Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2019 Aug;12(3):279-286. 10.21053/ceo.2018.01431.
Abrupt Change in Electrophysiological Properties Begins From Postnatal Day 7 Before Hearing Onset in the Developing Mice Auditory Cortical Layer II/III Neurons
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. ansil67@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2455369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2018.01431
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
In the developing auditory cortex, maturation of electrophysiological properties and cell types before and after hearing onset has been reported previously. However, the exact timing of firing pattern change has not been reported. In this study, firing pattern change was investigated from postnatal day 3 (P3) to P12 in auditory cortical layer II/III neurons to investigate whether firing pattern changes dramatically after a specific point during development.
METHODS
ICR mice pups aged from P3 to P12 were sacrificed to obtain 300-mm-thick brain slices containing the primary auditory cortex. From cortical layer II/III neurons, the patterns of action potential firing generated by current injection were examined using whole cell current clamp technique and the characteristics of Na⺠currents involved in action potential firing were investigated using whole cell voltage clamp technique.
RESULTS
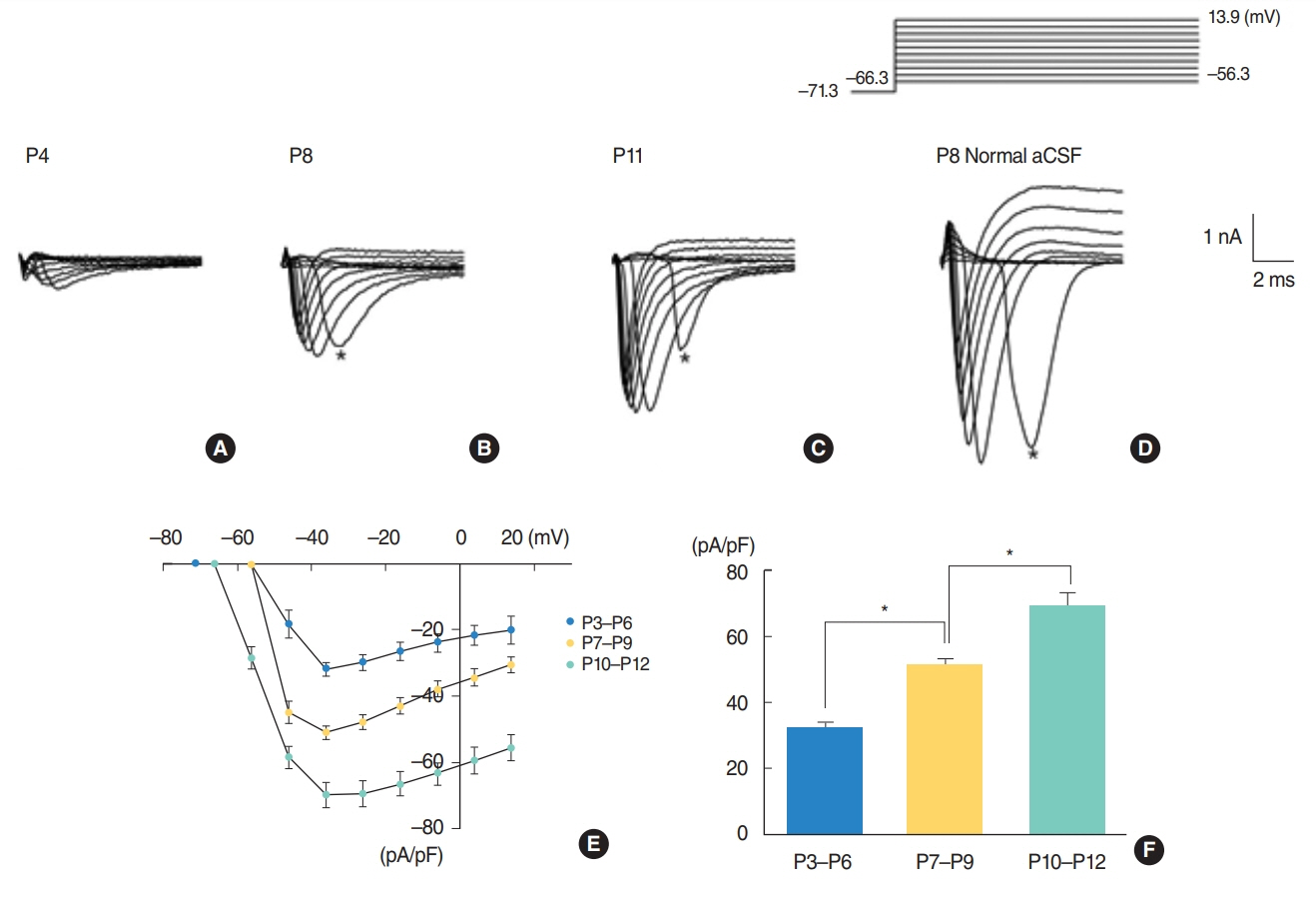
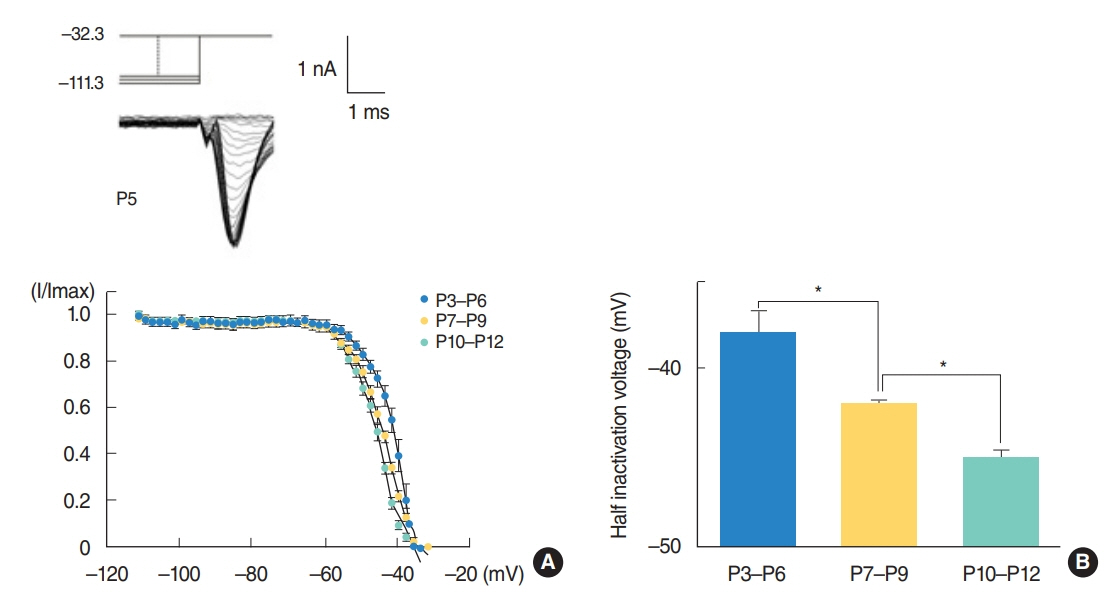
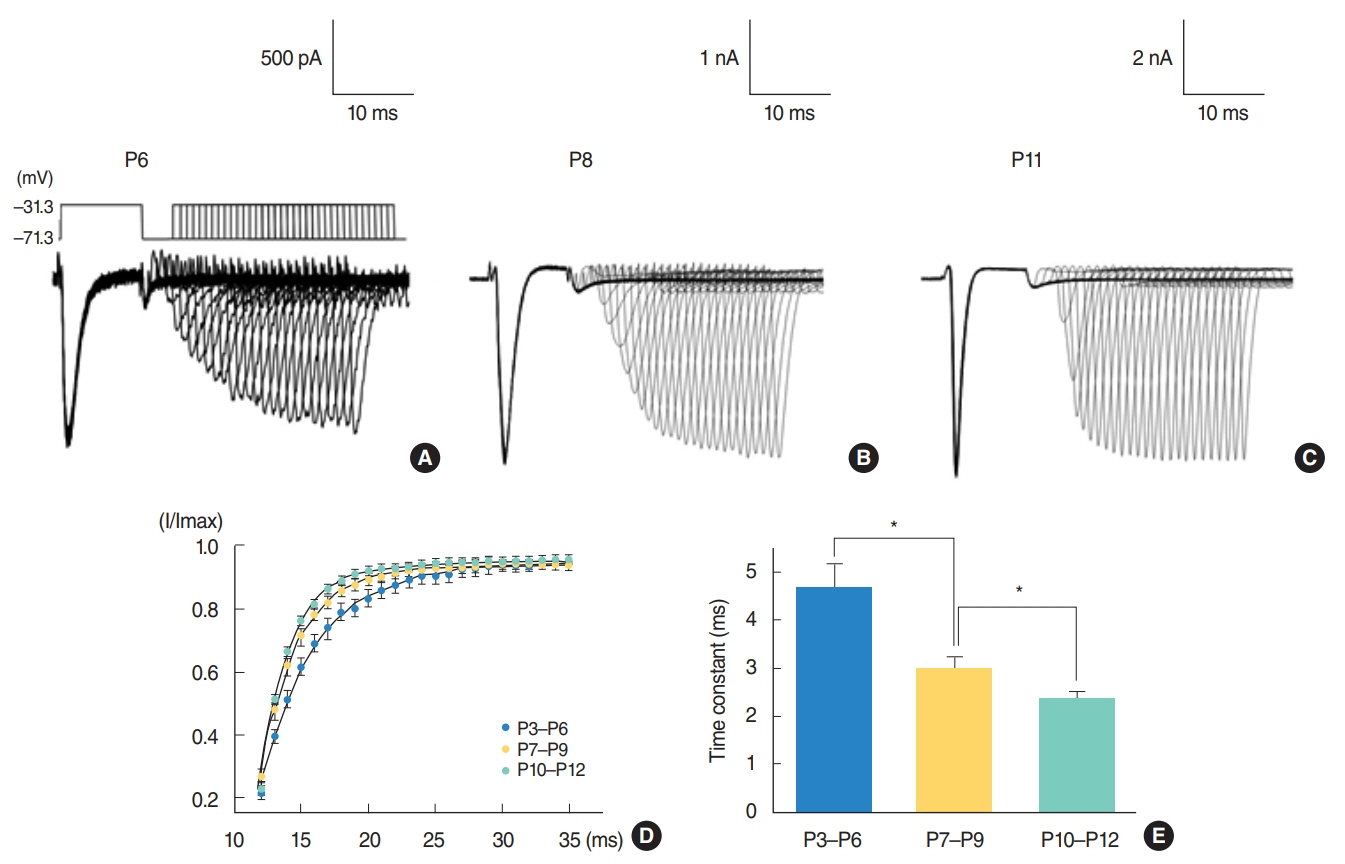
From P3 to P6, most cells did not show action potential firing (29 of 46 cells), and some cells responding to current injection showed a single action potential at the initial depolarizing current step (17 of 46 cells). This firing pattern changes from P7. From P7 to P9, cells begin to show regular spiking to current injection. The spiking frequency increased after P10. In studying Na⺠current with whole cell voltage clamp, Na⺠current densities increased gradually (32.0±2.0 pA/pF [P3-P6, n=7], 51.2±2.0 pA/pF [P7-P9, n=13], and 69.5±3.7 pA/pF [P10-P12, n=13]) in low external [Naâº] condition. Na⺠current recovery was accelerated and inactivation curves shifted to hyperpolarization with age.
CONCLUSION
As regular spiking cells were observed from P7 but never from P3 to P6, P7 might be regarded as an important milestone in the development of auditory cortical layer II/III neurons. This change might mainly result from the increase in Na⺠current density.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ehret G. Development of absolute auditory thresholds in the house mouse (Mus musculus). J Am Audiol Soc. 1976; Mar-Apr. 1(5):179–84.2. Chang EF, Merzenich MM. Environmental noise retards auditory cortical development. Science. 2003; Apr. 300(5618):498–502.
Article3. de Villers-Sidani E, Chang EF, Bao S, Merzenich MM. Critical period window for spectral tuning defined in the primary auditory cortex (A1) in the rat. J Neurosci. 2007; Jan. 27(1):180–9.
Article4. Iwasa H, Potsic WP. Maturational change of early, middle, and late components of the auditory evoked responses in rats. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1982; Jan-Feb. 90(1):95–102.
Article5. Mourek J, Himwich WA, Myslivecek J, Callison DA. The role of nutrition in the development of evoked cortical responses in rat. Brain Res. 1967; Oct. 6(2):241–51.
Article6. Wise SP, Jones EG. Developmental studies of thalamocortical and commissural connections in the rat somatic sensory cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1978; Mar. 178(2):187–208.
Article7. Gillespie DC, Kim G, Kandler K. Inhibitory synapses in the developing auditory system are glutamatergic. Nat Neurosci. 2005; Mar. 8(3):332–8.
Article8. Kim G, Kandler K. Elimination and strengthening of glycinergic/GABAergic connections during tonotopic map formation. Nat Neurosci. 2003; Mar. 6(3):282–90.
Article9. Kungel M, Friauf E. Physiology and pharmacology of native glycine receptors in developing rat auditory brainstem neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1997; Sep. 102(2):157–65.
Article10. Lohrke S, Srinivasan G, Oberhofer M, Doncheva E, Friauf E. Shift from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing glycine action occurs at different perinatal ages in superior olivary complex nuclei. Eur J Neurosci. 2005; Dec. 22(11):2708–22.11. Friauf E, Kandler K. Auditory projections to the inferior colliculus of the rat are present by birth. Neurosci Lett. 1990; Nov. 120(1):58–61.
Article12. Phillips DP, Orman SS, Musicant AD, Wilson GF. Neurons in the cat’s primary auditory cortex distinguished by their responses to tones and wide-spectrum noise. Hear Res. 1985; Apr. 18(1):73–86.
Article13. Pfeiffer RR. Classification of response patterns of spike discharges for units in the cochlear nucleus: tone-burst stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1966; 1(3):220–35.
Article14. Creutzfeldt O, Hellweg FC, Schreiner C. Thalamocortical transformation of responses to complex auditory stimuli. Exp Brain Res. 1980; 39(1):87–104.
Article15. Metherate R, Aramakis VB. Intrinsic electrophysiology of neurons in thalamorecipient layers of developing rat auditory cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999; Jun. 115(2):131–44.
Article16. Oswald AM, Reyes AD. Maturation of intrinsic and synaptic properties of layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons in mouse auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2008; Jun. 99(6):2998–3008.
Article17. Ryugo DK, Killackey HP. Differential telencephalic projections of the medial and ventral divisions of the medial geniculate body of the rat. Brain Res. 1974; Dec. 82(1):173–7.
Article18. Cruikshank SJ, Rose HJ, Metherate R. Auditory thalamocortical synaptic transmission in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 2002; Jan. 87(1):361–84.
Article19. Burgard EC, Hablitz JJ. Developmental changes in NMDA and non-NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic potentials in rat neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 1993; Jan. 69(1):230–40.
Article20. Ramoa AS, McCormick DA. Developmental changes in electrophysiological properties of LGNd neurons during reorganization of retinogeniculate connections. J Neurosci. 1994; Apr. 14(4):2089–97.
Article21. Zhou FM, Hablitz JJ. Postnatal development of membrane properties of layer I neurons in rat neocortex. J Neurosci. 1996; Feb. 16(3):1131–9.
Article22. Huguenard JR, Hamill OP, Prince DA. Developmental changes in Na+ conductances in rat neocortical neurons: appearance of a slowly inactivating component. J Neurophysiol. 1988; Mar. 59(3):778–95.
Article23. McCormick DA, Prince DA. Post-natal development of electrophysiological properties of rat cerebral cortical pyramidal neurones. J Physiol. 1987; Dec. 393:743–62.
Article24. Cummins TR, Xia Y, Haddad GG. Functional properties of rat and human neocortical voltage-sensitive sodium currents. J Neurophysiol. 1994; Mar. 71(3):1052–64.
Article25. Carrascal L, Nieto-Gonzalez JL, Cameron WE, Torres B, Nunez-Abades PA. Changes during the postnatal development in physiological and anatomical characteristics of rat motoneurons studied in vitro. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2005; Sep. 49(2):377–87.
Article26. Matzner O, Devor M. Na+ conductance and the threshold for repetitive neuronal firing. Brain Res. 1992; Nov. 597(1):92–8.
Article27. Tritsch NX, Yi E, Gale JE, Glowatzki E, Bergles DE. The origin of spontaneous activity in the developing auditory system. Nature. 2007; Nov. 450(7166):50–5.
Article28. Clause A, Kim G, Sonntag M, Weisz CJ, Vetter DE, Rubsamen R, et al. The precise temporal pattern of prehearing spontaneous activity is necessary for tonotopic map refinement. Neuron. 2014; May. 82(4):822–35.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Behavioural and Electrophysiological Correlates of Aided Performance in Individuals with Late Onset Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder: A Review
- Developmental changes of gustatory neurons in nucleus of solitary tract in rats
- Expression of tyrosine kinase A in the cerebral cortex of postnatal developing rat
- Immunohistochemical Localization of Phospholipase D1 in Developing Rat Forebrain
- Immunohistochemical Study on the Distribution of Neuropeptide Yand NADPH-Diaphorase Positive Neurons in the Cerebral Cortex of Mice