Korean J Ophthalmol.
2019 Aug;33(4):353-358. 10.3341/kjo.2019.0031.
Long-term Results of Slanted Recession of Bilateral Lateral Rectus Muscle for Intermittent Exotropia with Convergence Insufficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kris9352@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2454776
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2019.0031
Abstract
- PURPOSE
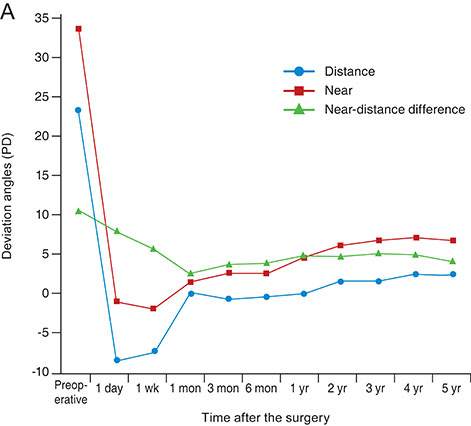
To evaluate the long-term efficacy of slanted lateral rectus recession in children for reducing distance and near exodeviation and near-distance deviation difference in intermittent exotropia with convergence insufficiency.
METHODS
The medical records of 53 patients with convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia who underwent slanted bilateral lateral rectus recession performed by a single surgeon and received follow-up for more than 12 months were retrospectively analyzed. Deviation angles at 1 day, 1 week, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months postoperatively and on the last visit were reviewed. Surgical success was defined as postoperative residual distance and near deviation angles ≤8 prism diopters and a difference between the near and distance angles ≤8 prism diopters.
RESULTS
The mean duration of follow-up was 24 months (range, 12 to 61 months). On the last visit, the residual deviation angles were ≤8 prism diopters in 75.5% for distance, 62.3% for near, and 81.1% for the near-distance difference. Surgical success was achieved in 31 (58.5%) patients, and none of them manifested limitations in eye movements or diplopia at the last follow-up visit.
CONCLUSIONS
Slanted lateral rectus recession is an effective surgical method for reducing distance and near exodeviation and near-distance deviation difference in intermittent exotropia with convergence insufficiency.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burian HM. Exodeviations: their classification, diagnosis and treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966; 62:1161–1166.
Article2. Kushner BJ, Morton GV. Distance/near differences in intermittent exotropia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1998; 116:478–486.
Article3. Snir M, Axer-Siegel R, Shalev B, et al. Slanted lateral rectus recession for exotropia with convergence weakness. Ophthalmology. 1999; 106:992–996.
Article4. Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti: effect of preoperative fusion and distance-near relationship. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975; 93:584–586.5. von Noorden GK. Resection of both medial rectus muscles in organic convergence insufficiency. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 81:223–226.
Article6. Choi MY, Hwang JM. The long-term result of slanted medial rectus resection in exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. Eye (Lond). 2006; 20:1279–1283.
Article7. Choi MY, Hyung SM, Hwang JM. Unilateral recession-resection in children with exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. Eye (Lond). 2007; 21:344–347.
Article8. Choi DG, Rosenbaum AL. Medial rectus resection(s) with adjustable suture for intermittent exotropia of the convergence insufficiency type. J AAPOS. 2001; 5:13–17.
Article9. Wang B, Wang L, Wang Q, Ren M. Comparison of different surgery procedures for convergence insufficiency-type intermittent exotropia in children. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:1409–1413.
Article10. Ma L, Yang L, Li N. Bilateral lateral rectus muscle recession for the convergence insufficiency type of intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 2016; 20:194–196.
Article11. Farid MF, Abdelbaset EA. Surgical outcomes of three different surgical techniques for treatment of convergence insufficiency intermittent exotropia. Eye (Lond). 2018; 32:693–700.
Article12. Haldi BA. Surgical management of convergence insufficiency. Am Orthopt J. 1978; 28:106–109.
Article13. Kushner BJ. Exotropic deviations: a functional classification and approach to treatment. Am Orthopt J. 1988; 38:81–93.
Article14. Scott AB. Strabismus muscle forces and innervation. In : Lenerstrand G, Bach-y-Rita P, editors. Basic mechanism of ocular motility and their clinical implications: proceedings of the International Symposium Held in Wenner-Gren Center, Stockholm, June 4–6, 1974. New York: Pergamon Press;1975. p. 181–191.15. Kraft SP, Levin AV, Enzenauer RW. Unilateral surgery for exotropia with convergence weakness. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1995; 32:183–187.
Article16. Song IJ, Lee SG. The effect of bilateral slanted lateral rectus recession in exotropia with near-far disparity. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:311–315.
Article17. Chun BY, Kang KM. Early results of slanted recession of the lateral rectus muscle for intermittent exotropia with convergence insufficiency. J Ophthalmol. 2015; 2015:380467.
Article18. Kushner BJ. Insertion slanting strabismus surgical procedures. Arch Ophthalmol. 2011; 129:1620–1625.
Article19. Park JS, Lee SJ, Roh YB, Choi HY. Monocular slanted lateral rectus recession for exotropia with convergence insufficiency. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1112–1118.
Article20. Ruttum MS. Initial versus subsequent postoperative motor alignment in intermittent exotropia. J AAPOS. 1997; 1:88–91.
Article21. Raab EL, Parks MM. Recession of the lateral recti. Early and late postoperative alignments. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969; 82:203–208.22. Cho YA, Kim SH. Postoperative minimal overcorrection in the surgical management of intermittent exotropia. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013; 97:866–869.
Article23. Ahn JH, Paik H. Long-term surgical outcomes of initial postoperative overcorrection in adults with intermittent exotropia. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2018; 32:228–233.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison between Down Transposition and Slanted Surgery for Bilateral Lateral Rectus Recession in Convergence Insufficiency-Type Exotropia
- How to Better Treat Patients with Intermittent Exotropia: A Review of Surgical Treatment of Intermittent Exotropia
- Comparison of Surgical Results Between Bilateral Recession and Unilateral Recession-Resection in Intermittent Exotropia
- The Clinical Analysis of Surgical Methods in Intermittent Exotropia
- The Surgical Results of Medial Rectus Muscle Resection of Dominant Eye and Lateral Rectus Muscle Recession of Non-dominant Eye in Intermittent Exotropia