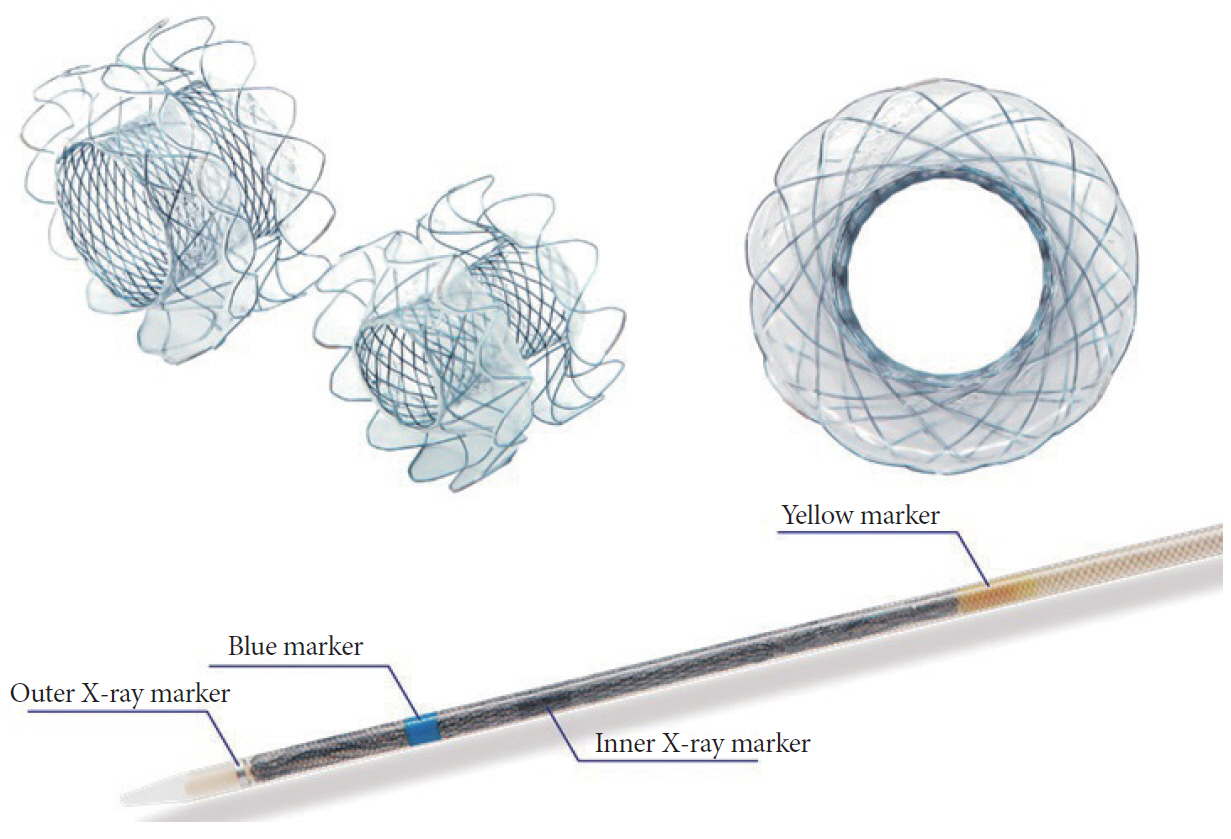
Clin Endosc.
2019 Jul;52(4):353-359. 10.5946/ce.2018.154.
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Plastic Stent and Novel Lumen-apposing Metal Stent for Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Peripancreatic Fluid Collections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea. cmcho@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2455632
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2018.154
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transmural drainage for peripancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) has gained wide acceptance as a nonsurgical intervention. Although a lumen-apposing metal stent (LAMS) was recently introduced, there are few data comparing the clinical outcomes between LAMS and plastic stent (PS) drainage.
METHODS
Endoscopy databases of all patients who had undergone EUS-guided drainage for PFCs were searched and the clinical outcomes of EUS-guided drainage according to stent-type used were compared.
RESULTS
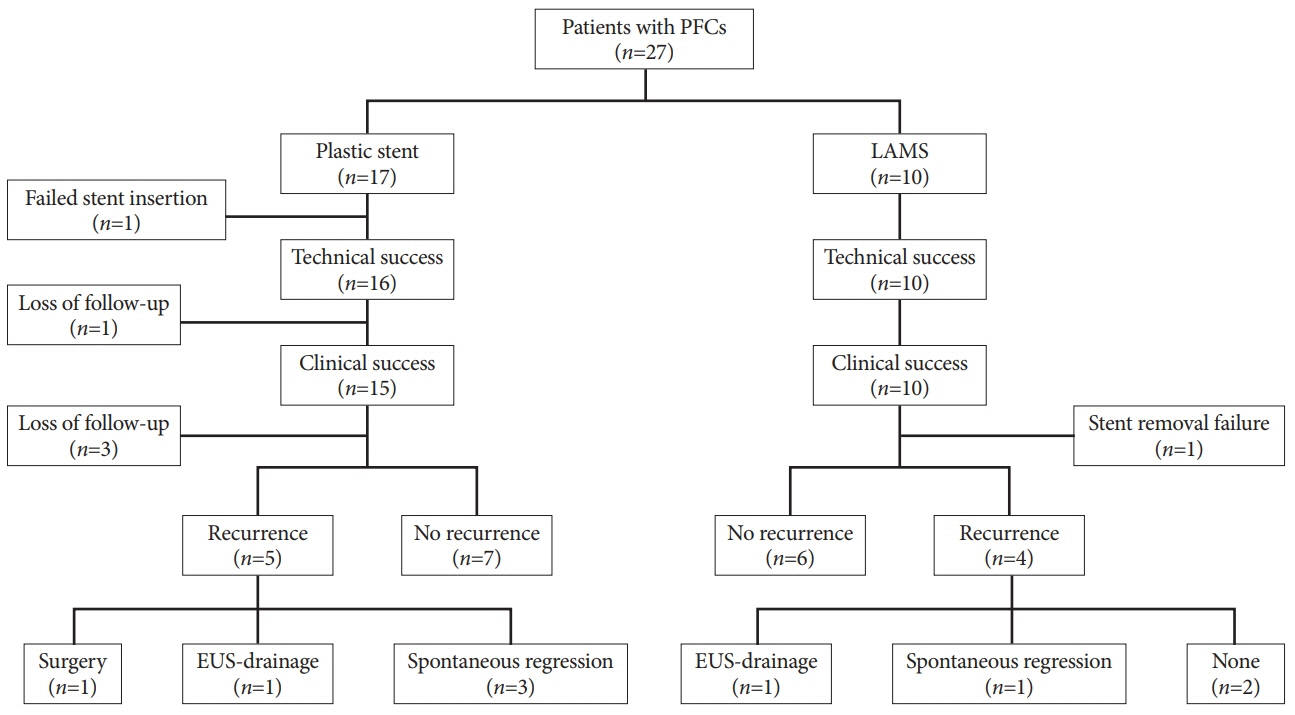
A total of 27 patients (median age, 56 years) with PFCs underwent EUS-guided transmural drainage between January 2011 and December 2017. Of these, 17 underwent PS placement and 10 underwent LAMS placement. There was no significant difference in the technical success rate between the 2 groups (94.1% vs. 100%, p=1.0). Procedure time was shorter in the LAMS group compared to that in the PS group (10.6±2.5 min vs. 21.4±9.5 min, p=0.002). Among subjects with clinical success, recurrence of PFC after stent removal occurred in 5 of 12 patients with PS and 4 of 10 with LAMS, without statistical difference (41.7% vs. 40.0%, p=1.0).
CONCLUSIONS
Although our study showed similar clinical outcomes for LAMS and PS, further prospective trials are required to validate the superiority of LAMS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Editors' Choice of Noteworthy Clinical Endoscopy Publications in the First Decade
Gwang Ha Kim, Kwang An Kwon, Do Hyun Park, Jimin Han
Clin Endosc. 2021;54(5):633-640. doi: 10.5946/ce.2021.216.Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Peripancreatic Fluid Collections
Eun Young Kim, Robert H. Hawes
Clin Endosc. 2019;52(4):299-300. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.135.
Reference
-
1. Lang GD, Fritz C, Bhat T, et al. EUS-guided drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections with lumen-apposing metal stents and plastic double-pigtail stents: comparison of efficacy and adverse event rates. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018; 87:150–157.
Article2. Sharaiha RZ, DeFilippis EM, Kedia P, et al. Metal versus plastic for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage: clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:822–827.
Article3. Aghdassi AA, Mayerle J, Kraft M, Sielenkämper AW, Heidecke CD, Lerch MM. Pancreatic pseudocysts--when and how to treat? HPB (Oxford). 2006; 8:432–441.4. Bang JY, Wilcox CM, Trevino JM, et al. Relationship between stent characteristics and treatment outcomes in endoscopic transmural drainage of uncomplicated pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc. 2014; 28:2877–2883.
Article5. Bakker OJ, van Santvoort HC, van Brunschot S, et al. Endoscopic transgastric vs surgical necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012; 307:1053–1061.
Article6. Ahn JY, Seo DW, Eum J, et al. Single-step EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: analysis of technical feasibility, efficacy, and safety. Gut Liver. 2010; 4:524–529.
Article7. Penn DE, Draganov PV, Wagh MS, Forsmark CE, Gupte AR, Chauhan SS. Prospective evaluation of the use of fully covered self-expanding metal stents for EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:679–684.
Article8. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013; 62:102–111.
Article9. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.
Article10. Akshintala VS, Saxena P, Zaheer A, et al. A comparative evaluation of outcomes of endoscopic versus percutaneous drainage for symptomatic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:921–928. quiz 983.e2, 983.e5.
Article11. Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:583–590. e1.
Article12. Varadarajulu S, Wilcox CM, Latif S, Phadnis M, Christein JD. Management of pancreatic fluid collections: a changing of the guard from surgery to endoscopy. Am Surg. 2011; 77:1650–1655.
Article13. Sadik R, Kalaitzakis E, Thune A, Hansen J, Jönson C. EUS-guided drainage is more successful in pancreatic pseudocysts compared with abscesses. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17:499–505.
Article14. Gluck M, Ross A, Irani S, et al. Endoscopic and percutaneous drainage of symptomatic walled-off pancreatic necrosis reduces hospital stay and radiographic resources. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8:1083–1088.
Article15. Ang TL, Kongkam P, Kwek AB, Orkoonsawat P, Rerknimitr R, Fock KM. A two-center comparative study of plastic and lumen-apposing large diameter self-expandable metallic stents in endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Endosc Ultrasound. 2016; 5:320–327.
Article16. Shah RJ, Shah JN, Waxman I, et al. Safety and efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections with lumen-apposing covered self-expanding metal stents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:747–752.
Article17. Moon JH, Choi HJ, Kim DC, et al. A newly designed fully covered metal stent for lumen apposition in EUS-guided drainage and access: a feasibility study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:990–995.
Article18. Gornals JB, De la Serna-Higuera C, Sánchez-Yague A, Loras C, Sánchez-Cantos AM, Pérez-Miranda M. Endosonography-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections with a novel lumen-apposing stent. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:1428–1434.
Article19. Itoi T, Binmoeller KF, Shah J, et al. Clinical evaluation of a novel lumen-apposing metal stent for endosonography-guided pancreatic pseudocyst and gallbladder drainage (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:870–876.
Article20. Bang JY, Hawes R, Bartolucci A, Varadarajulu S. Efficacy of metal and plastic stents for transmural drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: a systematic review. Dig Endosc. 2015; 27:486–498.21. Lin H, Zhan XB, Sun SY, et al. Stent selection for endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: a multicenter study in China. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014; 2014:193562.
Article22. Siddiqui AA, Kowalski TE, Loren DE, et al. Fully covered self-expanding metal stents versus lumen-apposing fully covered self-expanding metal stent versus plastic stents for endoscopic drainage of pancreatic walled-off necrosis: clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:758–765.
Article23. Lee BU, Song TJ, Lee SS, et al. Newly designed, fully covered metal stents for endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transmural drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections: a prospective randomized study. Endoscopy. 2014; 46:1078–1084.
Article24. Bang JY, Hasan M, Navaneethan U, Hawes R, Varadarajulu S. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) for pancreatic fluid collection (PFC) drainage: may not be business as usual. Gut. 2017; 66:2054–2056.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stent occlusion in endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage from bleeding mitigated by double pigtail plastic stent deployment within lumen apposing metal stent
- Past, Present, and Future of Gastrointestinal Stents: New Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Metal Stents and Future Developments
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Drainage in Pancreatobiliary Diseases
- Metal versus Plastic Stent for Transmural Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections
- A Newly Designed, Fully Covered, Metal Stent with Wide Flanges for EUS-Guided Drainage and Access