Korean J Orthod.
2019 Jul;49(4):214-221. 10.4041/kjod.2019.49.4.214.
Effects of reversing the coiling direction on the force-deflection characteristics of nickel-titanium closed-coil springs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. drwhite@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Mechanical System Engineering, Hansung University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Future Convergence Research Division, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Materials Science & Engineering, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. jhhan@cnu.ac.kr
- 5Dental Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2453058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2019.49.4.214
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the effects of reversing the coiling direction of nickeltitanium closed-coil springs (NiTi-CCSs) on the force-deflection characteristics.
METHODS
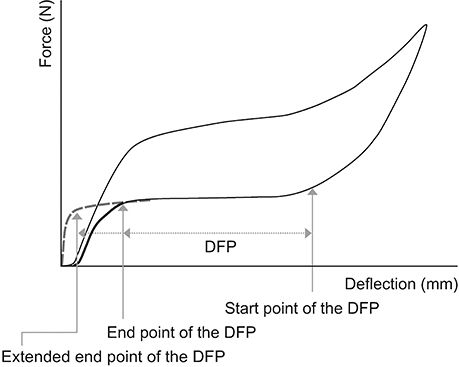
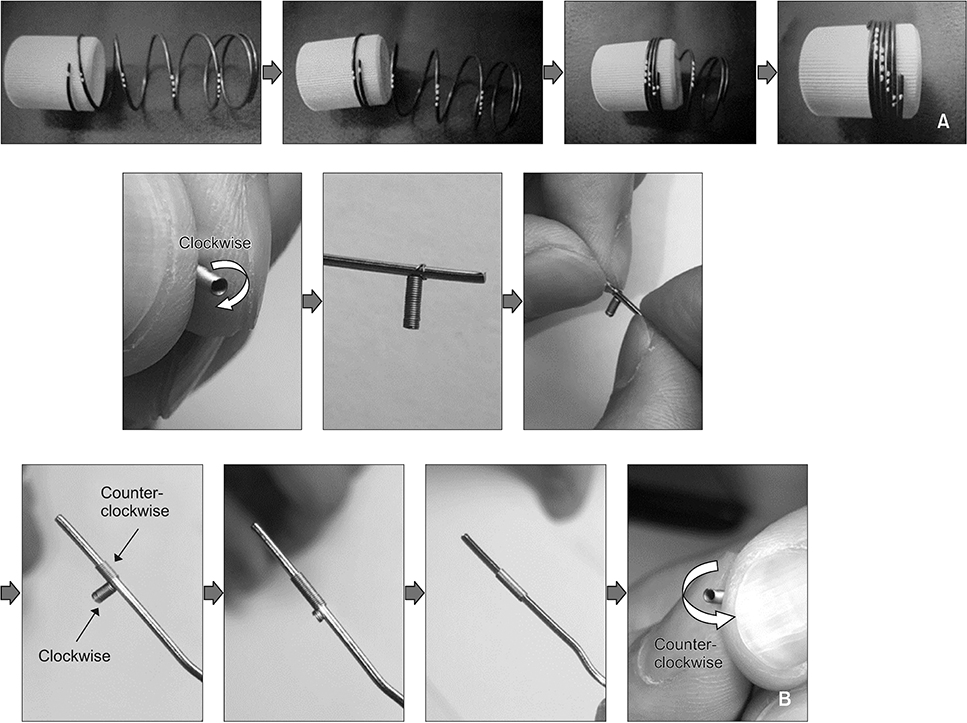
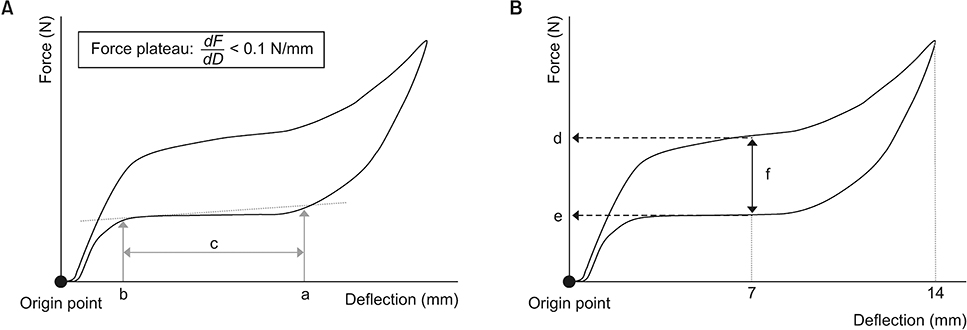
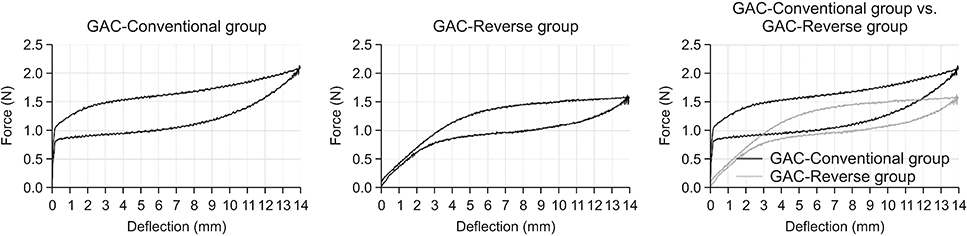
The samples consisted of two commercially available conventional NiTi-CCS groups and two reverse-wound NiTi-CCS groups (Ormco-Conventional vs. Ormco-Reverse; GAC-Conventional vs. GAC-Reverse; n = 20 per group). The reverse-wound NiTi-CCSs were directly made from the corresponding conventional NiTi-CCSs by reversing the coiling direction. Tensile tests were performed for each group in a temperature-controlled acrylic chamber (37 ± 1℃). After measuring the force level, the range of the deactivation force plateau (DFP) and the amount of mechanical hysteresis (MH), statistical analyses were performed.
RESULTS
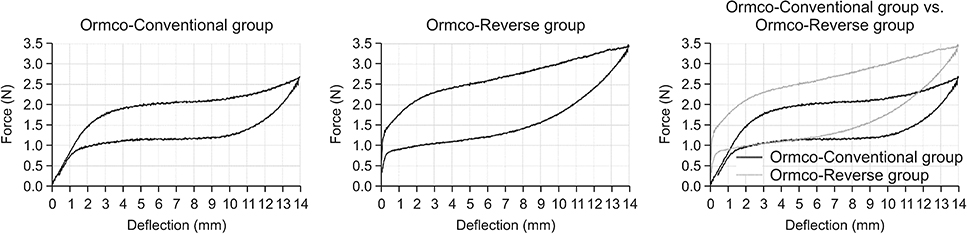
The Ormco-Reverse group exhibited a significant shift of the DFP end point toward the origin point (2.3 to 0.6 mm), an increase in the force level (1.2 to 1.3 N) and amount of MH (1.0 to 1.5 N) compared to the Ormco-Conventional group (all p < 0.001), which indicated that force could be constantly maintained until the end of the deactivation curve. In contrast, the GAC-Reverse group exhibited a significant shift of the DFP-end point away from the origin point (0.2 to 3.3 mm), a decrease in the force level (1.1 to 0.9 N) and amount of MH (0.6 to 0.4 N) compared to the GAC-Conventional group (all p < 0.001), which may hinder the maintenance of force until the end of the deactivation curve.
CONCLUSIONS
The two commercially available NiTi-CCS groups exhibited different patterns of change in the force-deflection characteristics when the coiling direction was reversed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wichelhaus A, Brauchli L, Ball J, Mertmann M. Mechanical behavior and clinical application of nickel-titanium closed-coil springs under different stress levels and mechanical loading cycles. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010; 137:671–678.
Article2. Bezrouk A, Balsky L, Smutny M, Selke Krulichova I, Zahora J, Hanus J, et al. Thermomechanical properties of nickel-titanium closed-coil springs and their implications for clinical practice. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014; 146:319–327.
Article3. Burstone CJ, Qin B, Morton JY. Chinese NiTi wire--a new orthodontic alloy. Am J Orthod. 1985; 87:445–452.
Article4. Miura F, Mogi M, Ohura Y, Hamanaka H. The superelastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1986; 90:1–10.
Article5. Miura F, Mogi M, Ohura Y, Karibe M. The super-elastic Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Part III. Studies on the Japanese NiTi alloy coil springs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988; 94:89–96.
Article6. Maganzini AL, Wong AM, Ahmed MK. Forces of various nickel titanium closed coil springs. Angle Orthod. 2010; 80:182–187.
Article7. Manhartsberger C, Seidenbusch W. Force delivery of Ni-Ti coil springs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996; 109:8–21.
Article8. Ravipati RR, Sivakumar A, Sudhakar P, Padmapriya CV, Bhaskar M, Azharuddin M. An adjustment in NiTi closed coil spring for an extended range of activation. Int J Orthod Milwaukee. 2014; 25:21–22.9. Vidoni G, Perinetti G, Antoniolli F, Castaldo A, Contardo L. Combined aging effects of strain and thermocycling on unload deflection modes of nickel-titanium closed-coil springs: an in-vitro comparative study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010; 138:451–457.
Article10. Alavi S, Haerian A. The effects of aging process and preactivation on mechanical properties of nickel-titanium closed coil springs. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2015; 12:231–234.11. Segner D, Ibe D. Properties of superelastic wires and their relevance to orthodontic treatment. Eur J Orthod. 1995; 17:395–402.
Article12. Bartzela TN, Senn C, Wichelhaus A. Load-deflection characteristics of superelastic nickel-titanium wires. Angle Orthod. 2007; 77:991–998.
Article13. Jee KK, Kim YB, Han JH. inventor; Korea Institute of Science and Technology, assignee. Method to provide initial tension for coil spring and its application. United States Patent US 8,186,060. 2012. 05. 29.14. Jee KK, Han JH, Jang WY. Improvement of actuating properties of a SMA coil spring by change in coil orientation. Mater Sci Forum. 2013; 738-739:589–594.
Article15. Santoro M, Nicolay OF, Cangialosi TJ. Pseudoelasticity and thermoelasticity of nickel-titanium alloys: a clinically oriented review. Part I: temperature transitional ranges. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2001; 119:587–593.
Article16. Vieira CI, Caldas SG, Martins LP, Martins RP. Superelasticity and force plateau of nickel-titanium springs: an in vitro study. Dental Press J Orthod. 2016; 21:46–55.
Article17. Martins RP, Buschang PH, Gandini LG Jr. Group A T-loop for differential moment mechanics: an implant study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009; 135:182–189.
Article18. von Fraunhofer JA, Bonds PW, Johnson BE. Force generation by orthodontic coil springs. Angle Orthod. 1993; 63:145–148.19. Tripolt H, Burstone CJ, Bantleon P, Manschiebel W. Force characteristics of nickel-titanium tension coil springs. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999; 115:498–507.
Article20. Vieira CIV, Reis JMDSN, Vaz LG, Martins LP, Martins RP. Deformation of nickel-titanium closed coil springs: an in vitro study. Dental Press J Orthod. 2017; 22:38–46.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Load-deflection characteristics and plastic deformation of NiTi closed coil springs
- Effects of heat treatment on the load-deflection properties of nickel-titanium wire
- The effect of temperature changes on force level of superelastic nickel-titanium archwires
- Three point bending test of recycled Nickel-Titanium alloy wires
- Effects of continuous force application for extrusive tipping movement on periapical root resorption in the rat mandibular first molar