J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2019 Sep;62(5):519-525. 10.3340/jkns.2019.0061.
Relationship between Circadian Variation in Ictus of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Physical Activity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurological Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. nskwon.sc@gmail.com
- KMID: 2457941
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2019.0061
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The circadian pattern of the onset time of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) has been reported by various authors. However, the effect of the degree of physical exertion on the circadian pattern has not been studied in detail. Therefore, we conducted this study to investigate the effect of physical exertion on the circadian pattern of aSAH.
METHODS
Of the 335 patients presenting with aSAH from January 2012 to December 2017, 234 patients with identifiable onset time and metabolic equivalent (MET) values were enrolled. The onset time of aSAH was divided into 4-hour intervals. The patient's physical exertion was then assessed on a scale between 1 and 8 METs using generally accepted MET values, and categorized into two groups"”light exertion (1 to 4 METs) and moderate to heavy exertion (5 to 8 METs)"”to determine the effect of the degree of physical exertion on the onset time distribution of aSAH. Multivariate analysis was used to calculate the odds ratio (OR) between the two groups to determine the effect of the degree of physical exertion on each set of time periods.
RESULTS
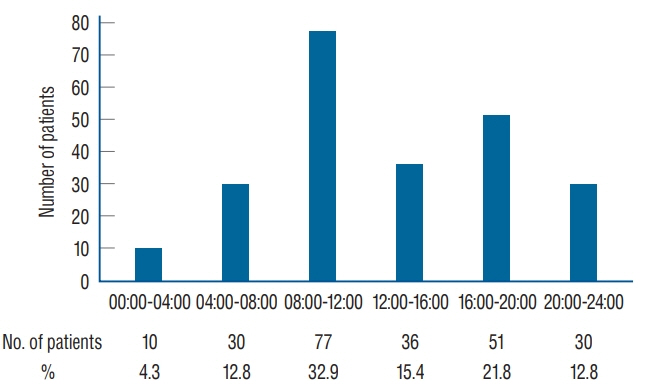
There was a definite bimodal onset pattern that peaked at 08:00-12:00 hours followed by 16:00-20:00 hours (p <0.001). MET values at all time intervals were found to be significantly higher than the night time (00:00-04:00 hours) values (p<0.031). The MET value distribution showed a unimodal pattern that slightly differed from the bimodal distribution of the onset time of aSAH. There were no significant differences in the ORs of each time interval according to the degree of the MET value.
CONCLUSION
This study reaffirmed that aSAH occurs in a bimodal pattern, especially showing the highest prevalence in the morning. Although aSAH could be related to daily activity, there were no significant changes in diurnal variations affected by the degree of physical exertion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abbott RD, Rodriguez BL, Burchfiel CM, Curb JD. Physical activity in older middle-aged men and reduced risk of stroke: the Honolulu Heart Program. Am J Epidemiol. 139:881–893. 1994.
Article2. Anderson C, Ni Mhurchu C, Scott D, Bennett D, Jamrozik K, Hankey G, et al. Triggers of subarachnoid hemorrhage: role of physical exertion, smoking, and alcohol in the Australasian Cooperative Research on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Study (ACROSS). Stroke. 34:1771–1776. 2003.3. Choi JH, Park HS. The incidence and characteristics of patients with small ruptured aneurysms (<5 mm) in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 60:424–432. 2017.
Article4. Fann J, Kukull WA, Katon WJ, Longstreth WT Jr. Physical activity and subarachnoid haemorrhage: a population based case-control study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 69:768–772. 2000.
Article5. Feigin VL, Rinkel GJ, Lawes CM, Algra A, Bennett DA, van Gijn J, et al. Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage: an updated systematic review of epidemiological studies. Stroke. 36:2773–2780. 2005.6. Fodor DM, Babiciu I, Perju-Dumbrava L. Circadian variation of stroke onset: a hospital-based study. Clujul Med. 87:242–249. 2014.7. Gallerani M, Portaluppi F, Maida G, Chieregato A, Calzolari F, Trapella G, et al. Circadian and circannual rhythmicity in the occurrence of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 27:1793–1797. 1996.
Article8. Gillum RF, Mussolino ME, Ingram DD. Physical activity and stroke incidence in women and men: The NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol. 143:860–869. 1996.
Article9. Han MH, Kim J, Choi KS, Kim CH, Kim JM, Cheong JH, et al. Monthly variations in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage incidence and mortality: correlation with weather and pollution. PLoS One. 12:e0186973. 2017.
Article10. Han MH, Yi HJ, Kim YS, Kim YS. Effect of seasonal and monthly variation in weather and air pollution factors on stroke incidence in Seoul, Korea. Stroke. 46:927–935. 2015.
Article11. Kocer A, Ilhan A, Ince N, Bilge C. The related causes in very early morning onset of stroke. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 29:983–988. 2005.
Article12. Lee IM, Hennekens CH, Berger K, Buring JE, Manson JE. Exercise and risk of stroke in male physicians. Stroke. 30:1–6. 1999.
Article13. Longstreth WT Jr, Nelson LM, Koepsell TD, van Belle G. Cigarette smoking, alcohol use, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 23:1242–1249. 1992.
Article14. Matsuda M, Ohashi M, Shiino A, Matsumura K, Handa J. Circumstances precipitating aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis. 3:285–288. 1993.
Article15. Mittleman MA, Maclure M, Tofler GH, Sherwood JB, Goldberg RJ, Muller JE. Triggering of acute myocardial infarction by heavy physical exertion--protection against triggering by regular exertion. N Engl J Med. 329:1677–1683. 1993.
Article16. Omama S, Yoshida Y, Ogawa A, Onoda T, Okayama A. Differences in circadian variation of cerebral infarction, intracerebral haemorrhage and subarachnoid haemorrhage by situation at onset. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 77:1345–1349. 2006.
Article17. Salonen JT, Puska P, Tuomilehto J. Physical activity and risk of myocardial infarction, cerebral stroke and death: a longitudinal study in Eastern Finland. Am J Epidemiol. 115:526–537. 1982.
Article18. Schievink WI, Karemaker JM, Hageman LM, van der Werf DJ. Circumstances surrounding aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol. 32:266–272. 1989.
Article19. Shinton R, Sagar G. Lifelong exercise and stroke. BMJ. 307:231–234. 1993.
Article20. Sloan MA, Price TR, Foulkes MA, Marler JR, Mohr JP, Hier DB, et al. Circadian rhythmicity of stroke onset. Intracerebral and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 23:1420–1426. 1992.
Article21. Temes RE, Bleck T, Dugar S, Ouyang B, Mohammad Y, John S, et al. Circadian variation in ictus of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. 16:219–223. 2012.
Article22. Tsementzis SA, Gill JS, Hitchcock ER, Gill SK, Beevers DG. Diurnal variation of and activity during the onset of stroke. Neurosurgery. 17:901–904. 1985.
Article23. Turin TC, Kita Y, Rumana N, Takashima N, Ichikawa M, Sugihara H, et al. Diurnal variation in onset of hemorrhagic stroke is independent of risk factor status: Takashima Stroke Registry. Neuroepidemiology. 34:25–33. 2010.
Article24. Wannamethee G, Shaper AG. Physical activity and stroke in British middle aged men. BMJ. 304:597–601. 1992.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis for Circumstantial Factors in Onset of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Computerized Tomography Findings Suggesting Non-aneurysmal Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- Frequency of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Need of 4-vessel Angiography
- Simultaneous Occurrence of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- Surgical Experiences of the Ruptured Giant Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm(2 Cases)