Investig Clin Urol.
2019 Sep;60(5):333-342. 10.4111/icu.2019.60.5.333.
Current surgical techniques of enucleation in holmium laser enucleation of the prostate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sjo@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2455960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/icu.2019.60.5.333
Abstract
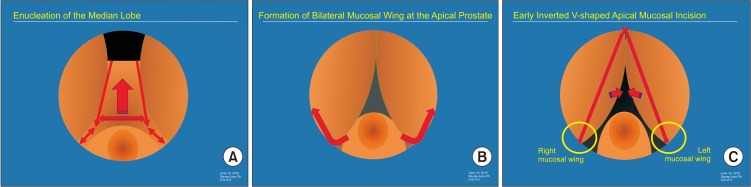
- Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) has been accepted as the most efficient method of transurethral surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The originally developed three-lobe technique has popularized this surgery; this method is based on three longitudinal incisions, by which the median lobe is removed, and subsequently, both lateral lobes are enucleated. To maintain a consistent surgical plane and to minimize sphincteric damage, the traditional three-lobe technique is continuously being refined and evolving. A few modifications of the original technique have been developed, and several en bloc enucleation methods have been introduced. However, more clinical evidence is required to show the superiority of newer techniques over the original three-lobe technique in terms of efficacy and long-term side effects. To date, none of the newer techniques have been accepted as a standard technique for HoLEP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fraundorfer MR, Gilling PJ. Holmium:YAG laser enucleation of the prostate combined with mechanical morcellation: preliminary results. Eur Urol. 1998; 33:69–72. PMID: 9471043.
Article2. Cornu JN, Ahyai S, Bachmann A, de la Rosette J, Gilling P, Gratzke C, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic obstruction: an update. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:1066–1096. PMID: 24972732.
Article3. Lee SW, Choi JB, Lee KS, Kim TH, Son H, Jung TY, et al. Transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement: a quality and meta-analysis. Int Neurourol J. 2013; 17:59–66. PMID: 23869269.
Article4. Elzayat EA, Elhilali MM. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP): the endourologic alternative to open prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2006; 49:87–91. PMID: 16314033.
Article5. Kuntz RM, Lehrich K, Ahyai SA. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus open prostatectomy for prostates greater than 100 grams: 5-year follow-up results of a randomised clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2008; 53:160–166. PMID: 17869409.
Article6. Kim M, Piao S, Lee HE, Kim SH, Oh SJ. Efficacy and safety of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for extremely large prostatic adenoma in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2015; 56:218–226. PMID: 25763126.
Article7. Krambeck AE, Handa SE, Lingeman JE. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for prostates larger than 175 grams. J Endourol. 2010; 24:433–437. PMID: 19852722.
Article8. Krambeck AE, Handa SE, Lingeman JE. Experience with more than 1,000 holmium laser prostate enucleations for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2010; 183:1105–1109. PMID: 20092844.
Article9. Kuntz RM, Ahyai S, Lehrich K, Fayad A. Transurethral holmium laser enucleation of the prostate versus transurethral electrocautery resection of the prostate: a randomized prospective trial in 200 patients. J Urol. 2004; 172:1012–1016. PMID: 15311026.
Article10. Bae J, Choo M, Park JH, Oh JK, Paick JS, Oh SJ. Holmium laser enucleation of prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia: Seoul National University hospital experience. Int Neurourol J. 2011; 15:29–34. PMID: 21468284.
Article11. Gilling PJ, Aho TF, Frampton CM, King CJ, Fraundorfer MR. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: results at 6 years. Eur Urol. 2008; 53:744–749. PMID: 17475395.
Article12. Montorsi F, Naspro R, Salonia A, Suardi N, Briganti A, Zanoni M, et al. Holmium laser enucleation versus transurethral resection of the prostate: results from a 2-center, prospective, randomized trial in patients with obstructive benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2004; 172:1926–1929. PMID: 15540757.
Article13. Gratzke C, Bachmann A, Descazeaud A, Drake MJ, Madersbacher S, Mamoulakis C, et al. EAU Guidelines on the assessment of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur Urol. 2015; 67:1099–1109. PMID: 25613154.
Article14. Bae J, Oh SJ, Paick JS. The learning curve for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a single-center experience. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:688–693. PMID: 21031088.
Article15. Kampantais S, Dimopoulos P, Tasleem A, Acher P, Gordon K, Young A. Assessing the learning curve of holmium laser enucleation of prostate (HoLEP). A systematic review. Urology. 2018; 120:9–22. PMID: 30403609.
Article16. Elmansy HM, Kotb A, Elhilali MM. Is there a way to predict stress urinary incontinence after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate? J Urol. 2011; 186:1977–1981. PMID: 21944135.
Article17. Vavassori I, Valenti S, Naspro R, Vismara A, Dell'Acqua V, Manzetti A, et al. Three-year outcome following holmium laser enucleation of the prostate combined with mechanical morcellation in 330 consecutive patients. Eur Urol. 2008; 53:599–604. PMID: 17997021.
Article18. Cho KJ, Koh JS, Choi JB, Kim JC. Factors associated with early recovery of stress urinary incontinence following holmium laser enucleation of the prostate in patients with benign prostatic enlargement. Int Neurourol J. 2018; 22:200–205. PMID: 30286583.
Article19. Gilling PJ, Cass CB, Cresswell MD, Fraundorfer MR. Holmium laser resection of the prostate: preliminary results of a new method for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1996; 47:48–51. PMID: 8560662.
Article20. Gilling PJ, Cass CB, Malcolm AR, Fraundorfer MR. Combination holmium and Nd:YAG laser ablation of the prostate: initial clinical experience. J Endourol. 1995; 9:151–153. PMID: 7633476.
Article21. Kabalin JN. Holmium:YAG laser prostatectomy: results of U.S. pilot study. J Endourol. 1996; 10:453–457. PMID: 8905493.
Article22. Endo F, Shiga Y, Minagawa S, Iwabuchi T, Fujisaki A, Yashi M, et al. Anteroposterior dissection HoLEP: a modification to prevent transient stress urinary incontinence. Urology. 2010; 76:1451–1455. PMID: 20579706.
Article23. Gong YG, He DL, Wang MZ, Li XD, Zhu GD, Zheng ZH, et al. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a modified enucleation technique and initial results. J Urol. 2012; 187:1336–1340. PMID: 22342512.
Article24. Kim M, Lee HE, Oh SJ. Technical aspects of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2013; 54:570–579. PMID: 24044089.
Article25. Scoffone CM, Cracco CM. The en-bloc no-touch holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) technique. World J Urol. 2016; 34:1175–1181. PMID: 26658753.
Article26. Minagawa S, Okada S, Sakamoto H, Toyofuku K, Morikawa H. En-Bloc technique with anteroposterior dissection holmium laser enucleation of the prostate allows a short operative time and acceptable outcomes. Urology. 2015; 86:628–633. PMID: 26126696.
Article27. Ito T, Tamura K, Otsuka A, Shinbo H, Takada S, Kurita Y, et al. Development of a complete En-Bloc technique with direct bladder neck incision: a newly modified approach for holmium laser enucleation of the prostate. J Endourol. 2019; 6. 12. DOI: 10.1089/end.2018.0773. [Epub].
Article28. Saitta G, Becerra JEA, Del Álamo JF, González LL, Elbers JR, Suardi N, et al. ‘En Bloc’ HoLEP with early apical release in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. World J Urol. 2019; 2. 08. DOI: 10.1007/s00345-019-02671-4. [Epub].
Article29. Miernik A, Schoeb DS. “Three horse shoe-like incision” holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: first experience with a novel en bloc technique for anatomic transurethral prostatectomy. World J Urol. 2019; 37:523–528. PMID: 30039386.
Article30. Gilling PJ, Kennett K, Das AK, Thompson D, Fraundorfer MR. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) combined with transurethral tissue morcellation: an update on the early clinical experience. J Endourol. 1998; 12:457–459. PMID: 9847070.
Article31. Tan AH, Gilling PJ. Holmium laser prostatectomy: current techniques. Urology. 2002; 60:152–156. PMID: 12100945.
Article32. Gilling P. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP). BJU Int. 2008; 101:131–142. PMID: 18086107.
Article33. Kuo RL, Paterson RF, Kim SC, Siqueira TM Jr, Elhilali MM, Lingeman JE. Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP): a technical update. World J Surg Oncol. 2003; 1:6. PMID: 12818001.34. Serretta V, Morgia G, Fondacaro L, Curto G, Lo bianco A, Pirritano D, et al. Members of the Sicilian-Calabrian Society of Urology. Open prostatectomy for benign prostatic enlargement in southern Europe in the late 1990s: a contemporary series of 1800 interventions. Urology. 2002; 60:623–627. PMID: 12385922.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technical Aspects of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Enucleated Weight/Enucleation Time, Is It Appropriate for Estimating Enucleation Skills for Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate? A Consideration of Energy Consumption
- Von Brunn’s Nest in an Incidental Bladder Mass Found during Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate
- Recent advances in laser treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia
- The Learning Curve for Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate: A Single-Center Experience