Yonsei Med J.
2012 Sep;53(5):1022-1027.
Spontaneous Reporting of Adverse Drug Reactions through Electronic Submission from Regional Society Healthcare Professionals in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cshong@yuhs.ac
- 2Pharmacovigilance Research Network, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Medical Observer Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Pharmacovigilance Research Network built a spontaneous reporting system and collected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) by electronic submission (e-sub) in Korea. We analyzed ADRs spontaneously reported through e-sub from regional health professionals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Nine hundred and thirty three ADR cases were collected and analyzed from January to December in 2008. "A matter" was defined as one symptom matched to one culprit drug included in an ADR case. We collected and analyzed e-sub ADR cases and matters to determine common culprits and organ specified ADR matters.
RESULTS
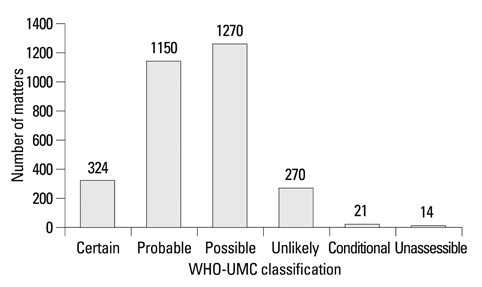
There were 3,049 matters in 933 ADR cases for 1 year, and 3.3 matters per case were reported. In organ specific ADR classification, skin reactions which took the first place in 866 matters (28%) included urticaria and rash. The next cases were neurologic symptom (624 matters, 21%) and gastrointestinal symptom (581 matters, 19%). Doctor (53%) and pharmacist (31%) were the most important participants in e-sub spontaneous reporting system, and 3% of ADR cases were reported by patients or their guardians. WHO-Uppsala Monitoring Center causality assessment results showed certain 10.6%, probable 37.7%, possible 41.7% and below unlikely 10.0%. Culprit drugs were antibiotics (23.4%), neurologic agents (14.7%) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (9.4%).
CONCLUSION
In our study, antibiotic was most common culprit drug, and skin manifestation was most common symptom in e-sub ADRs collected from regional healthcare practitioners in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Einarson TR. Drug-related hospital admissions. Ann Pharmacother. 1993. 27:832–840.
Article2. Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA. 1998. 279:1200–1205.
Article3. Rossi AC, Knapp DE, Anello C, O'Neill RT, Graham CF, Mendelis PS, et al. Discovery of adverse drug reactions. A comparison of selected phase IV studies with spontaneous reporting methods. JAMA. 1983. 249:2226–2228.
Article4. Evans SJ, Waller PC, Davis S. Use of proportional reporting ratios (PRRs) for signal generation from spontaneous adverse drug reaction reports. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2001. 10:483–486.
Article5. Choi NK, Park BJ. [Adverse drug reaction surveillance system in Korea]. J Prev Med Public Health. 2007. 40:278–284.
Article6. Dal Pan GJ. Update on post-marketing drug safety activities at the US FDA. Uppsala Rep. 2008. 40:10–11.7. Jhung MA, Budnitz DS, Mendelsohn AB, Weidenbach KN, Nelson TD, Pollock DA. Evaluation and overview of the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-Cooperative Adverse Drug Event Surveillance Project (NEISS-CADES). Med Care. 2007. 45:10 Suppl 2. S96–S102.
Article8. Olmsted SS, Grabenstein JD, Jain AK, Lurie N. Patient experience with, and use of, an electronic monitoring system to assess vaccination responses. Health Expect. 2006. 9:110–117.
Article9. Edwards IR, Aronson JK. Adverse drug reactions: definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet. 2000. 356:1255–1259.
Article10. Shin YS, Lee YW, Choi YH, Park B, Jee YK, Choi SK, et al. Spontaneous reporting of adverse drug events by Korean regional pharmacovigilance centers. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2009. 18:910–915.
Article11. Jarernsiripornkul N, Kakaew W, Loalukkana W, Krska J. Adverse drug reaction monitoring: comparing doctor and patient reporting for new drugs. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2009. 18:240–245.
Article12. Jose J, Rao PG. Pattern of adverse drug reactions notified by spontaneous reporting in an Indian tertiary care teaching hospital. Pharmacol Res. 2006. 54:226–233.
Article13. Joshua L, Devi PD, Guido S. Adverse drug reactions in nephrology ward inpatients of a tertiary care hospital. Indian J Med Sci. 2007. 61:562–569.
Article14. Okezie EO, Olufunmilayo F. Adverse drug reactions reporting by physicians in Ibadan, Nigeria. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2008. 17:517–522.
Article15. van Hunsel F, Passier A, van Grootheest K. Comparing patients' and healthcare professionals' ADR reports after media attention: the broadcast of a Dutch television programme about the benefits and risks of statins as an example. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009. 67:558–564.
Article16. Sun YQ, Ma YG, Xing XY, Xiao XH. [Probing into objectivity of adverse drug reaction of traditional Chinese medicine]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006. 31:1381–1383.17. Zhang L, Yang XH, Cao LY, Ji S. [Current status and development of monitoring on adverse reaction of traditional Chinese medicine in China]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2005. 25:581–584.18. Wright A, Zignol M, Van Deun A, Falzon D, Gerdes SR, Feldman K, et al. Epidemiology of antituberculosis drug resistance 2002-07: an updated analysis of the Global Project on Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Resistance Surveillance. Lancet. 2009. 373:1861–1873.
Article19. Suh SI, Kim HJ, Park EC, Sohn M, Kim DK. The comparison of computerized tomography utilization between before and after coverage of medical insurance. Korean J Hosp Manage. 1997. 2:121–133.20. Kim YJ, Jung SY, Choi NK, Kim HJ, Kim JY, Chang Y, et al. Benzodiazepine prescription patterns for the elderly patients at ambulatory care in Korea. J Pharmacoepidemiol Risk Manag. 2008. 1:60–67.21. Curtis LH, Østbye T, Sendersky V, Hutchison S, Dans PE, Wright A, et al. Inappropriate prescribing for elderly Americans in a large outpatient population. Arch Intern Med. 2004. 164:1621–1625.
Article22. Tamblyn R, Abrahamowicz M, du Berger R, McLeod P, Bartlett G. A 5-year prospective assessment of the risk associated with individual benzodiazepines and doses in new elderly users. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2005. 53:233–241.
Article23. Hunziker T, Künzi UP, Braunschweig S, Zehnder D, Hoigné R. Comprehensive hospital drug monitoring (CHDM): adverse skin reactions, a 20-year survey. Allergy. 1997. 52:388–393.
Article24. Ufer M, Kimland E, Bergman U. Adverse drug reactions and off-label prescribing for paediatric outpatients: a one-year survey of spontaneous reports in Sweden. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2004. 13:147–152.
Article25. Lopez-Gonzalez E, Herdeiro MT, Figueiras A. Determinants of under-reporting of adverse drug reactions: a systematic review. Drug Saf. 2009. 32:19–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Educating Healthcare Professionals in Pharmacovigilance: Global Trends and Korea’s Status
- Fentanyl PCA Monotherapy and Fentanyl TTS Combination Therapy in Post-Operative Pain Management: Analyses of Spontaneous Adverse Drug Reaction Reports
- Past, present, and future of pharmacovigilance in Korea
- Adverse Drug Reactions in Adult Patients Visiting an Emergency Department: Based on Spontaneous Reporting System
- Active Participation in Reporting Adverse Drug Reactions