Ann Lab Med.
2020 Jan;40(1):72-75. 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.72.
Performance Evaluation of the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS Droplet Digital PCR Assay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dearmina@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul Clinical Laboratories, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 2457497
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.72
Abstract
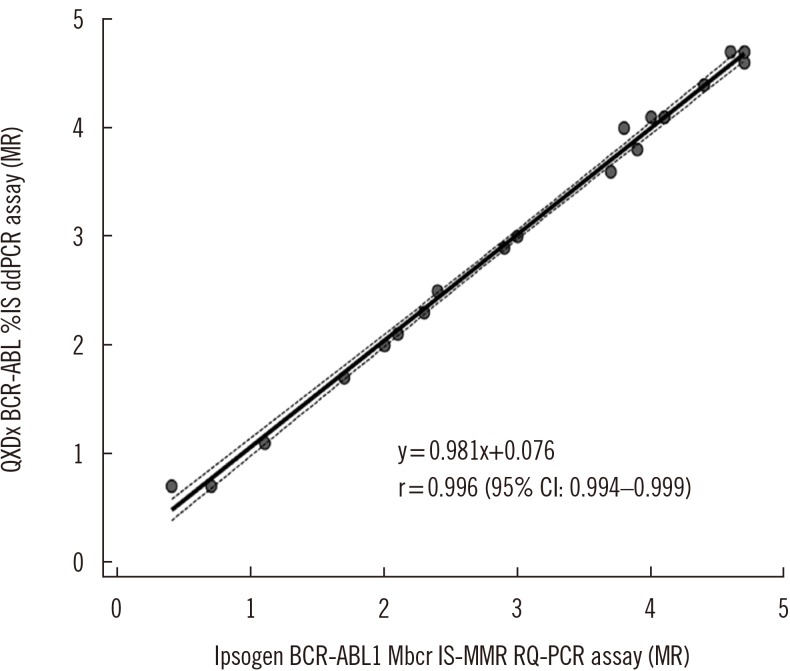
- Accurate detection of BCR-ABL fusion transcripts at and below molecular response (MR) 4 (0.01% International Scale [IS]) is required for disease monitoring in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). We evaluated the analytical performance of the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) assay, which is the first commercially available ddPCR-based in vitro diagnostics product. In precision analysis, the %CV was 9.3% and 3.0%, with mean values of 0.031% IS and 9.4% IS, respectively. The assay was linear in the first order, ranging from 0.032% IS to 20% IS. The manufacturer-claimed limit of blank, limit of detection, and limit of quantification were verified successfully. There was a very strong correlation between the results of the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS ddPCR assay and the ipsogen BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) real-time quantitative PCR assay (r=0.996). In conclusion, the QXDx BCR-ABL %IS ddPCR assay can provide reliable results for CML patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
혈액종양 정량 분자유전 검사법의 검정 권고안
Jin Ju Kim, Sunggyun Park, Yonggeun Cho, Jihye Ha, Saeam Shin, Seung-Tae Lee
Lab Med Online. 2022;12(4):227-234. doi: 10.47429/lmo.2022.12.4.227.Measurable Residual Disease Testing Using Next-Generation Sequencing in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Seon Young Kim, Hee Jin Huh
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(4):323-324. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.323.
Reference
-
1. Baccarani M, Castagnetti F, Gugliotta G, Rosti G. A review of the European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of CML. Ann Hematol. 2015; 94:S141–S147. PMID: 25814080.2. Radich JP, Deininger M, Abboud CN, Altman JK, Berman E, Bhatia R, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia, version 1.2019, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018; 16:1108–1135. PMID: 30181422.3. Branford S, Cross NC, Hochhaus A, Radich J, Saglio G, Kaeda J, et al. Rationale for the recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2006; 20:1925–1930. PMID: 16990771.4. Jennings LJ, George D, Czech J, Yu M, Joseph L. Detection and quantification of BCR-ABL1 fusion transcripts by droplet digital PCR. J Mol Diagn. 2014; 16:174–179. PMID: 24389534.5. Kong JH, Winton EF, Heffner LT, Chen Z, Langston AA, Hill B, et al. Does the frequency of molecular monitoring after tyrosine kinase inhibitor discontinuation affect outcomes of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia? Cancer. 2017; 123:2482–2488. PMID: 28241101.6. Cross NC, White HE, Colomer D, Ehrencrona H, Foroni L, Gottardi E, et al. Laboratory recommendations for scoring deep molecular responses following treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2015; 29:999–1003. PMID: 25652737.7. Alikian M, Whale AS, Akiki S, Piechocki K, Torrado C, Myint T, et al. RT-qPCR and RT-digital PCR: a comparison of different platforms for the evaluation of residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Chem. 2017; 63:525–531. PMID: 27979961.8. Wang WJ, Zheng CF, Liu Z, Tan YH, Chen XH, Zhao BL, et al. Droplet digital PCR for BCR/ABL (P210) detection of chronic myeloid leukemia: a high sensitive method of the minimal residual disease and disease progression. Eur J Haematol. 2018; 101:291–296. PMID: 29691899.9. Maier J, Lange T, Cross M, Wildenberger K, Niederwieser D, Franke GN. Optimized digital droplet PCR for BCR-ABL. J Mol Diagn. 2019; 21:27–37. PMID: 30347270.10. Bio-Rad. QXDx BCR-ABL %IS Kit. Instructions for use. Updated on June 2019. http://www.bio-rad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/12006672.pdf.11. QIAGEN ipsogen BCR-ABL1 Mbcr IS-MMR DX Kit Handbook. Updated on June 2019. https://www.qiagen.com/np/resources/resourcedetail?id=ce61c6fb-dc8d-4cae-8b37-3d3422dbd38e&lang=en.12. Gabert J, Beillard E, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Grimwade D, Pallisgaard N, et al. Standardization and quality control studies of ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction of fusion gene transcripts for residual disease detection in leukemia–a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia. 2003; 17:2318–2357. PMID: 14562125.13. Beillard E, Pallisgaard N, van der Velden VH, Bi W, Dee R, van der Schoot E, et al. Evaluation of candidate control genes for diagnosis and residual disease detection in leukemic patients using ‘real-time’ quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR)–a Europe against cancer program. Leukemia. 2003; 17:2474–2486. PMID: 14562124.14. CLSI. User verification of precision and estimation of bias; approved guideline. 3rd ed. CLSI EP15-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2014.15. CLSI. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative measurement procedures: a statistical approach; approved guideline. CLSI EP06-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2003.16. CLSI. Evaluation of detection capability for clinical laboratory measurement procedures; approved guideline. 2nd ed. CLSI EP17-A2. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2012.17. CLSI. Measurement procedure comparison and bias estimation using patients; approved guideline. 3rd ed. CLSI EP09-A3. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2013.18. Huggett JF, Cowen S, Foy CA. Considerations for digital PCR as an accurate molecular diagnostic tool. Clin Chem. 2015; 61:79–88. PMID: 25338683.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of BCR-ABL Fusion Transcripts of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients in Korea
- Hematological Significance of RT-PCR Test for bcr-abl Rearrangement and the Breakpoint Distribution within the Major bcr in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients
- Can Minor bcr/abl Translocation in Acute Leukemia Be Discriminated from Major bcr/abl by Modified FISH Analysis?
- Evaluation of a new flow cytometry based method for detection of BCR-ABL1 fusion protein in chronic myeloid leukemia
- Monitoring of bcr-abl Fusion Transcript Levels by Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Bone Marrow Transplantation