Investig Clin Urol.
2019 Nov;60(6):425-431. 10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.425.
Prolyl hydroxylase-3 is a novel renal cell carcinoma biomarker
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanwk@yuhs.ac
- 5Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Institute of Genetic Science, Integrated Genomic Research Center for Metabolic Regulation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Brain Korean 21 PLUS Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2461053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.6.425
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine the suitability of serum prolyl hydroxylase-3 (PHD3) as a diagnostic or monitoring biomarker of renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between October 2013 and March 2015, we prospectively recruited study participants. The RCC group consisted of 56 patients who underwent radical or partial nephrectomy. The control group included 56 healthy kidney donors and 13 patients with benign renal masses. Blood from the RCC patients was sampled prior to surgery and again 1 and 3 months after the operation. Serum PHD3 levels were measured via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and compared between RCC patients and controls.
RESULTS
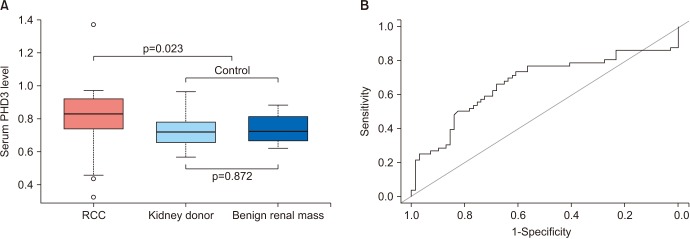
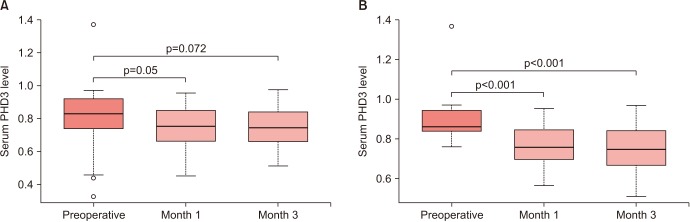
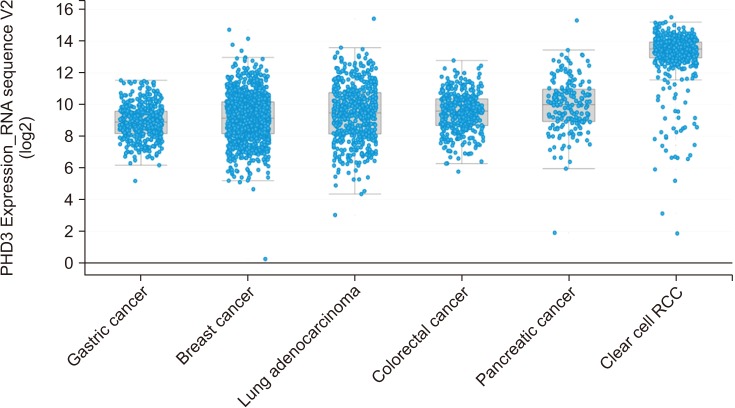
RCC patients had higher serum PHD3 levels than controls (0.79±0.17 ng/mL vs. 0.73±0.09 ng/mL, p=0.023), with an area under curve (AUC) of 0.668. With a cutoff value of 0.761 ng/ml, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value were 66.1%, 68.1%, 28.8%, and 37.3%, respectively. No significant difference in PHD3 level was observed between healthy kidney donors and patients with benign renal masses. The predictive performance of PHD3 was improved in subgroup analyses of RCC patients with a tumor size >2 cm (n=40) or clear-cell histology (n=44), with AUCs of 0.709 and 0.688, respectively. Among 37 patients with PHD3 levels greater than the cutoff value of 0.761 ng/mL, the postoperative PHD3 levels at 1 and 3 months were significantly lower than the preoperative PHD3 levels (both p<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS
Serum PHD3 represents a novel RCC biomarker that shows acceptable diagnostic performance.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004; 351:1296–1305. PMID: 15385656.
Article2. Schödel J, Grampp S, Maher ER, Moch H, Ratcliffe PJ, Russo P, et al. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and renal cancer. Eur Urol. 2016; 69:646–657. PMID: 26298207.
Article3. Mole DR, Blancher C, Copley RR, Pollard PJ, Gleadle JM, Ragoussis J, et al. Genome-wide association of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha DNA binding with expression profiling of hypoxia-inducible transcripts. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:16767–16775. PMID: 19386601.4. Weiss RH, Lin PY. Kidney cancer: identification of novel targets for therapy. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:224–232. PMID: 16408110.
Article5. Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, et al. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science. 2001; 292:464–468. PMID: 11292862.6. Jokilehto T, Jaakkola PM. The role of HIF prolyl hydroxylases in tumour growth. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14:758–770. PMID: 20178464.
Article7. Su Y, Loos M, Giese N, Hines OJ, Diebold I, Görlach A, et al. PHD3 regulates differentiation, tumour growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010; 103:1571–1579. PMID: 20978507.
Article8. Cui L, Qu J, Dang S, Mao Z, Wang X, Fan X, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase 3 inhibited the tumorigenecity of gastric cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 2014; 53:736–743. PMID: 23533015.
Article9. Tanaka T, Kitamura H, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Sato E, Masumori N, et al. Autoantibody against hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase-3 is a potential serological marker for renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011; 137:789–794. PMID: 20676679.
Article10. Sato E, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Kitamura H, Tanaka T, Honma I, et al. Identification of an immunogenic CTL epitope of HIFPH3 for immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008; 14:6916–6923. PMID: 18980986.
Article11. Amatschek S, Koenig U, Auer H, Steinlein P, Pacher M, Gruenfelder A, et al. Tissue-wide expression profiling using cDNA subtraction and microarrays to identify tumor-specific genes. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:844–856. PMID: 14871811.
Article12. Ambani SN, Morgan TM, Montgomery JS, Gadzinski AJ, Jacobs BL, Hawken S, et al. Predictors of delayed intervention for patients on active surveillance for small renal masses: does renal mass biopsy influence our decision? Urology. 2016; 98:88–96. PMID: 27450936.
Article13. Dong D, Jia L, Zhou Y, Ren L, Li J, Zhang J. Serum level of ANGPTL4 as a potential biomarker in renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2017; 35:279–285. PMID: 28110976.
Article14. Leroy X, Aubert S, Zini L, Franquet H, Kervoaze G, Villers A, et al. Vascular endocan (ESM-1) is markedly overexpressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2010; 56:180–187. PMID: 20102396.
Article15. Morrissey JJ, Mellnick VM, Luo J, Siegel MJ, Figenshau RS, Bhayani S, et al. Evaluation of urine aquaporin-1 and perilipin-2 concentrations as biomarkers to screen for renal cell carcinoma: a prospective cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 2015; 1:204–212. PMID: 26181025.16. Stillebroer AB, Mulders PF, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Oosterwijk E. Carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy. Eur Urol. 2010; 58:75–83. PMID: 20359812.
Article17. Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004; 5:343–354. PMID: 15122348.
Article18. Xue J, Li X, Jiao S, Wei Y, Wu G, Fang J. Prolyl hydroxylase-3 is down-regulated in colorectal cancer cells and inhibits IKKbeta independent of hydroxylase activity. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:606–615. PMID: 19786027.19. Fox SB, Generali D, Berruti A, Brizzi MP, Campo L, Bonardi S, et al. The prolyl hydroxylase enzymes are positively associated with hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in human breast cancer and alter in response to primary systemic treatment with epirubicin and tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13:R16. PMID: 21291529.
Article20. Gossage L, Zaitoun A, Fareed KR, Turley H, Aloysius M, Lobo DN, et al. Expression of key hypoxia sensing prolyl-hydroxylases PHD1, -2 and -3 in pancreaticobiliary cancer. Histopathology. 2010; 56:908–920. PMID: 20497244.
Article21. Tanaka T, Torigoe T, Hirohashi Y, Sato E, Honma I, Kitamura H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-independent expression mechanism and novel function of HIF prolyl hydroxylase-3 in renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014; 140:503–513. PMID: 24477694.
Article22. Andersen S, Donnem T, Stenvold H, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Busund LT, et al. Overexpression of the HIF hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, PHD3 and FIH are individually and collectively unfavorable prognosticators for NSCLC survival. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e23847. PMID: 21887331.
Article23. Miikkulainen P, Högel H, Rantanen K, Suomi T, Kouvonen P, Elo LL, et al. HIF prolyl hydroxylase PHD3 regulates translational machinery and glucose metabolism in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Metab. 2017; 5:5. PMID: 28680592.
Article24. Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mole DR, Lee S, Torres-Cabala C, Chung YL, et al. HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell. 2005; 8:143–153. PMID: 16098467.
Article25. Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012; 2:401–404. PMID: 22588877.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New Oral Agent for Treatment of Anemia in Patient with Chronic Kidney Disease: Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor
- Prolyl 4 Hydroxylase: A Critical Target in the Pathophysiology of Diseases
- A Case of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Childhood
- A Case of Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma
- A Case of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to the Gallbladder