J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Aug;54(2):136-138. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.136.
Pulsed Radiofrequency Neuromodulation for the Treatment of Saphenous Neuralgia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. painsurgery@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Kyung-Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1814252
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.136
Abstract
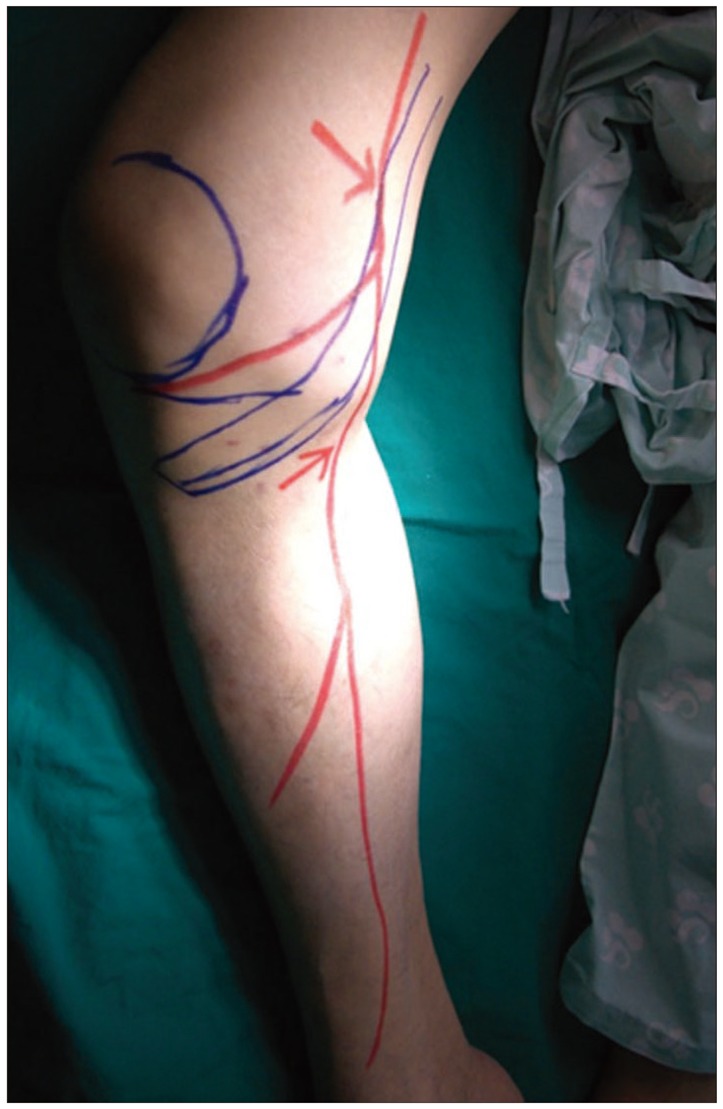
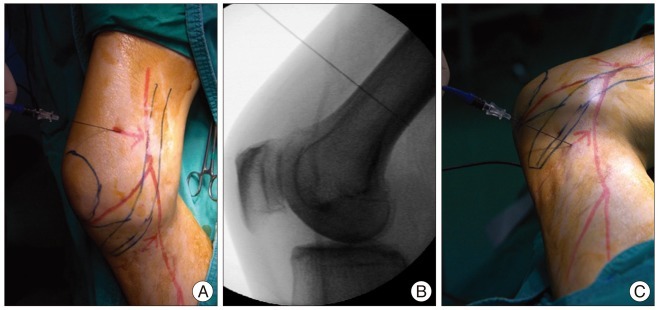
- A 65-year-old male presented with pain in his right medial calf. An imaging study revealed no acute lesions, and a diagnosis of saphenous neuralgia was made by a nerve conduction study. He received temporary pain relief with saphenous nerve blocks twice in a one-week interval. Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation reduced pain to 10% of the maximal pain intensity. At 6 months after the procedure, the pain intensity was not aggravated even without medication. Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation of the saphenous nerve may offer an effective and minimally invasive treatment for patients with saphenous neuralgia who are refractory to conservative management.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adar R, Meyer E, Zweig A. Saphenous neuralgia : a complication of vascular reconstructions below the inguinal ligament. Ann Surg. 1979; 190:609–613. PMID: 507971.
Article2. Ahadi T, Raissi GR, Togha M, Nejati P. Saphenous neuropathy in a patient with low back pain. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2010; 5:2. PMID: 20205890.
Article3. Bertram C, Porsch M, Hackenbroch MH, Terhaag D. Saphenous neuralgia after arthroscopically assisted anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with a semitendinosus and gracilis tendon graft. Arthroscopy. 2000; 16:763–766. PMID: 11027764.
Article4. Cahana A, Vutskits L, Muller D. Acute differential modulation of synaptic transmission and cell survival during exposure to pulsed and continuous radiofrequency energy. J Pain. 2003; 4:197–202. PMID: 14622704.
Article5. Cosman ER Jr, Cosman ER Sr. Electric and thermal field effects in tissue around radiofrequency electrodes. Pain Med. 2005; 6:405–424. PMID: 16336478.
Article6. Dunaway DJ, Steensen RN, Wiand W, Dopirak RM. The sartorial branch of the saphenous nerve : its anatomy at the joint line of the knee. Arthroscopy. 2005; 21:547–551. PMID: 15891719.
Article7. Higuchi Y, Nashold BS Jr, Sluijter M, Cosman E, Pearlstein RD. Exposure of the dorsal root ganglion in rats to pulsed radiofrequency currents activates dorsal horn lamina I and II neurons. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:850–855. discussion 856. PMID: 11904038.
Article8. House JH, Ahmed K. Entrapment neuropathy of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve. Am J Sports Med. 1977; 5:217–224. PMID: 907036.
Article9. Kokubun K. [Anatomical and clinical study on the femoral nerve lesion]. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1983; 57:65–77. PMID: 6864036.10. Kopell HP, Thompson WA. Knee pain due to saphenousnerve entrapment. N Engl J Med. 1960; 263:351–353. PMID: 14410944.
Article11. Lippitt AB. Neuropathy of the saphenous nerve as a cause of knee pain. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 1993; 52:31–33. PMID: 8443553.12. Luerssen TG, Campbell RL, Defalque RJ, Worth RM. Spontaneous saphenous neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 1983; 13:238–241. PMID: 6621837.
Article13. Mozes M, Ouaknine G, Nathan H. Saphenous nerve entrapment simulating vascular disorder. Surgery. 1975; 77:299–303. PMID: 1129703.14. Munglani R. The longer term effect of pulsed radiofrequency for neuropathic pain. Pain. 1999; 80:437–439. PMID: 10204759.
Article15. Romanoff ME, Cory PC Jr, Kalenak A, Keyser GC, Marshall WK. Saphenous nerve entrapment at the adductor canal. Am J Sports Med. 1989; 17:478–481. PMID: 2782531.
Article16. Saal JA, Dillingham MF, Gamburd RS, Fanton GS. The pseudoradicular syndrome. Lower extremity peripheral nerve entrapment masquerading as lumbar radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13:926–930. PMID: 2847334.17. Senegor M. Iatrogenic saphenous neuralgia : successful therapy with neuroma resection. Neurosurgery. 1991; 28:295–298. PMID: 1997901.
Article18. Tranier S, Durey A, Chevallier B, Liot F. Value of somatosensory evoked potentials in saphenous entrapment neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992; 55:461–465. PMID: 1619412.
Article19. Worth RM, Kettelkamp DB, Defalque RJ, Duane KU. Saphenous nerve entrapment. A cause of medial knee pain. Am J Sports Med. 1984; 12:80–81. PMID: 6703186.20. Yang DS. [Diagnosis and treatment of saphenous nerve entrapment]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1988; 26:464–465. 509–510. PMID: 3229266.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency treatment for postherpetic neuralgia of supraorbital nerve: A case report
- Clinical Outcomes of Pulsed Radiofrequency Neuromodulation for the Treatment of Occipital Neuralgia
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment in Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: A report of 2 cases
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Neuromodulation Treatment on the Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve for the Treatment of Meralgia Paresthetica
- Pulsed Radiofrequency Treatment of the Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve in a Case of Trigeminal Neuralgia: A case report