Yonsei Med J.
2019 Aug;60(8):782-790. 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.8.782.
Explantation of Adjustable Gastric Bands: An Observation Study of 10 Years of Experience at a Tertiary Center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. seongmin_kim@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2452960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2019.60.8.782
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although laparoscopic adjustable gastric bands are considered a standard treatment for severe obesity, their use remains controversial. We evaluated rates of band explantation and the incidences of complications leading to and following band explantation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective review was performed on patients that underwent adjustable gastric band explantation. For each of the three groups of patients that underwent explantation, we compared demographic and anthropometric data, band duration in situ, operative approach, and morbidities.
RESULTS
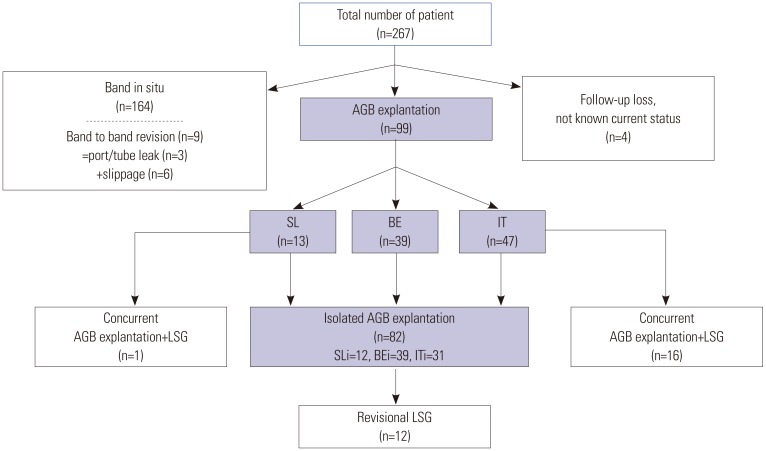
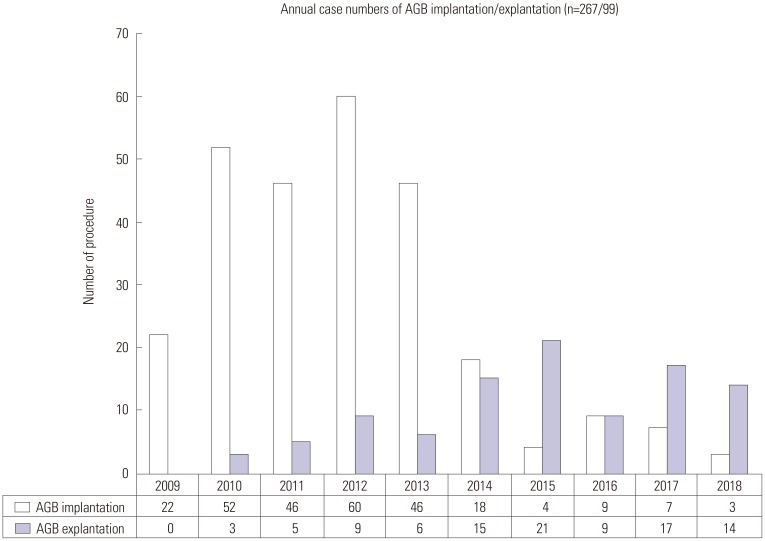
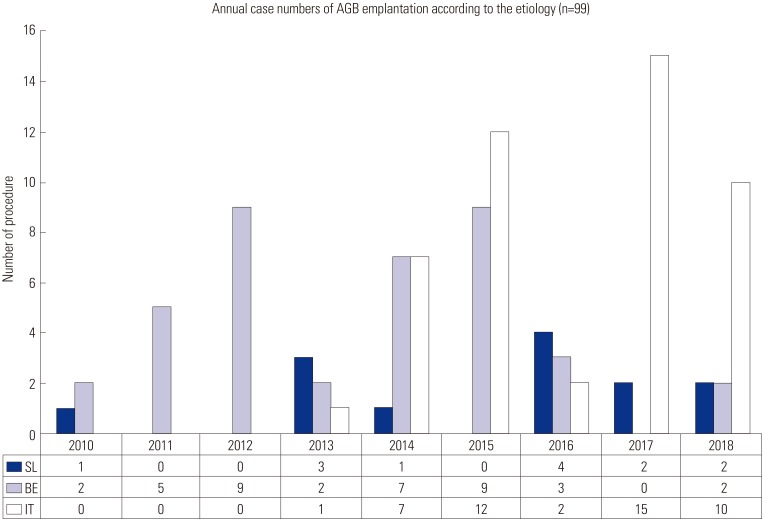
Between January 2009 and October 2018, a total of 267 patients underwent primary laparoscopic adjustable gastric band surgery. Of these 267 patients, 99 (37.1%) underwent band explantation. Numbers (%) of patients in the slippage (SL), band erosion (BE), and intolerance (IT) groups were 13 (13.1%), 39 (39.4), and 47 (47.5%), respectively. Mean %EBMIL values at explantation in these groups were 74.6±45.5, 79.7±40.3, and 36.1±46.0, respectively (p<0.001), and mean times for maintaining bands in situ were 45.1±28.0, 39.4±24.3, and 51.2±22.7 months, respectively. Isolated band removal was performed for slippage (SLi, n=12), band erosion (BEi, n=39), and intolerance (ITi, n=31). The numbers (%) of patients in the SLi, BEi, and ITi groups that experienced a surgical complication (Clavien-Dindo class ≥1) were 0 (0.0%), 24 (61.5%), and 3 (9.7%), respectively (p<0.001). In the BEi group, four patients (4/39, 10.3%) underwent reoperation after AGB removal.
CONCLUSION
During our 10 years of experience, 37.1% of adjustable gastric band had to be removed. Intra-abdominal abscess and intragastric bleeding were rare but serious complications after explantation. Potential candidates for adjustable gastric band should be informed of the high long-term risk of band explantation and its associated morbidities.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Seo MH, Lee WY, Kim SS, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim KK, et al. 2018 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity Guideline for the Management of Obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:40–45. PMID: 31089578.
Article2. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC). Health promotion statistics year book [Internet]. Cheongju: KCDC;c2017. accessed on 2018 November 1. Available at: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub01/sub01_05_02.jsp#s5_01_10.3. Khorgami Z, Shoar S, Andalib A, Aminian A, Brethauer SA, Schauer PR. Trends in utilization of bariatric surgery, 2010–2014: sleeve gastrectomy dominates. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017; 13:774–778. PMID: 28256393.
Article4. Carandina S, Tabbara M, Galiay L, Polliand C, Azoulay D, Barrat C, et al. Long-term outcomes of the laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: weight loss and removal rate. A single center experience on 301 patients with a minimum follow-up of 10 years. Obes Surg. 2017; 27:889–895. PMID: 27699566.5. Froylich D, Abramovich-Segal T, Pascal G, Haskins I, Appel B, Kafri N, et al. Long-term (over 10 years) retrospective follow-up of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2018; 28:976–980. PMID: 29159551.6. Arapis K, Tammaro P, Parenti LR, Pelletier AL, Chosidow D, Kousouri M, et al. Long-term results after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for morbid obesity: 18-year follow-up in a single university unit. Obes Surg. 2017; 27:630–640. PMID: 27448233.
Article7. Kowalewski PK, Olszewski R, Kwiatkowski A, Gałązka-Świderek N, Cichon´ K, Pas´nik K. Life with a gastric band. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding-a retrospective study. Obes Surg. 2017; 27:1250–1253. PMID: 27787760.
Article8. Toolabi K, Golzarand M, Farid R. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: efficacy and consequences over a 13-year period. Am J Surg. 2016; 212:62–68. PMID: 26303882.
Article9. Trujillo MR, Muller D, Widmer JD, Warschkow R, Muller MK. Long-term follow-up of gastric banding 10 years and beyond. Obes Surg. 2016; 26:581–587. PMID: 26202418.10. Himpens J, Cadière GB, Bazi M, Vouche M, Cadière B, Dapri G. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Arch Surg. 2011; 146:802–807. PMID: 21422330.
Article11. O'Brien PE, MacDonald L, Anderson M, Brennan L, Brown WA. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: fifteen-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg. 2013; 257:87–94. PMID: 23235396.12. Fielding GA, Allen JW. A step-by-step guide to placement of the LAP-BAND adjustable gastric banding system. Am J Surg. 2002; 184(6B):26S–30S. PMID: 12527347.
Article13. Ponce J, Paynter S, Fromm R. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: 1,014 consecutive cases. J Am Coll Surg. 2005; 201:529–535. PMID: 16183490.
Article14. Lee WK, Kim SM. Three-year experience of pouch dilatation and slippage management after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Yonsei Med J. 2014; 55:149–156. PMID: 24339300.
Article15. Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999; 45:172–180. PMID: 10403727.
Article16. Nocca D, Frering V, Gallix B, de Seguin des Hons C, Noël P, Foulonge MA, et al. Migration of adjustable gastric banding from a cohort study of 4236 patients. Surg Endosc. 2005; 19:947–950. PMID: 15920690.
Article17. Yoon CI, Pak KH, Kim SM. Early experience with diagnosis and management of eroded gastric bands. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:18–27. PMID: 22324042.
Article18. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:205–213. PMID: 15273542.19. Koh CY, Inaba CS, Sujatha-Bhaskar S, Hohmann S, Ponce J, Nguyen NT. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric band explantation and implantation at academic centers. J Am Coll Surg. 2017; 225:532–537. PMID: 28754410.
Article20. Altieri MS, Yang J, Telem DA, Meng Z, Frenkel C, Halbert C, et al. Lap band outcomes from 19,221 patients across centers and over a decade within the state of New York. Surg Endosc. 2016; 30:1725–1732. PMID: 26201412.
Article21. Jackson TD, Saleh F, Quereshy FA, Sockalingam S, Urbach D, Okrainec A. Short-term morbidity associated with removal and revision of the laparoscopic adjustable gastric band. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2014; 10:1110–1115. PMID: 24913589.
Article22. Nguyen NT, Nguyen B, Gebhart A, Hohmann S. Changes in the makeup of bariatric surgery: a national increase in use of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013; 216:252–257. PMID: 23177371.
Article23. Ohta M, Seki Y, Wong SK, Wang C, Huang CK, Aly A, et al. Bariatric/metabolic surgery in the Asia-Pacific region: APMBSS 2018 survey. Obes Surg. 2019; 29:534–541. PMID: 30306499.
Article24. O'Brien PE, Dixon JB, Laurie C, Anderson M. A prospective randomized trial of placement of the laparoscopic adjustable gastric band: comparison of the perigastric and pars flaccida pathways. Obes Surg. 2005; 15:820–826. PMID: 15978154.25. Basa NR, Dutson E, Lewis C, Derezin M, Han S, Mehran A. Laparoscopic transgastric removal of eroded adjustable band: a novel approach. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008; 4:194–197. PMID: 18359458.
Article26. Regusci L, Groebli Y, Meyer JL, Walder J, Margalith D, Schneider R. Gastroscopic removal of an adjustable gastric band after partial intragastric migration. Obes Surg. 2003; 13:281–284. PMID: 12740139.
Article27. Weiss H, Nehoda H, Labeck B, Peer R, Aigner F. Gastroscopic band removal after intragastric migration of adjustable gastric band: a new minimal invasive technique. Obes Surg. 2000; 10:167–170. PMID: 10782179.
Article28. Neto MP, Ramos AC, Campos JM, Murakami AH, Falcão M, Moura EH, et al. Endoscopic removal of eroded adjustable gastric band: lessons learned after 5 years and 78 cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010; 6:423–427. PMID: 19926530.
Article29. Campos JM, Evangelista LF, Neto MP, Pagnossin G, Fernandes A, Ferraz AA, et al. Translumenal endoscopic drainage of abdominal abscess due to early migration of adjustable gastric band. Obes Surg. 2010; 20:247–250. PMID: 19727979.
Article30. Png KS, Rao J, Lim KH, Chia KH. Lap-band causing left gastric artery erosion presenting with torrential hemorrhage. Obes Surg. 2008; 18:1050–1052. PMID: 18392902.
Article31. O'Brien PE, Hindle A, Brennan L, Skinner S, Burton P, Smith A, et al. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of weight loss at 10 or more years for all bariatric procedures and a single-centre review of 20-year outcomes after adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2019; 29:3–14. PMID: 30293134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Snakeskin Appearance of Gastric Mucosa Compressed by Adjustable Gastric Bands: A Novel Diagnostic Marker of Band Migration
- Appropriate Time for Gastric Band Removal
- Pulmonary aspiration during anesthetic induction in a patient with laparoscopic adjustable gastric band: A case report
- Spontaneous Unbuckling of the Adjustable Gastric Band; A Rare Complication
- Band Slippage after Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)