–1541.15. Azari P, Lindsay DR, Briones D, Clarke C, Buchheit T, Pyati S. Efficacy and safety of ketamine in patients with complex regional pain syndrome. CNS drugs. 2012; 26:215–228.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Deep sedation for dental treatment in a Down syndrome patient with Eisenmenger syndrome: A case report
- Dental treatment under general anesthesia for patients with severe disabilities
- Contralateral Mirror Image Spreading in Post-Stroke Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Anesthetic management for a patient with Eisenmenger syndrome undergoing dacryocystorhinostomy: A case report
- Clinical Experience of a Complex Regional Pain Syndrome II after Neurectomy of Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle: A case report