Anat Cell Biol.
2019 Sep;52(3):262-268. 10.5115/acb.19.031.
Morphology of saphenous nerve in cadavers: a guide to saphenous block and surgical interventions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Medical University of the Americas, Charlestown, Saint Kitts and Nevis, West Indies. dranasuya7@gmail.com
- KMID: 2459541
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.19.031
Abstract
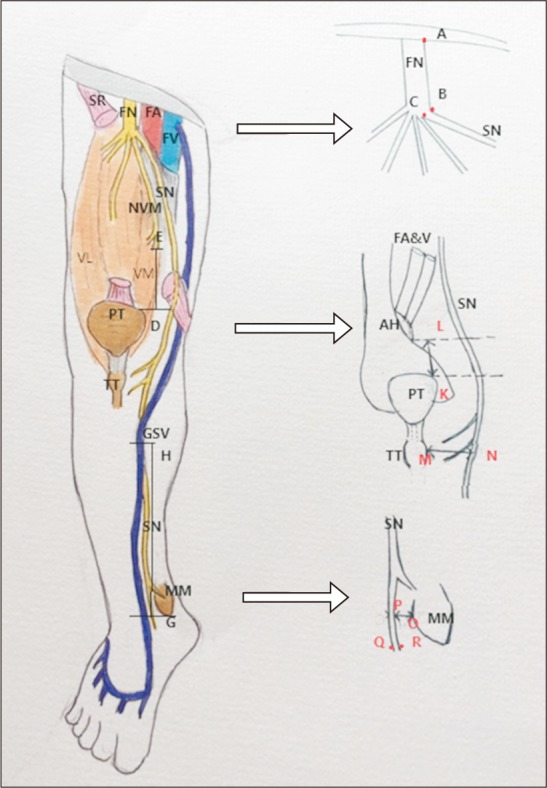
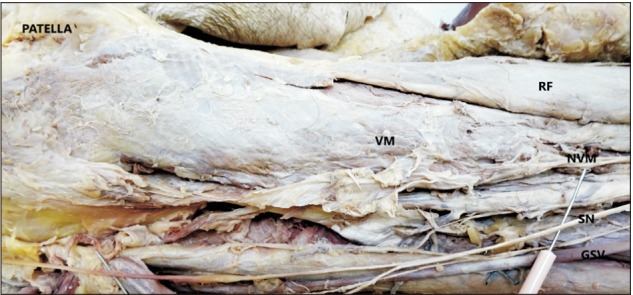
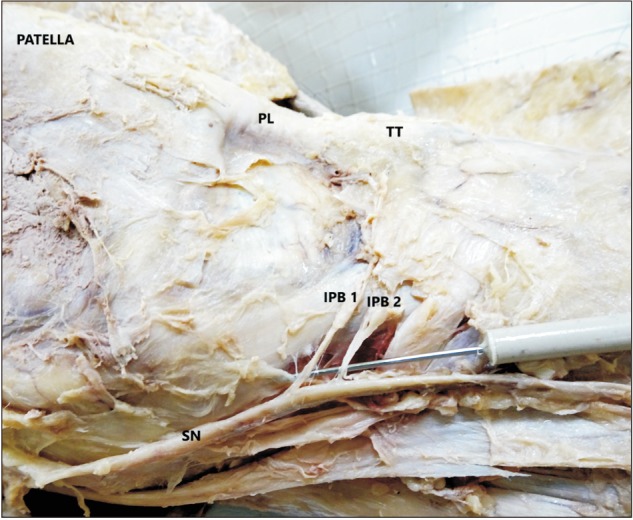
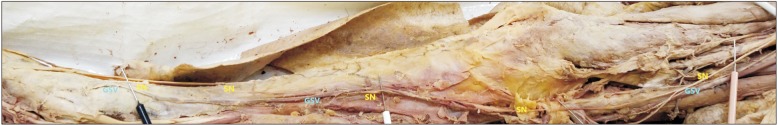
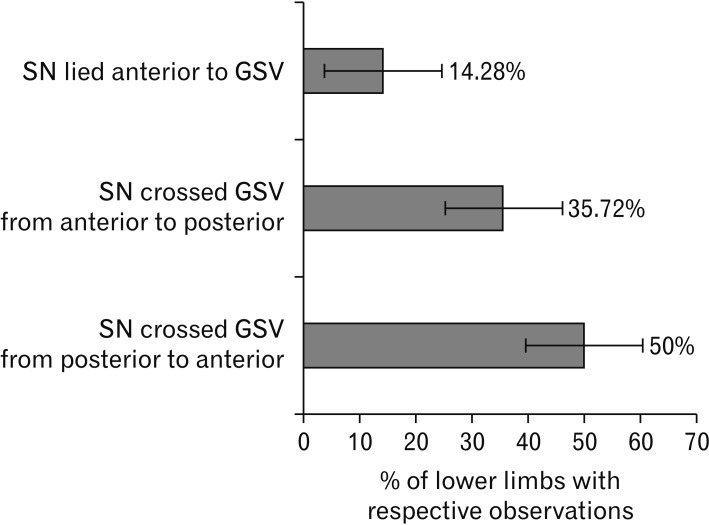
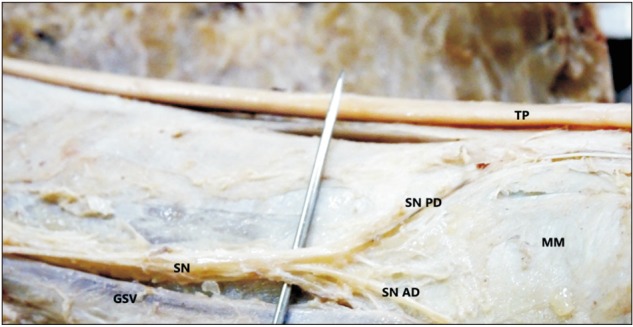
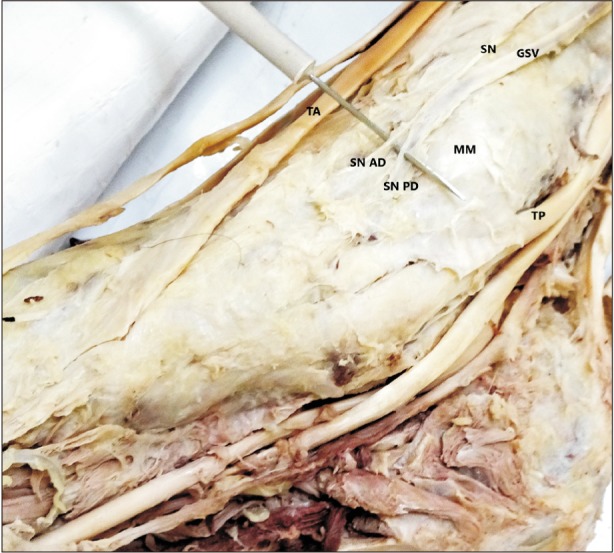
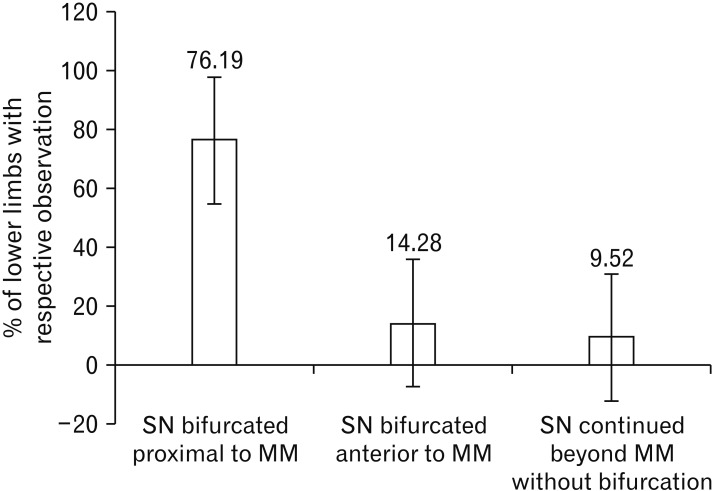
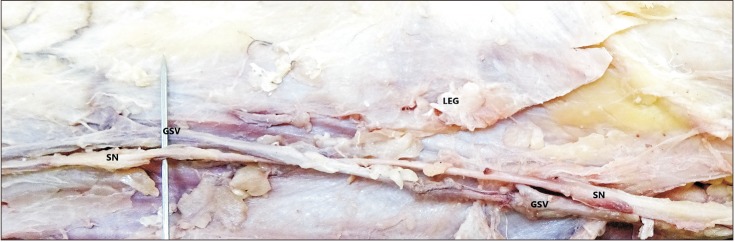
- The knowledge about detailed morphology and relation of saphenous nerve is important to obtain successful saphenous nerve regional blocks to achieve pre- and post-operative anesthesia and analgesia, nerve entrapment treatments and to avoid damage of saphenous nerve during knee and ankle surgeries. The literature describing detailed morphology of saphenous nerve is very limited. We dissected 42 formalin fixed well embalmed cadaveric lower limbs to explore detailed anatomy, relation and mode of termination of saphenous nerve and measured the distances from the nearby palpable bony landmarks. The average distance of origin of saphenous nerve from inguinal crease was 7.89±1.42 cm, the distance from upper end of medial border of patella to saphenous nerve at that level was 8.11±0.85 cm, distance from tibial tuberosity was 7.53±0.98 cm and from midpoint of anterior border of medial malleolus was 0.45±0.14 cm. Saphenous nerve provided two infrapatellar branches at the level of mid to lower limit of patellar ligament in 90% cases. It was in close contact or adhered to great saphenous vein across the lower 2/3rd of leg lying either anterior, posterior or deep to the vein. The saphenous nerve terminated by bifurcating proximal to medial malleolus in majority of cases though no obvious bifurcation was observed in 9.52% cases. The detailed morphology, relations and the distances from palpable bony landmarks may be helpful for clinicians to achieve successful saphenous nerve block and to avoid saphenous nerve damage and related complications during orthopedic procedures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hunter LY, Louis DS, Ricciardi JR, O'Connor GA. The saphenous nerve: its course and importance in medial arthrotomy. Am J Sports Med. 1979; 7:227–230. PMID: 474860.2. Dayan V, Cura L, Cubas S, Carriquiry G. Surgical anatomy of the saphenous nerve. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008; 85:896–900. PMID: 18291167.3. Mercer D, Morrell NT, Fitzpatrick J, Silva S, Child Z, Miller R, DeCoster TA. The course of the distal saphenous nerve: a cadaveric investigation and clinical implications. Iowa Orthop J. 2011; 31:231–235. PMID: 22096447.4. Jenstrup MT, Jaeger P, Lund J, Fomsgaard JS, Bache S, Mathiesen O, Larsen TK, Dahl JB. Effects of adductor-canal-blockade on pain and ambulation after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56:357–364. PMID: 22221014.5. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer;2018.6. Benzon HT, Sharma S, Calimaran A. Comparison of the different approaches to saphenous nerve block. Anesthesiology. 2005; 102:633–638. PMID: 15731603.7. Donohue CM, Goss LR, Metz S, Weingarten MS, Dyal LB Jr. Combined popliteal and saphenous nerve blocks at the knee: an underused alternative to general or spinal anesthesia for foot and ankle surgery. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2004; 94:368–374. PMID: 15265996.8. Romanoff ME, Cory PC Jr, Kalenak A, Keyser GC, Marshall WK. Saphenous nerve entrapment at the adductor canal. Am J Sports Med. 1989; 17:478–481. PMID: 2782531.9. Chauhan BM, Kim DJ, Wainapel SF. Saphenous neuropathy: following coronary artery bypass surgery. N Y State J Med. 1981; 81:222–223. PMID: 6258112.10. Nair UR, Griffiths G, Lawson RA. Postoperative neuralgia in the leg after saphenous vein coronary artery bypass graft: a prospective study. Thorax. 1988; 43:41–43. PMID: 3281308.11. Portland GH, Martin D, Keene G, Menz T. Injury to the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: comparison of horizontal versus vertical harvest site incisions. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:281–285. PMID: 15756180.12. Mochida H, Kikuchi S. Injury to infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve in arthroscopic knee surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (320):88–94. PMID: 7586847.13. Pyne D, Jawad AS, Padhiar N. Saphenous nerve injury after fasciotomy for compartment syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2003; 37:541–542. PMID: 14665597.14. Kapoor R, Adhikary SD, Siefring C, McQuillan PM. The saphenous nerve and its relationship to the nerve to the vastus medialis in and around the adductor canal: an anatomical study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012; 56:365–367. PMID: 22335278.15. Saranteas T, Anagnostis G, Paraskeuopoulos T, Koulalis D, Kokkalis Z, Nakou M, Anagnostopoulou S, Kostopanagiotou G. Anatomy and clinical implications of the ultrasound-guided subsartorial saphenous nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011; 36:399–402. PMID: 21697687.16. Andersen HL, Andersen SL, Tranum-Jensen J. The spread of injectate during saphenous nerve block at the adductor canal: a cadaver study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2015; 59:238–245. PMID: 25496028.17. van der Wal M, Lang SA, Yip RW. Transsartorial approach for saphenous nerve block. Can J Anaesth. 1993; 40:542–546. PMID: 8403121.18. Krombach J, Gray AT. Sonography for saphenous nerve block near the adductor canal. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007; 32:369–370. PMID: 17720129.19. Manickam B, Perlas A, Duggan E, Brull R, Chan VW, Ramlogan R. Feasibility and efficacy of ultrasound-guided block of the saphenous nerve in the adductor canal. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2009; 34:578–580. PMID: 19916251.20. De Mey JC, Deruyck LJ, Cammu G, De Baerdemaeker LE, Mortier EP. A paravenous approach for the saphenous nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001; 26:504–506. PMID: 11707786.21. Bonner SM, Pridie AK. Sciatic nerve palsy following uneventful sciatic nerve block. Anaesthesia. 1997; 52:1205–1207. PMID: 9485977.22. Pannell WC, Wisco JJ. A novel saphenous nerve plexus with important clinical correlations. Clin Anat. 2011; 24:994–996. PMID: 21800370.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Conduction Studies of the Saphenous Nerve in Normal Subjects and Patients with Femoral Neuropathy
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Neuromodulation for the Treatment of Saphenous Neuralgia
- Regional Anesthesia of Lower Extremity using Tibial Nerve and Saphenous Nerve Block
- Prevalence and Clinical Implication of Nonsaphenous Vein Reflux with or without Pelvic Venous Disease
- Anatomical observation on draining patterns of saphenous tributaries in Korean adults