Korean J Radiol.
2016 Oct;17(5):797-800. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.797.
Percutaneous Pancreatic Stent Placement for Postoperative Pancreaticojejunostomy Stenosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea. yooncj1@gmail.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Korea.
- KMID: 2458073
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.797
Abstract
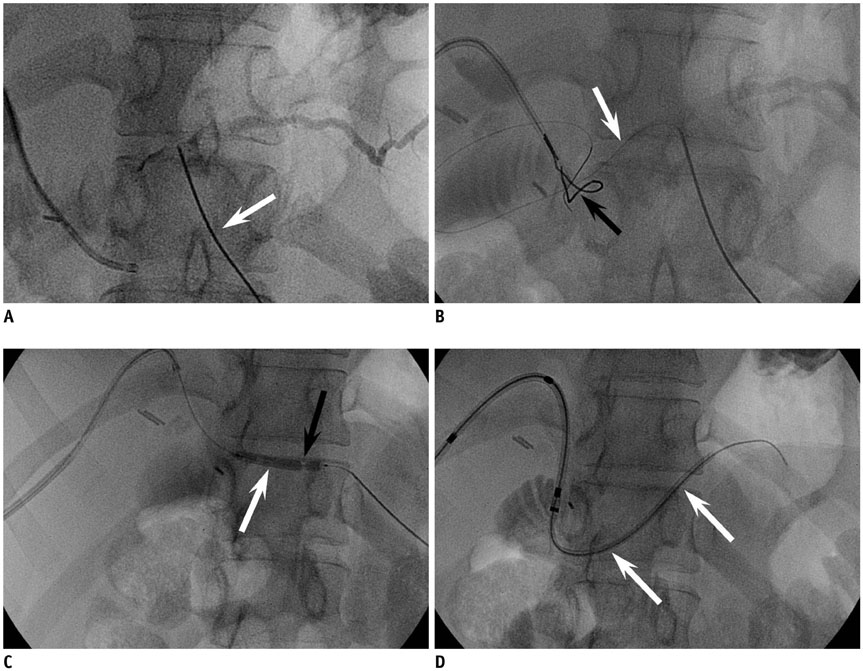
- Stenosis of the pancreatico-enteric anastomosis is one of the major complications of pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD). Endoscopic stent placement, has limited success rate as a nonsurgical treatment due to altered gastrointestinal anatomy. Percutaneous treatment is rarely attempted due to the technical difficulty in accessing the pancreatic duct. We reported a case of pancreaticojejunostomy stenosis after PD, in which a pancreatic stent was successfully placed using a rendezvous technique with a dual percutaneous approach.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Adolescent
Constriction, Pathologic/diagnostic imaging/etiology/surgery
Female
Humans
Pancreatic Ducts/diagnostic imaging/*surgery
Pancreaticoduodenectomy/*adverse effects
Pancreaticojejunostomy/*adverse effects
Pancreatitis/diagnostic imaging/etiology/surgery
Radiography
*Stents
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tani M, Kawai M, Terasawa H, Ueno M, Hama T, Hirono S, et al. Complications with reconstruction procedures in pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Surg. 2005; 29:881–884.2. Reid-Lombardo KM, Ramos-De la, Thomsen K, Harmsen WS, Farnell MB. Long-term anastomotic complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy for benign diseases. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:1704–1711.3. Itoi T, Kasuya K, Sofuni A, Itokawa F, Kurihara T, Yasuda I, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic duct access: techniques and literature review of pancreatography, transmural drainage and rendezvous techniques. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25:241–252.4. Mathieson JR, Cooperberg PL, Murray DJ, Dashefsky S, Christensen R, Schmidt N. Pancreatic duct obstruction treated with percutaneous antegrade insertion of a metal stent: report of two cases. Radiology. 1992; 185:465–467.5. Simianu VV, Ramsey MP, Sherman S, Zyromski NJ. Necrotizing pancreatitis caused by pancreatoduodenectomy. Pancreas. 2010; 39:942–943.6. Mallery S, Matlock J, Freeman ML. EUS-guided rendezvous drainage of obstructed biliary and pancreatic ducts: Report of 6 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:100–107.7. Barkay O, Sherman S, McHenry L, Yoo BM, Fogel EL, Watkins JL, et al. Therapeutic EUS-assisted endoscopic retrograde pancreatography after failed pancreatic duct cannulation at ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:1166–1173.8. Will U, Fueldner F, Thieme AK, Goldmann B, Gerlach R, Wanzar I, et al. Transgastric pancreatography and EUS-guided drainage of the pancreatic duct. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2007; 14:377–382.9. Dumonceau JM, Delhaye M, Tringali A, Dominguez-Munoz JE, Poley JW, Arvanitaki M, et al. Endoscopic treatment of chronic pancreatitis: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:784–800.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Feasibility of Percutaneous Pancreatic Stent Placement in Postoperative Pancreaticojejunostomy Stenosis
- Migrated Pancreaticojejunal Stent Forming a Stent–Stone Complex in the Jejunum with Resultant Small Bowel Obstruction: A Case Report
- Early Result of Suction Pancreatic Stent in Pancreaticojejunostomy
- Simultaneous Duodenal Metal Stent Placement and EUS-Guided Choledochoduodenostomy for Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer
- Supra-aortic Arterial Recanalization: Report of 5 cases