Korean J Radiol.
2016 Oct;17(5):565-580. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.565.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Early Spondylodiscitis: Interpretive Challenges and Atypical Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan 50612, Korea. lis@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Biomedical Research Institute, Yangsan 50612, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Hospital, Biomedical Research Institute, Busan 49241, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan 48108, Korea.
- KMID: 2458049
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.565
Abstract
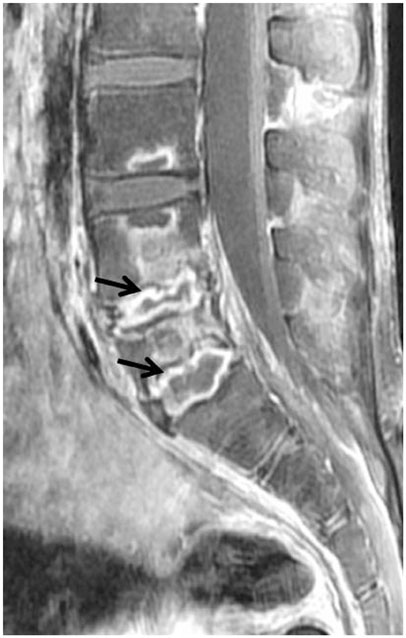
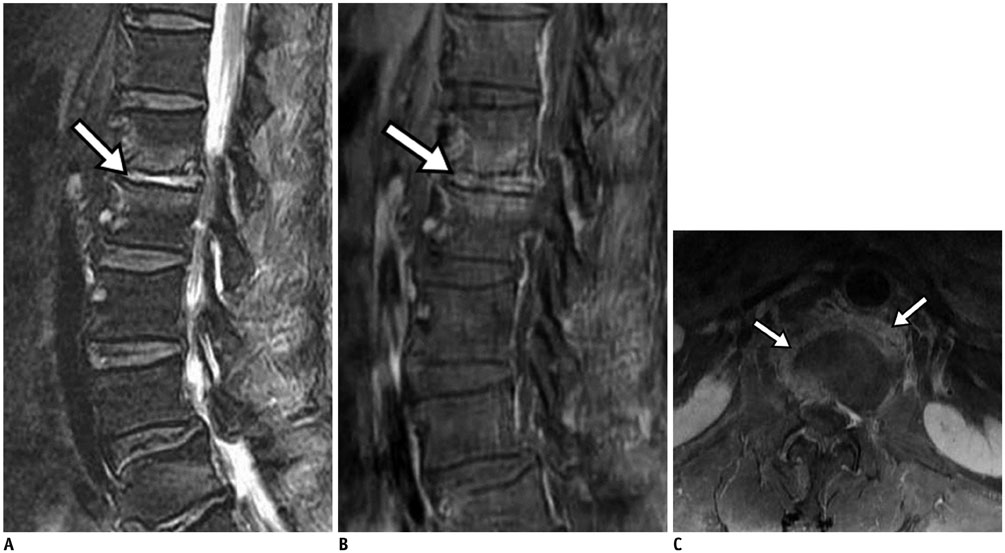
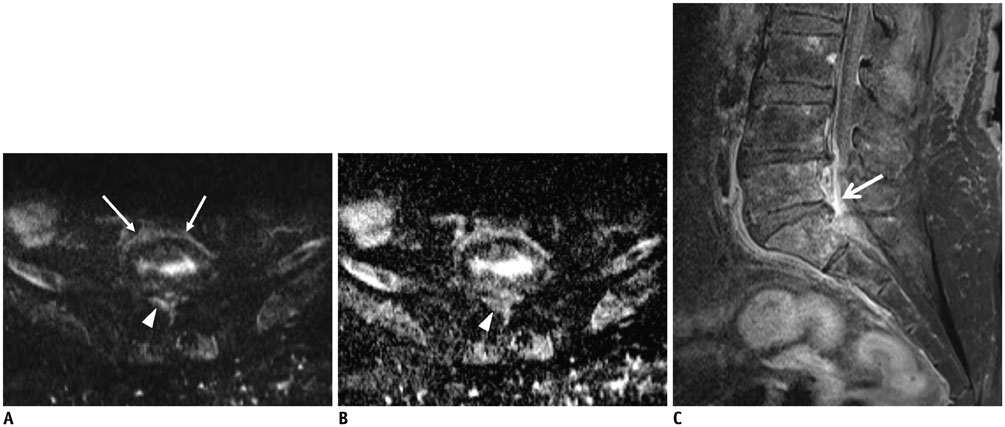
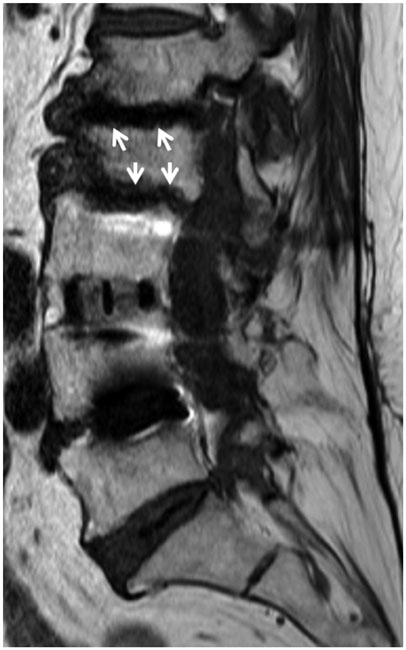
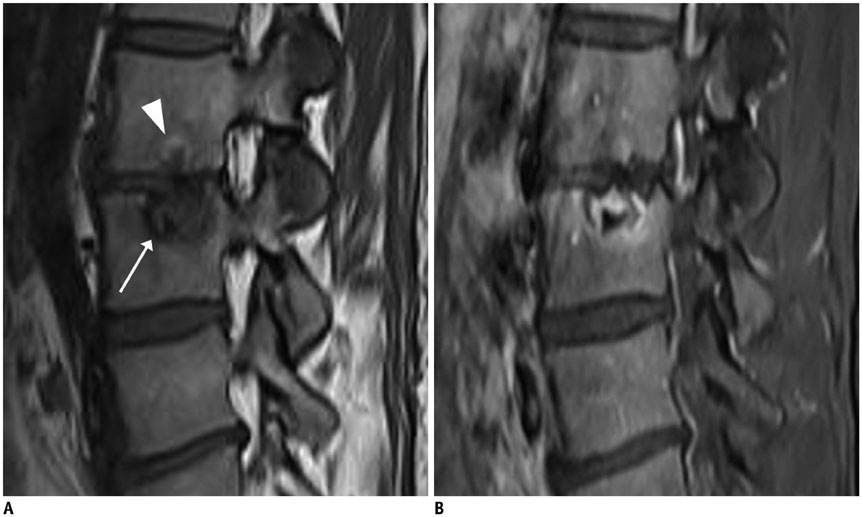
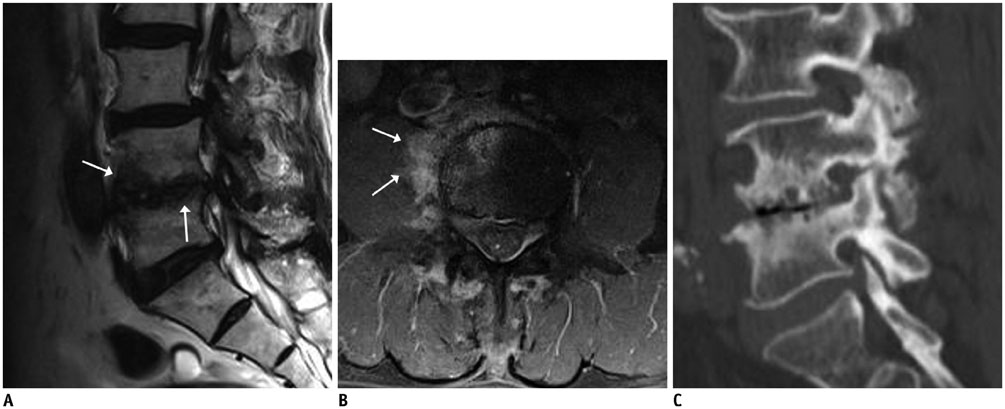
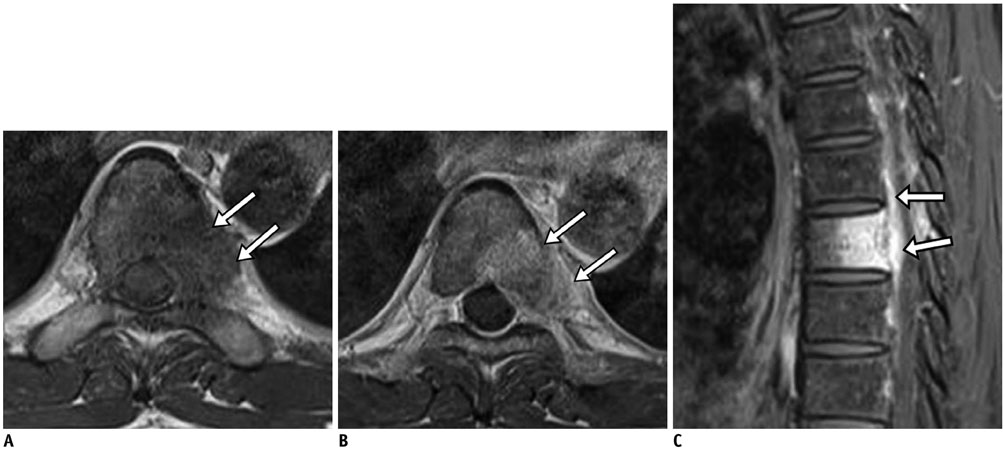
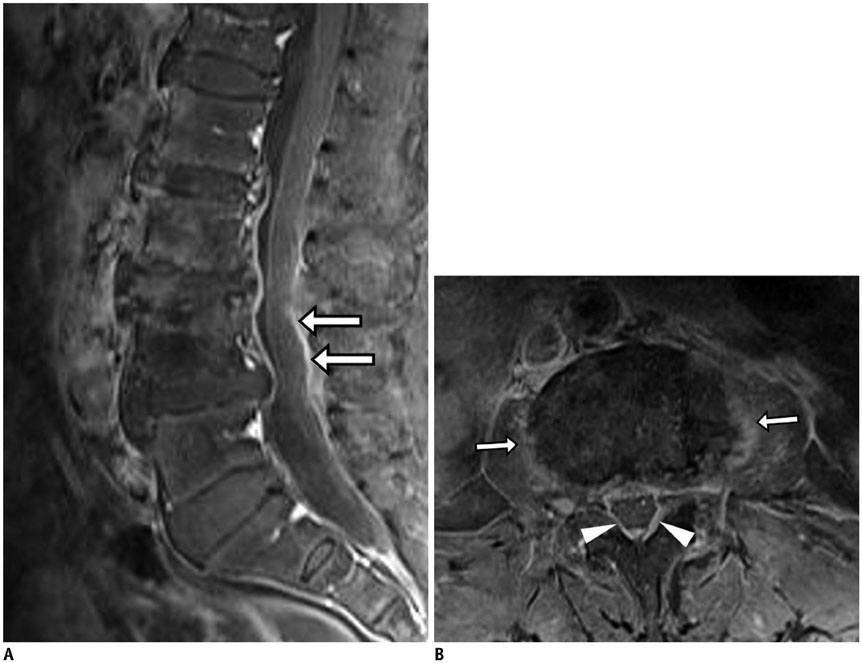
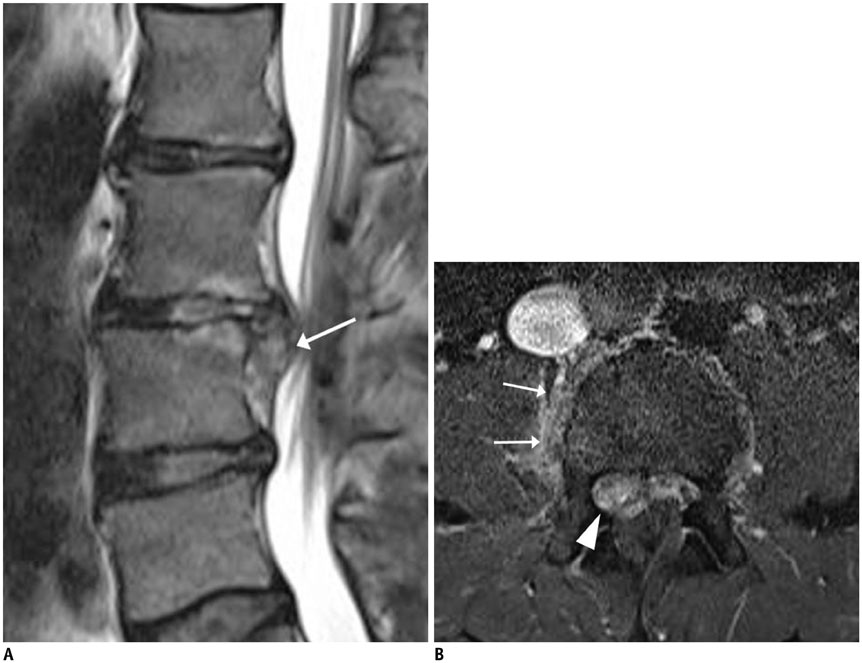
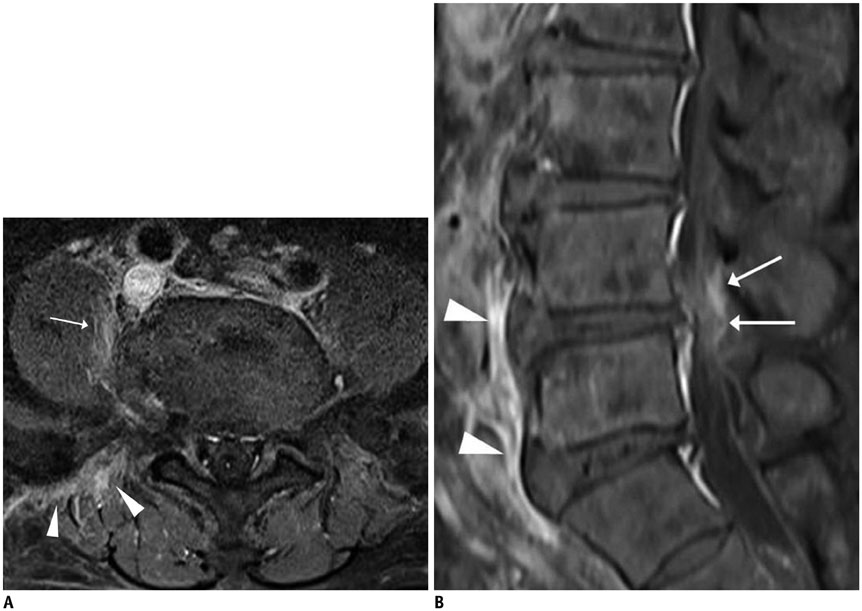
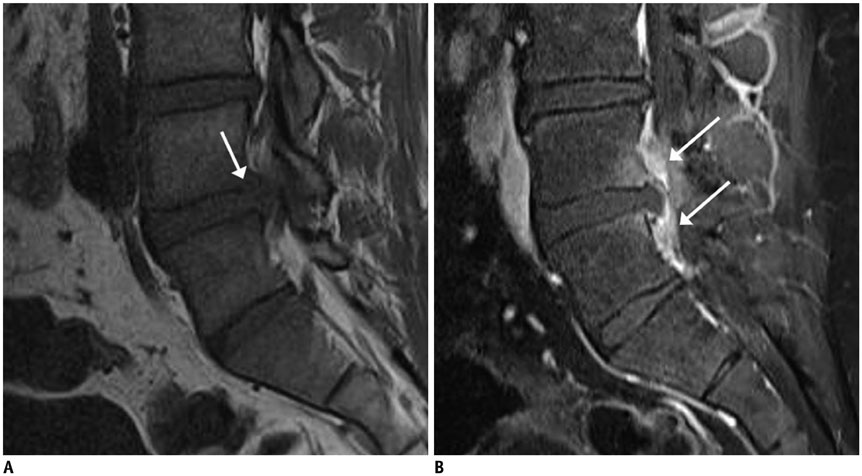
- MR findings of early infectious spondylodiscitis are non-specific and may be confused with those of other conditions. Therefore, it is important to recognize early MR signs of conditions, such as inappreciable cortical changes in endplates, confusing marrow signal intensities of vertebral bodies, and inflammatory changes in paraspinal soft tissues, and subligamentous and epidural spaces. In addition, appreciation of direct inoculation, such as in iatrogenic spondylodiscitis may be important, because the proportion of patients who have undergone recent spine surgery or a spinal procedure is increasing. In this review, the authors focus on the MR findings of early spondylodiscitis, atypical findings of iatrogenic infection, and the differentiation between spondylodiscitis and other disease entities mimicking infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnosis and management of infections related to spinal pain interventions
Sang Cheol Yoon, Eun Joo Choi
Anesth Pain Med. 2024;19(4):294-301. doi: 10.17085/apm.24140.
Reference
-
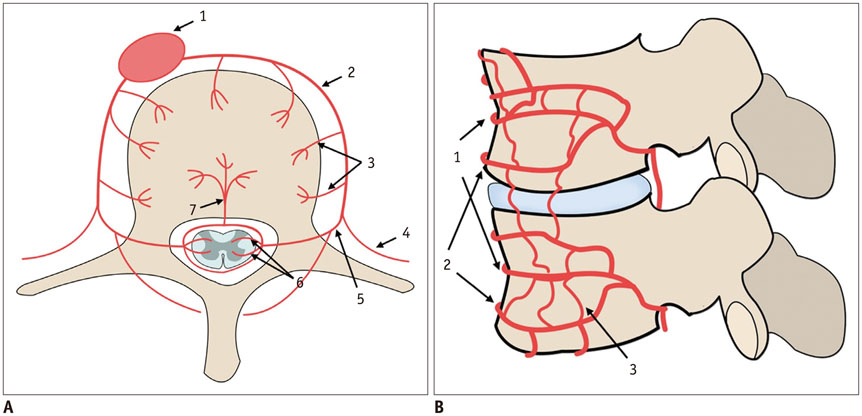
1. Diehn FE. Imaging of spine infection. Radiol Clin North Am. 2012; 50:777–798.2. Leone A, Dell'Atti C, Magarelli N, Colelli P, Balanika A, Casale R, et al. Imaging of spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 16:Suppl 2. 8–19.3. DeSanto J, Ross JS. Spine infection/inflammation. Radiol Clin North Am. 2011; 49:105–127.4. Gürbüz MS, Berkman MZ. Spondylodiscitis occurring after diagnostic lumbar puncture: a case report. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2013; 2013:843592.5. Mackenzie AR, Laing RB, Smith CC, Kaar GF, Smith FW. Spinal epidural abscess: the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 65:209–212.6. Dunbar JA, Sandoe JA, Rao AS, Crimmins DW, Baig W, Rankine JJ. The MRI appearances of early vertebral osteomyelitis and discitis. Clin Radiol. 2010; 65:974–981.7. Ziegelbein J, El-Khoury GY. Early spondylodiscitis presenting with single vertebral body involvement: a report of two cases. Iowa Orthop J. 2011; 31:219–224.8. Ratcliffe JF. An evaluation of the intra-osseous arterial anastomoses in the human vertebral body at different ages. A microarteriographic study. J Anat. 1982; 134(Pt 2):373–382.9. Gouliouris T, Aliyu SH, Brown NM. Spondylodiscitis: update on diagnosis and management. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65:Suppl 3. iii11–iii24.10. Ratcliffe JF. Anatomic basis for the pathogenesis and radiologic features of vertebral osteomyelitis and its differentiation from childhood discitis. A microarteriographic investigation. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1985; 26:137–143.11. Wiley AM, Trueta J. The vascular anatomy of the spine and its relationship to pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959; 41-B:796–809.12. Bergman I, Wald ER, Meyer JD, Painter MJ. Epidural abscess and vertebral osteomyelitis following serial lumbar punctures. Pediatrics. 1983; 72:476–480.13. Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT, Muffoletto AJ. Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1668–1679.14. Go JL, Rothman S, Prosper A, Silbergleit R, Lerner A. Spine infections. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2012; 22:755–772.15. Ratcliffe JF. The arterial anatomy of the developing human dorsal and lumbar vertebral body. A microarteriographic study. J Anat. 1981; 133(Pt 4):625–638.16. Babinchak TJ, Riley DK, Rotheram EB Jr. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis of the posterior elements. Clin Infect Dis. 1997; 25:221–224.17. Turunc T, Demiroglu YZ, Uncu H, Colakoglu S, Arslan H. A comparative analysis of tuberculous, brucellar and pyogenic spontaneous spondylodiscitis patients. J Infect. 2007; 55:158–163.18. Lee CM, Lee S, Bae J. Contiguous spinal metastasis mimicking infectious spondylodiscitis. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2015; 73:408–412.19. Sans N, Faruch M, Lapégue F, Ponsot A, Chiavassa H, Railhac JJ. Infections of the spinal column--spondylodiscitis. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2012; 93:520–529.20. Kim YJ, Lee JY, Kim BM, Kim YM, Min SH. MRI findings on iatrogenic spinal infection following various pain management procedures. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2014; 71:296–303.21. Dullerud R, Nakstad PH. Side effects and complications of automated percutaneous lumbar nucleotomy. Neuroradiology. 1997; 39:282–285.22. Guyer RD, Ohnmeiss DD, Mason SL, Shelokov AP. Complications of cervical discography: findings in a large series. J Spinal Disord. 1997; 10:95–101.23. Jiménez-Mejías ME, de Dios Colmenero J, Sánchez-Lora FJ, Palomino-Nicás J, Reguera JM, García de la Heras J, et al. Postoperative spondylodiskitis: etiology, clinical findings, prognosis, and comparison with nonoperative pyogenic spondylodiskitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:339–345.24. Sung S, Kwon JW. Image-guided percutaneous needle biopsy for infectious spondylitis: factors affecting culture positivity. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2015; 73:300–306.25. Jevtic V. Vertebral infection. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:Suppl 3. E43–E52.26. Jung NY, Jee WH, Ha KY, Park CK, Byun JY. Discrimination of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:1405–1410.27. Thurnher MM, Bammer R. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and spinal cord. Semin Roentgenol. 2006; 41:294–311.28. Eastwood JD, Vollmer RT, Provenzale JM. Diffusion-weighted imaging in a patient with vertebral and epidural abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:496–498.29. Moritani T, Kim J, Capizzano AA, Kirby P, Kademian J, Sato Y. Pyogenic and non-pyogenic spinal infections: emphasis on diffusion-weighted imaging for the detection of abscesses and pus collections. Br J Radiol. 2014; 87:20140011.30. Millot F, Bonnaire B, Clavel G, Deramond H, Fardellone P, Grados F. Hematogenous Staphylococcus aureus discitis in adults can start outside the vertebral body. Joint Bone Spine. 2010; 77:76–77.31. Tali ET. Spinal infections. Eur J Radiol. 2004; 50:120–133.32. Jevtic V. Magnetic resonance imaging appearances of different discovertebral lesions. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1123–1135.33. Hong SH, Choi JY, Lee JW, Kim NR, Choi JA, Kang HS. MR imaging assessment of the spine: infection or an imitation? Radiographics. 2009; 29:599–612.34. Tyrrell PN, Cassar-Pullicino VN, McCall IW. Spinal infection. Eur Radiol. 1999; 9:1066–1077.35. Bron JL, de Vries MK, Snieders MN, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van Royen BJ. Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis revisited. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28:883–892.36. Battikha JG, Garcia JF, Wettstein P. Aspects of atypical degenerative lesions of vertebrae. Skeletal Radiol. 1981; 6:103–107.37. Kwon JW, Yoon YC, Choi SH, Jung JY, Choe BK. MR imaging for the differentiation of early infectious spondylitis and modic type I change in the lumbar spine. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2010; 62:563–570.38. Oztekin O, Calli C, Kitis O, Adibelli ZH, Eren CS, Apaydin M, et al. Reliability of diffusion weighted MR imaging in differentiating degenerative and infectious end plate changes. Radiol Oncol. 2010; 44:97–102.39. Smith AS, Blaser SI. Infectious and inflammatory processes of the spine. Radiol Clin North Am. 1991; 29:809–827.40. Cuénod CA, Laredo JD, Chevret S, Hamze B, Naouri JF, Chapaux X, et al. Acute vertebral collapse due to osteoporosis or malignancy: appearance on unenhanced and gadolinium-enhanced MR images. Radiology. 1996; 199:541–549.41. Palmer WE, Suri R, Kattapuram SV. Benign versus malignant vertebral collapse: value of a fracture line on MR images. Radiology (Suppl). 1999; 213–229.42. Yuh WT, Zachar CK, Barloon TJ, Sato Y, Sickels WJ, Hawes DR. Vertebral compression fractures: distinction between benign and malignant causes with MR imaging. Radiology. 1989; 172:215–218.43. Van Lom KJ, Kellerhouse LE, Pathria MN, Moreland SI, Brown JJ, Zlatkin M, et al. Infection versus tumor in the spine: criteria for distinction with CT. Radiology. 1988; 166:851–855.44. Shih TT, Huang KM, Hou SM. Early diagnosis of single segment vertebral osteomyelitis--MR pattern and its characteristics. Clin Imaging. 1999; 23:159–167.45. Wagner AL, Murtagh FR, Arrington JA, Stallworth D. Relationship of Schmorl's nodes to vertebral body endplate fractures and acute endplate disk extrusions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:276–281.46. Park P, Tran NK, Gala VC, Hoff JT, Quint DJ. The radiographic evolution of a Schmorl's node. Br J Neurosurg. 2007; 21:224–227.47. Grivé E, Rovira A, Capellades J, Rivas A, Pedraza S. Radiologic findings in two cases of acute Schmörl's nodes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1717–1721.48. Friedmand DP, Hills JR. Cervical epidural spinal infection: MR imaging characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 163:699–704.49. Küker W, Mull M, Mayfrank L, Töpper R, Thron A. Epidural spinal infection. Variability of clinical and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:544–550. discussion 551.50. Ortiz AO, Bordia R. Injury to the vertebral endplate-disk complex associated with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:115–120.51. Abdel-Wanis ME, Solyman MT, Hasan NM. Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating vertebral compression fractures caused by malignancy, osteoporosis, and infections. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011; 19:145–150.52. Fouquet B, Goupille P, Jattiot F, Cotty P, Lapierre F, Valat JP, et al. Discitis after lumbar disc surgery Features of "aseptic" and "septic" forms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992; 17:356–358.53. Narváez J, Nolla JM, Narváez JA, Martinez-Carnicero L, De Lama E, Gómez-Vaquero C, et al. Spontaneous pyogenic facet joint infection. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 35:272–283.54. Weingarten TN, Hooten WM, Huntoon MA. Septic facet joint arthritis after a corticosteroid facet injection. Pain Med. 2006; 7:52–56.55. Reihsaus E, Waldbaur H, Seeling W. Spinal epidural abscess: a meta-analysis of 915 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2000; 23:175–204. discussion 205.56. Tompkins M, Panuncialman I, Lucas P, Palumbo M. Spinal epidural abscess. J Emerg Med. 2010; 39:384–390.57. Ehara S, Khurana JS, Kattapuram SV. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis of the posterior elements. Skeletal Radiol. 1989; 18:175–178.58. Heenan SD, Britton J. Septic arthritis in a lumbar facet joint: a rare cause of an epidural abscess. Neuroradiology. 1995; 37:462–464.59. Hickey NA, White PG. Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint causing multiple abscesses. Clin Radiol. 2000; 55:481–483.60. Numaguchi Y, Rigamonti D, Rothman MI, Sato S, Mihara F, Sadato N. Spinal epidural abscess: evaluation with gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging. Radiographics. 1993; 13:545–559. discussion 559-560.61. Sandhu FS, Dillon WP. Spinal epidural abscess: evaluation with contrast-enhanced MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1991; 12:1087–1093.62. Ross JS, Zepp R, Modic MT. The postoperative lumbar spine: enhanced MR evaluation of the intervertebral disk. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:323–331.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spondylodiscitis after Cervical Nucleoplasty without Any Abnormal Laboratory Findings
- Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis
- A Case of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis Caused by Campylobacter fetus for Which Early Diagnosis by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Was Difficult
- Spondylodiscitis Complicated by the Ingestion of a Button Battery: a Case Report
- Paratesticular Liposarcoma with Atypical Image Findings: a Case Report