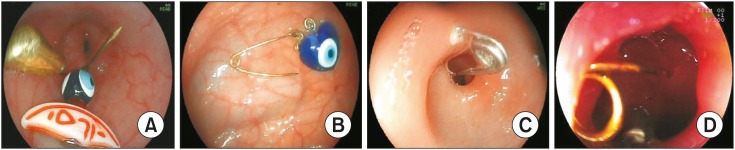
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr.
2019 Sep;22(5):441-446. 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.5.441.
A Case Series of Ingested Open Safety Pin Removal Using a Proposed Endoscopic Removal Technique Algorithm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, University of Health Sciences, Yuksek Ihtisas Teaching Hospital, Bursa, Turkey. kaandemiroren@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2457745
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2019.22.5.441
Abstract
- PURPOSE
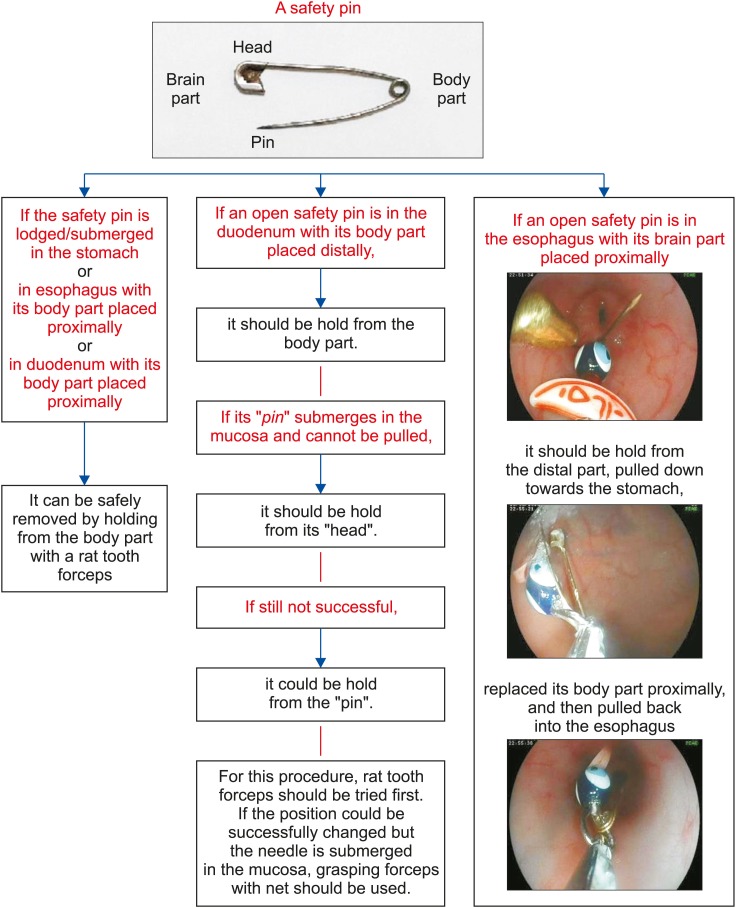
Safety pin ingestion is common in some regions of the world and may lead to severe morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study was to present some practical suggestions for ingested safety pins using an accompanying algorithm, presented for the first time in the literature to the best of our knowledge.
METHODS
Twenty children with ingested safety pins during a 4-year period were retrospectively included in the study.
RESULTS
Median age of patients was 9.5 months (interquartile range, 6.3-14 months), and 70% were girls. On endoscopic examination, safety pins were observed in the stomach (25%), duodenal bulb (20%), upper esophagus (15%), middle esophagus (10%), and second part of the duodenum (10%) but were not observed in 20% of the cases. Safety pins were removed using endoscopy in 15 cases (75%). In four cases (20%), no safety pin was observed on endoscopic examination. In one case (5%) involving a 6-month-old infant, the safety pin could not be removed although it was observed using endoscopy. No surgical intervention was needed for any patient. No complications such as perforation or deaths developed, except for erosions, due to the foreign body removal procedure.
CONCLUSION
Safety pins are easily removed endoscopically. The best option is to remove the safety pin using endoscopy while it is still in the esophagus and stomach. For this reason, endoscopic procedures should be performed as soon as possible in children who have ingested safety pins.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Uyemura MC. Foreign body ingestion in children. Am Fam Physician. 2005; 72:287–291. PMID: 16050452.2. Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Brooks DE, Zimmerman A, Schauben JL. 2015 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 33rd Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016; 54:924–1109. PMID: 28004588.
Article3. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Ikenberry SO, Jue TL, Anderson MA, Appalaneni V, Banerjee S, et al. Management of ingested foreign bodies and food impactions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73:1085–1091. PMID: 21628009.
Article4. Sink JR, Kitsko DJ, Mehta DK, Georg MW, Simons JP. Diagnosis of pediatric foreign body ingestion: clinical presentation, physical examination, and radiologic findings. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2016; 125:342–350. PMID: 26475838.5. Dereci S, Koca T, Serdaroğlu F, Akçam M. Foreign body ingestion in children. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2015; 50:234–240. PMID: 26884693.
Article6. Aydoğdu S, Arikan C, Cakir M, Baran M, Yüksekkaya HA, Saz UE, et al. Foreign body ingestion in Turkish children. Turk J Pediatr. 2009; 51:127–132. PMID: 19480323.7. Kramer RE, Lerner DG, Lin T, Manfredi M, Shah M, Stephen TC, et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Endoscopy Committee. Management of ingested foreign bodies in children: a clinical report of the NASPGHAN Endoscopy Committee. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015; 60:562–574. PMID: 25611037.8. Thomson M, Tringali A, Dumonceau JM, Tavares M, Tabbers MM, Furlano R, et al. Paediatric gastrointestinal endoscopy: European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Guidelines. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017; 64:133–153. PMID: 27622898.
Article9. Sarihan H, Kaklikkaya I, Ozcan F. Pediatric safety pin ingestion. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 1998; 39:515–518.10. Kalayci A, Tander B, Kocak S, Rizalar R, Bernay F. Removal of open safety pins in infants by flexible endoscopy is effective and safe. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2007; 17:242–245. PMID: 17484658.
Article11. Gün F, Salman T, Abbasoglu L, Celik R, Celik A. Safety-pin ingestion in children: a cultural fact. Pediatr Surg Int. 2003; 19:482–484. PMID: 12756595.12. Bass RM, Hurshman LF, Winkler LF. Rupture of the carotid artery from a hypopharyngeal foreign body. Arch Otolaryngol. 1978; 104:471–473. PMID: 678197.
Article13. Sugunan S, Ajith Krishnan AS, Devakumar VK, Arif AK. Safety-pin induced hemopericardium and cardiac tamponade in an infant. Indian Pediatr. 2018; 55:521–522. PMID: 29978823.
Article14. Cay A, Imamoğlu M, Sarihan H, Sayil O. Duodenocolic fistula due to safety pin ingestion. Turk J Pediatr. 2004; 46:186–188. PMID: 15214754.15. Mirza B, Sheikh A. Open safety pin ingestion presenting as incarcerated umbilical hernia. APSP J Case Rep. 2011; 2:25. PMID: 22953292.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral Subtrochanteric fracture After Pin Removal in Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis: A Case Report
- Endoscopic Removal of Multiple Toothbrushes: A Case Report
- Two Cases of Colonoscopic Retrieval of a Foreign Body in Children: A Button Battery and an Open Safety Pin
- Removal of Broken Screws of Interlocking Nail: technical note
- Foreign Body in the Gastrointestinal Tract in Children