Perinatology.
2019 Jun;30(2):105-109. 10.14734/PN.2019.30.2.105.
Obstetrical Vacuum Extraction for Ping-Pong Fracture of Newborn
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. psimy81@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2453046
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/PN.2019.30.2.105
Abstract
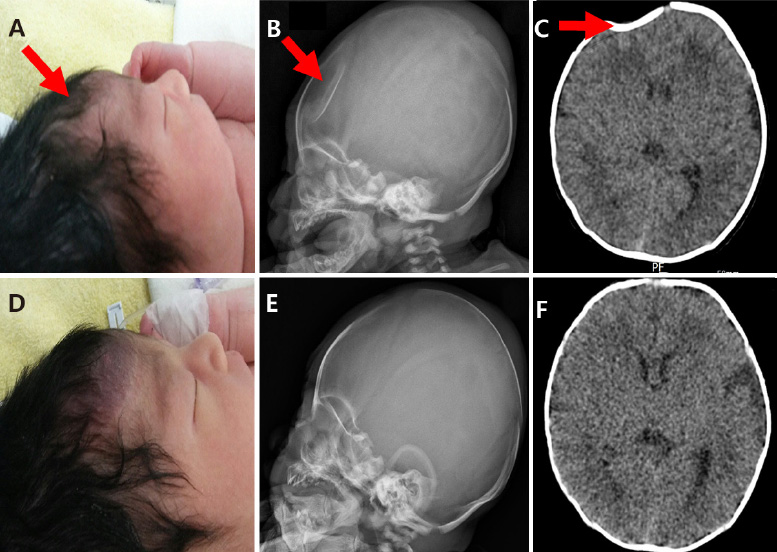
- Depressed skull fracture is an inward buckling of the skull bones. It is referred to as a ping-pong fracture in neonates. It is usually not associated with significant neurological injury. However cosmetic concerns persist. Obstetrical vacuum extractor is a less invasive procedure than other treatment modalities. The vacuum extraction is especially warranted for the obstetricians, because the ping-pong fractures are mainly found immediately after birth. We describe cases of ping-pong fracture successfully treated by obstetrical vacuum extractor with review of literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ben-Ari Y, Merlob P, Hirsch M, Reisner SH. Congenital depression of the neonatal skull. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1986; 22:249–255.
Article2. Zalatimo O, Ranasinghe M, Dias M, Iantosca M. Treatment of depressed skull fractures in neonates using percutaneous microscrew elevation. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012; 9:676–679.
Article3. Sorar M, Fesli R, Gürer B, Kertmen H, Sekerci Z. Spontaneous elevation of a ping-pong fracture: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2012; 48:324–326.
Article4. Preston D, Jackson S, Gandhi S. Non-traumatic depressed skull fracture in a neonate or 'ping pong' fracture. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015:pii: bcr2014207077.
Article5. Heise RH, Srivatsa PJ, Karsell PR. Spontaneous intrauterine linear skull fracture: a rare complication of spontaneous vaginal delivery. Obstet Gynecol. 1996; 87:851–854.6. Paul MA, Fahner T. Closed depressed skull fracture in childhood reduced with suction cup method: case report. J Trauma. 1991; 31:1551–1552.7. Jennett B, Miller JD, Braakman R. Epilepsy after monmissile depressed skull fracture. J Neurosurg. 1974; 41:208–216.8. Tysvaer A, Nysted A. Depression fractures of the skull in newborn infants. Treatment with vacuum extractor. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1994; 114:3315–3316.9. Chugh A, Dang RS, Mamgain A, Husain M, Ojha BK, Rastogi M, et al. Cerebral edema spontaneously elevating a compound depressed fracture. Case illustration. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2008; 1:172.10. Raynor R, Parsa M. Nonsurgical elevation of depressed skull facture in an infant. J Pediatr. 1968; 72:262–264.11. Hung KL, Liao HT, Huang JS. Rational management of simple depressed skull fractures in infants. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:69–72.
Article12. Kim YJ, Lee SK, Cho MK, Kim YJ. Elevation of depressed skull fracture with a cup of breast pump and a suction generator: a case report in technical aspects. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2007; 42:346–348.13. Beyers N, Moosa A, Bryce RL, Kent A. Depressed skull fracture in the newborn. A report of 3 cases. S Afr Med J. 1978; 54:830–832.14. Van Enk A. Reduction of pond fracture. Br Med J. 1972; 2:353.
Article15. Miksovsky P, Watson WJ. Obstetric vacuum extraction: state of the art in the new millennium. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2001; 56:736–751.16. Plauché WC. Fetal cranial injuries related to delivery with the Malmström vacuum extractor. Obstet Gynecol. 1979; 53:750–757.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stroke Patients: Effects of Combining Sitting Table Tennis Exercise with Neurological Physical Therapy on Brain Waves
- Vacuum extraction vaginal delivery: current trend and safety
- Clinical Study on Newborn Infants Born by Vacuum Extraction
- A case of scalp abscess caused by Achromobacter xylosoxidans after vacuum delivery
- Clavicle Fracture during Delivery