Urogenit Tract Infect.
2019 Aug;14(2):46-54. 10.14777/uti.2019.14.2.46.
How Women Evaluate Syndromic Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. yhkuro@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2456609
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2019.14.2.46
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the clinical manifestations of patients with the principal complaint of syndromic recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI), correlate these symptoms with the results of urine cultures, and identify the characteristics that can be used to differentiate UTI from similar diseases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
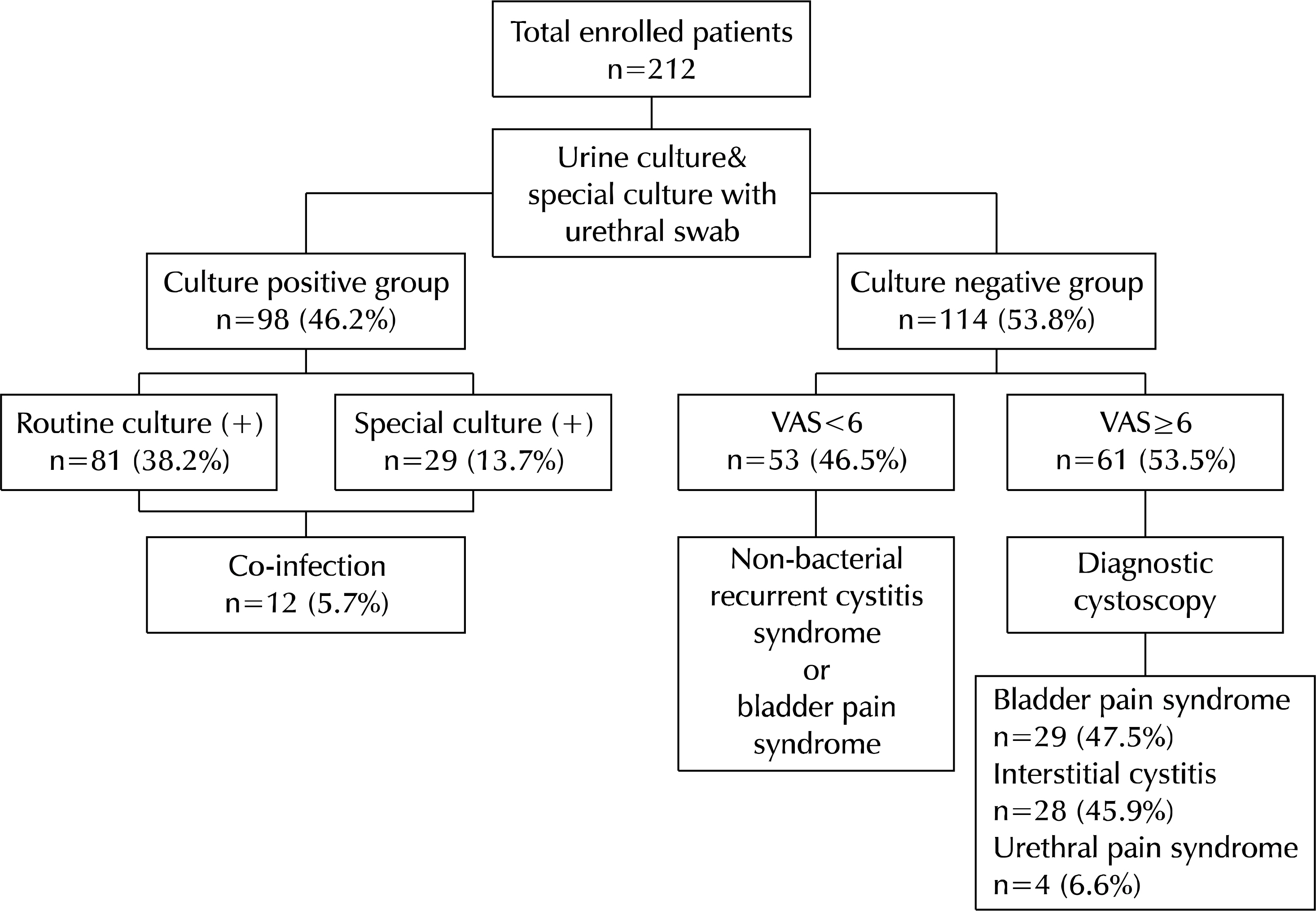
A total of 212 consecutive patients with syndromic recurrent UTIs over a 24 month period were evaluated. The major symptoms were recorded using the UTISA questionnaire and VAS. The patients were divided into group A (n=98; positive urine and urethral swab cultures) and group B (n=114; negative cultures), and the symptoms were compared. For group B, cystoscopy was used to diagnose 61 patients who complained of pain levels ≥6 on the VAS.
RESULTS
The proportion of patients with the classic symptoms of UTI (dysuria, urinary frequency, lower abdominal discomfort during bladder filling, and urgency) was similar in groups A and B. Significantly more patients complained of urethral pain in group B, and significantly fewer patients had gross hematuria, low back pain, a post-voiding sensation of residual urine, and general symptoms compared to group A. Of the 61 patients with a VAS ≥6, 29, 28, and four were diagnosed with bladder pain syndrome, interstitial cystitis, and urethral pain syndrome, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
In patients with syndromic recurrent UTI, the classic symptoms were not sufficiently characteristic to allow bacterial cystitis to be differentiated from other bladder diseases. Diagnostic cystoscopy and VAS can assist in making a differential diagnosis in patients with non-bacterial syndromic recurrent UTIs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hooton TM, Scholes D, Hughes JP, Winter C, Roberts PL, Stapleton AE, et al. A prospective study of risk factors for symptomatic urinary tract infection in young women. N Engl J Med. 1996; 335:468–74.
Article2. Mabeck CE. Treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection in nonpregnant women. Postgrad Med J. 1972; 48:69–75.
Article3. Scholes D, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Stapleton AE, Gupta K, Stamm WE. Risk factors for recurrent urinary tract infection in young women. J Infect Dis. 2000; 182:1177–82.
Article4. Min KS, Kim YH, Kim JM, Shin KL, Hong JY, Kim ME. Development of a Korean version of the urinary tract infection symptoms assessment questionnaire. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:361–8.
Article5. Clayson D, Wild D, Doll H, Keating K, Gondek K. Validation of a patient-administered questionnaire to measure the severity and bothersomeness of lower urinary tract symptoms in uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI): the UTI Symptom Assessment questionnaire. BJU Int. 2005; 96:350–9.
Article6. Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002; 21:167–78.
Article7. van de Merwe JP, Nordling J, Bouchelouche P, Bouchelouche K, Cervigni M, Daha LK, et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: an ESSIC proposal. Eur Urol. 2008; 53:60–7.
Article8. Gillenwater JY, Wein AJ. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases workshop on interstitial cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, August 28–29, 1987. J Urol. 1988; 140:203–6.
Article9. Albert X, Huertas I, Pereiró II, Sanfélix J, Gosalbes V, Perrota C. Antibiotics for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in nonpregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; 3:CD001209.
Article10. Fihn SD. Clinical practice. Acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:259–66.11. Gupta K, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Stamm WE. Patient-initiated treatment of uncomplicated recurrent urinary tract infections in young women. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:9–16.
Article12. Stapleton A. Prevention of recurrent urinary-tract infections in women. Lancet. 1999; 353:7–8.
Article13. Gupta K, Trautner BW. Diagnosis and management of recurrent urinary tract infections in nonpregnant women. BMJ. 2013; 346:f3140.
Article14. Bent S, Nallamothu BK, Simel DL, Fihn SD, Saint S. Does this woman have an acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection? JAMA. 2002; 287:2701–10.
Article15. Komaroff AL. Acute dysuria in women. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310:368–75.
Article16. Potts JM, Ward AM, Rackley RR. Association of chronic urinary symptoms in women and Ureaplasma urealyticum. Urology. 2000; 55:486–9.
Article17. Ingham HR, MacFarlane WV, Hale JH, Selkon JB, Codd AA. Controlled study of the prevalence of T strain mycoplasmata in males with nongonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1966; 42:269–71.
Article18. Rajasekaran M, Stein P, Parsons CL. Toxic factors in human urine that injure urothelium. Int J Urol. 2006; 13:409–14.
Article19. Parsons CL, Forrest J, Nickel JC, Evans R, Lloyd LK, Barkin J, et al. Effect of pentosan polysulfate therapy on intravesical potassium sensitivity. Urology. 2002; 59:329–33.
Article20. Weng TI, Chen WJ, Wu HY, Liu SH. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli alters muscle contractions in rat urinary bladder via a nitric oxide synthase-related signaling pathway. J Infect Dis. 2006; 194:1774–82.21. Arya LA, Northington GM, Asfaw T, Harvie H, Malykhina A. Evidence of bladder oversensitivity in the absence of an infection in premenopausal women with a history of recurrent urinary tract infections. BJU Int. 2011; 110:247–51.
Article22. Seller RH. Differential diagnosis of common complaints. 3rd ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;1996. p. 341–52.23. Bremnor JD, Sadovsky R. Evaluation of dysuria in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2002; 65:1589–96.24. Kurowski K. The women with dysuria. Am Fam Physician. 1998; 57:2155–64. 2169–70.25. Tanagho EA, McAninch JW. Smith's general urology. 16th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill;2004. p. 203–27.26. Gomes CM, Sánchez-Ortiz RF, Harris C, Wein AJ, Rovner ES. Significance of hematuria in patients with interstitial cystitis: review of radiographic and endoscopic findings. Urology. 2001; 57:262–5.
Article27. Braunstein R, Shapiro E, Kaye J, Moldwin R. The role of cystoscopy in the diagnosis of Hunner's ulcer disease. J Urol. 2008; 180:1383–6.
Article28. Irwin P, Samsudin A. Reinvestigation of patients with a diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: common things are sometimes common. J Urol. 2005; 174:584–7. ; discussion 587.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevention of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections in Women
- The Association between Chronic Inflammation and Recurrent Cystitis in Women
- How Do You Diagnose Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections and Confirm the Diagnosis?
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection from Urethral Mesh Erosion after Midurethral Mesh Sling Surgery
- Differences in Urine Microbiome of Acute Cystitis and Chronic Recurrent Cystitis in Women