Korean J Radiol.
2016 Aug;17(4):533-540. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.4.533.
Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Malignant versus Benign Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul 06273, Korea. yjsrad97@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2455423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.4.533
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To validate the diffusion-weighted MRI (DWI) for differentiation of benign from malignant portal vein thrombosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
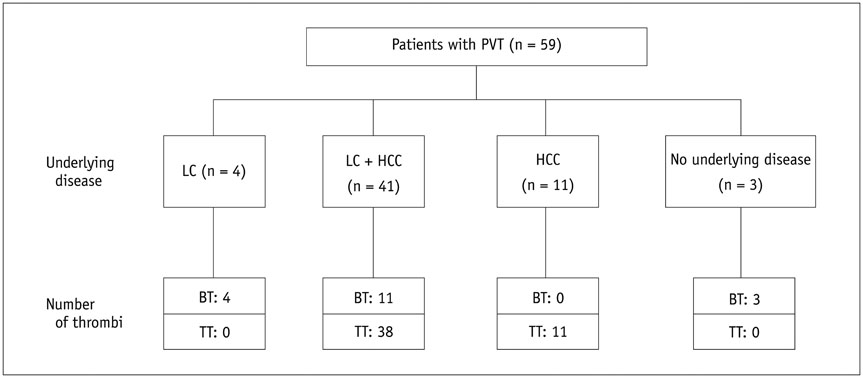
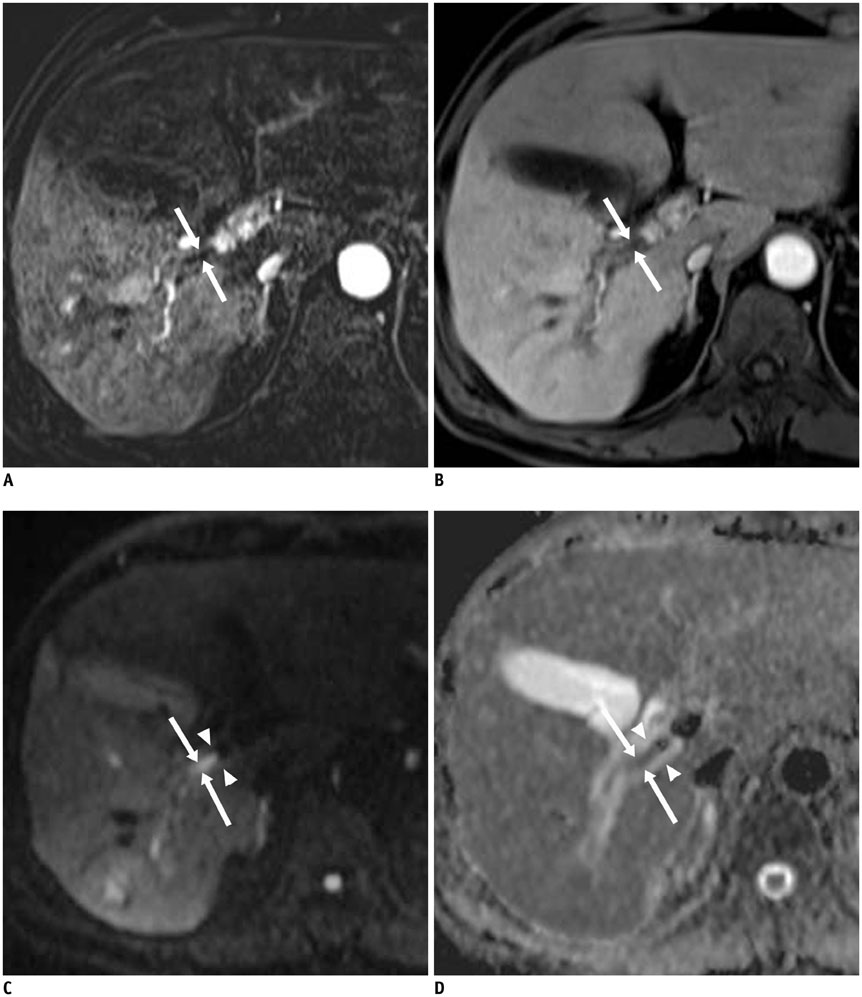
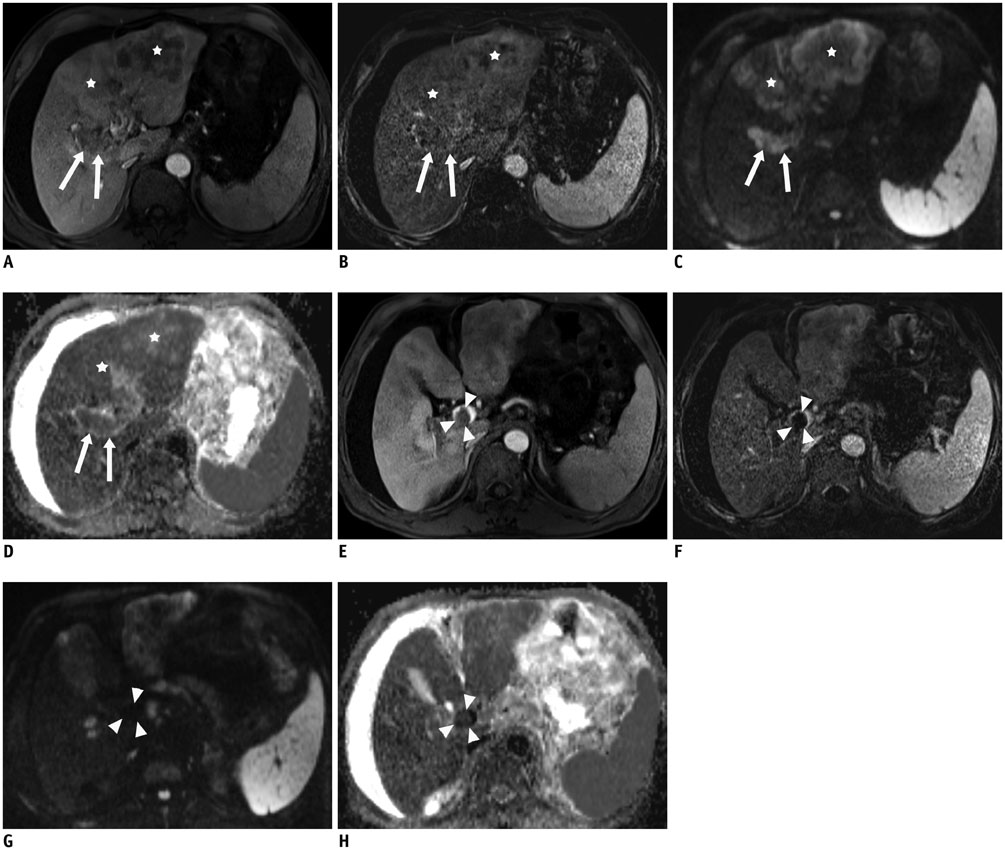
The Institutional Review Board approved this retrospective study and waived informed consent. A total of 59 consecutive patients (52 men and 7 women, aged 40-85 years) with grossly defined portal vein thrombus (PVT) on hepatic MRI were retrospectively analyzed. Among them, liver cirrhosis was found in 45 patients, and hepatocellular carcinoma in 47 patients. DWI was performed using b values of 50 and 800 sec/mm2 at 1.5-T unit. A thrombus was considered malignant if it enhanced on dynamic CT or MRI; otherwise, it was considered bland. There were 18 bland thrombi and 49 malignant thrombi in 59 patients, including 8 patients with simultaneous benign and malignant PVT. Mean apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) of benign and malignant PVTs were compared by using Mann-Whitney U test. Diagnostic accuracy was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
RESULTS
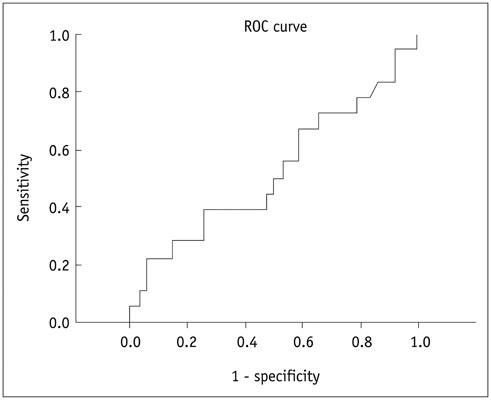
The mean ADC ± standard deviation of bland and malignant PVT were 1.00 ± 0.39 × 10(-3) mm2/sec and 0.92 ± 0.25 × 10(-3) mm2/sec, respectively; without significant difference (p = 0.799). The area under ROC curve for ADC was 0.520. An ADC value of > 1.35 × 10(-3) mm2/sec predicted bland PVT with a specificity of 94.6% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 84.9-98.9%) and a sensitivity of 22.2% (95% CI: 6.4-47.6%), respectively.
CONCLUSION
Due to the wide range and considerable overlap of the ADCs, DWI cannot differentiate the benign from malignant thrombi efficiently.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Area Under Curve
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging
Diagnosis, Differential
*Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Female
Humans
Liver Neoplasms/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging
Male
Middle Aged
Portal Vein/*diagnostic imaging
ROC Curve
Retrospective Studies
Sensitivity and Specificity
Venous Thrombosis/*diagnosis/diagnostic imaging
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Diffusion-Weighted MRI for the Initial Viability Evaluation of Parasites in Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis: Comparison with Positron Emission Tomography
Jianjun Zheng, Jing Wang, Jianqing Zhao, Xianyun Meng
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(1):40-46. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.1.40.The Diagnostic Performance of Liver MRI without Intravenous Contrast for Detecting Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Case-Controlled Feasibility Study
Seunghee Han, Joon-Il Choi, Michael Yong Park, Moon Hyung Choi, Sung Eun Rha, Young Joon Lee
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(4):568-577. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.568.
Reference
-
1. Okuda K, Ohnishi K, Kimura K, Matsutani S, Sumida M, Goto N, et al. Incidence of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis. An angiographic study in 708 patients. Gastroenterology. 1985; 89:279–286.2. Ogren M, Bergqvist D, Björck M, Acosta S, Eriksson H, Sternby NH. Portal vein thrombosis: prevalence, patient characteristics and lifetime risk: a population study based on 23,796 consecutive autopsies. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:2115–2119.3. Cohen J, Edelman RR, Chopra S. Portal vein thrombosis: a review. Am J Med. 1992; 92:173–182.4. Witte CL, Brewer ML, Witte MH, Pond GB. Protean manifestations of pylethrombosis. A review of thirty-four patients. Ann Surg. 1985; 202:191–202.5. Akin O, Dixit D, Schwartz L. Bland and tumor thrombi in abdominal malignancies: magnetic resonance imaging assessment in a large oncologic patient population. Abdom Imaging. 2011; 36:62–68.6. Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Schmitz KJ, Molmenti EP, Schroeder T, Saner FH, et al. Liver transplantation in the setting of hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein thrombosis: a challenging dilemma? Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53:1994–1999.7. Takizawa D, Kakizaki S, Sohara N, Sato K, Takagi H, Arai H, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: clinical characteristics, prognosis, and patient survival analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:3290–3295.8. Pirisi M, Avellini C, Fabris C, Scott C, Bardus P, Soardo G, et al. Portal vein thrombosis in hepatocellular carcinoma: age and sex distribution in an autopsy study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1998; 124:397–400.9. Sakata J, Shirai Y, Wakai T, Kaneko K, Nagahashi M, Hatakeyama K. Preoperative predictors of vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:900–905.10. Mathieu D, Grenier P, Lardé D, Vasile N. Portal vein involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma: dynamic CT features. Radiology. 1984; 152:127–132.11. Tublin ME, Dodd GD 3rd, Baron RL. Benign and malignant portal vein thrombosis: differentiation by CT characteristics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 168:719–723.12. Kaufman LB, Yeh BM, Breiman RS, Joe BN, Qayyum A, Coakley FV. Inferior vena cava filling defects on CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 185:717–726.13. Aslam Sohaib SA, Teh J, Nargund VH, Lumley JS, Hendry WF, Reznek RH. Assessment of tumor invasion of the vena caval wall in renal cell carcinoma cases by magnetic resonance imaging. J Urol. 2002; 167:1271–1275.14. Ergen FB, Hussain HK, Caoili EM, Korobkin M, Carlos RC, Weadock WJ, et al. MRI for preoperative staging of renal cell carcinoma using the 1997 TNM classification: comparison with surgical and pathologic staging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:217–225.15. Catalano OA, Choy G, Zhu A, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Differentiation of malignant thrombus from bland thrombus of the portal vein in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: application of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology. 2010; 254:154–162.16. Battal B, Kocaoglu M, Akgun V, Karademir I, Deveci S, Guvenc I, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in the characterization of focal liver lesions: efficacy of visual assessment. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2011; 35:326–331.17. Xu PJ, Yan FH, Wang JH, Shan Y, Ji Y, Chen CZ. Contribution of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010; 34:506–512.18. Miller FH, Hammond N, Siddiqi AJ, Shroff S, Khatri G, Wang Y, et al. Utility of diffusion-weighted MRI in distinguishing benign and malignant hepatic lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 32:138–147.19. Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology. 2010; 254:47–66.20. Sandrasegaran K, Akisik FM, Lin C, Tahir B, Rajan J, Aisen AM. The value of diffusion-weighted imaging in characterizing focal liver masses. Acad Radiol. 2009; 16:1208–1214.21. Parikh T, Drew SJ, Lee VS, Wong S, Hecht EM, Babb JS, et al. Focal liver lesion detection and characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: comparison with standard breath-hold T2-weighted imaging. Radiology. 2008; 246:812–822.22. Bruegel M, Holzapfel K, Gaa J, Woertler K, Waldt S, Kiefer B, et al. Characterization of focal liver lesions by ADC measurements using a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging technique. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:477–485.23. Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, et al. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol. 2001; 35:421–430.24. Sandrasegaran K, Tahir B, Nutakki K, Akisik FM, Bodanapally U, Tann M, et al. Usefulness of conventional MRI sequences and diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating malignant from benign portal vein thrombus in cirrhotic patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 201:1211–1219.25. Earls JP, Rofsky NM, DeCorato DR, Krinsky GA, Weinreb JC. Hepatic arterial-phase dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging: optimization with a test examination and a power injector. Radiology. 1997; 202:268–273.26. Connolly GC, Chen R, Hyrien O, Mantry P, Bozorgzadeh A, Abt P, et al. Incidence, risk factors and consequences of portal vein and systemic thromboses in hepatocellular carcinoma. Thromb Res. 2008; 122:299–306.27. Jonas S, Bechstein WO, Steinmüller T, Herrmann M, Radke C, Berg T, et al. Vascular invasion and histopathologic grading determine outcome after liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2001; 33:1080–1086.28. Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Tsuda K, Nakamura H. Diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging for liver disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 173:393–398.29. Gourtsoyianni S, Papanikolaou N, Yarmenitis S, Maris T, Karantanas A, Gourtsoyiannis N. Respiratory gated diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: value of apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in the differentiation between most commonly encountered benign and malignant focal liver lesions. Eur Radiol. 2008; 18:486–492.30. Kang BK, Na DG, Ryoo JW, Byun HS, Roh HG, Pyeun YS. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of intracerebral hemorrhage. Korean J Radiol. 2001; 2:183–191.31. Silvera S, Oppenheim C, Touzé E, Ducreux D, Page P, Domigo V, et al. Spontaneous intracerebral hematoma on diffusion-weighted images: influence of T2-shine-through and T2-blackout effects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:236–241.32. Kuwahara S, Miyake H, Fukuoka M, Koan Y, Ono Y, Moriki A, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of organized subdural hematoma--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2004; 44:376–379.33. Brooks RA, Di Chiro G, Patronas N. MR imaging of cerebral hematomas at different field strengths: theory and applications. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989; 13:194–206.34. Does MD, Zhong J, Gore JC. In vivo measurement of ADC change due to intravascular susceptibility variation. Magn Reson Med. 1999; 41:236–240.35. Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology. 2000; 217:331–345.36. Bradley WG Jr. MR appearance of hemorrhage in the brain. Radiology. 1993; 189:15–26.37. Yu JS, Chung JJ, Kim JH, Kim KW. Limited value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for differentiating bland from malignant portal venous thrombi. Radiology. 2010; 256:673–674. author reply 674.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Non-invasive MR Demonstration of the Fistula between Pancreatic Pseudocyst and Portal Vein: A Case Report
- Radiologic Findings of Neonatal Cerebral Infarction related with Portal Vein Thrombosis: Case Report
- Reappraisal of transarterial radioembolization for liver-confined hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: Editorial on “Transarterial radioembolization versus tyrosine kinase inhibitor in hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis”
- Acute Appendicitis with Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis
- Portal Vein Thrombosis during Pregnancy