Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2019 Jun;24(2):137-141. 10.6065/apem.2019.24.2.137.
A case of vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A caused by 2 novel pathogenic variants in CYP27B1 gene
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. kimjk@cu.ac.kr
- 2Green Cross Genome, Yongin, Korea.
- KMID: 2452092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2019.24.2.137
Abstract
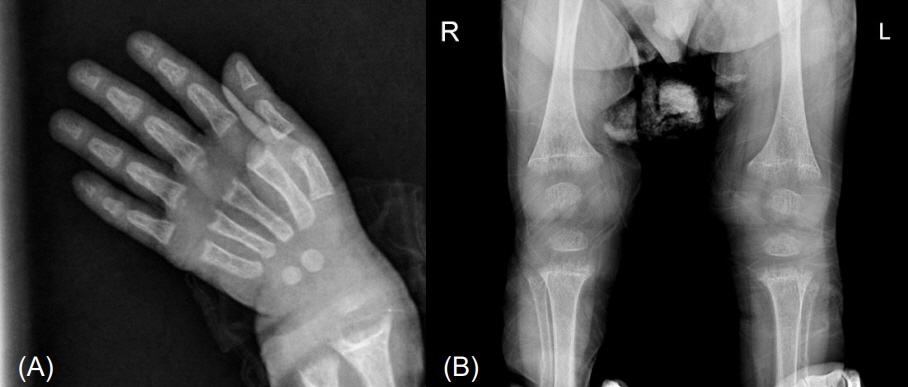
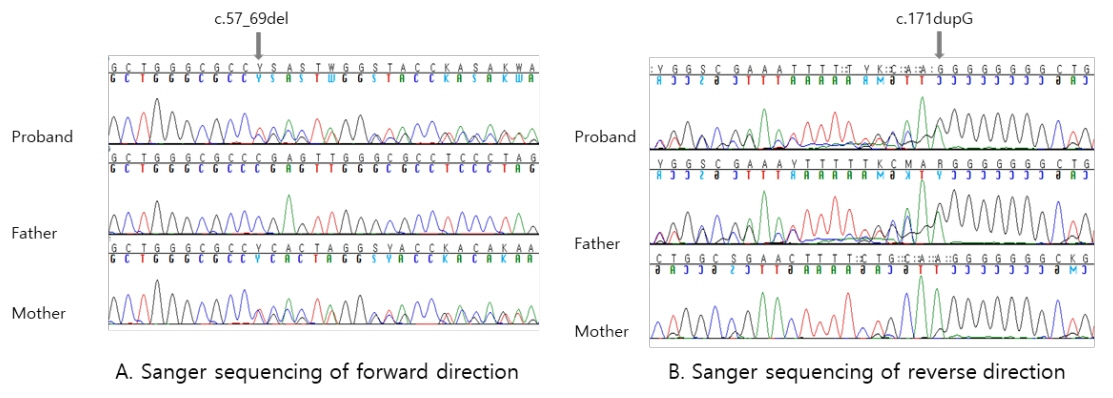
- Vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A (VDDR1A, OMIM 264700) is a rare autosomal recessive inherited disorder. Pathogenic variants in the CYP27B1 gene lead to loss of 1α-hydroxylase activity. We report the case of a 22-month-old toddler who presented with growth retardation and delayed development. The patient exhibited the typical laboratory findings of VDDR1A, including hypocalcemia (calcium: 5.2 mg/dL), elevated serum level of alkaline phosphatase (2,600 U/L), elevated serum level of intact-parathyroid hormone (238 pg/mL), low 1,25(OH)₂D₃ level (11.2 pg/mL), and normal 25(OH)D₃ level (40.7 ng/mL). His height and weight were 76.5 cm and 9.5 kg, respectively (both <3rd percentile). The Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development II indicated significantly delayed development (mental development index <50, psychomotor development index <50). The patient was a compound heterozygous for two novel pathogenic variants in the CYP27B1 gene: c.57_69del (p.Glu20Profs*2) and c.171dupG (p.Leu58Alafs*275), inherited from his mother and father, respectively. The patient showed remarkable improvement after treatment with calcitriol and calcium carbonate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Elder CJ, Bishop NJ. Rickets. Lancet. 2014; 383:1665–76.
Article2. Miller WL. Genetic disorders of Vitamin D biosynthesis and degradation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017; 165(Pt A):101–8.
Article3. Fu GK, Lin D, Zhang MY, Bikle DD, Shackleton CH, Miller WL, et al. Cloning of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha-hydroxylase and mutations causing vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. Mol Endocrinol. 1997; 11:1961–70.4. Fu GK, Portale AA, Miller WL. Complete structure of the human gene for the vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase, P450c1alpha. DNA Cell Biol. 1997; 16:1499–507.5. St-Arnaud R, Messerlian S, Moir JM, Omdahl JL, Glorieux FH. The 25-hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase gene maps to the pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets (PDDR) disease locus. J Bone Miner Res. 1997; 12:1552–9.
Article6. Kitanaka S, Takeyama K, Murayama A, Sato T, Okumura K, Nogami M, et al. Inactivating mutations in the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase gene in patients with pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:653–61.
Article7. Creo AL, Thacher TD, Pettifor JM, Strand MA, Fischer PR. Nutritional rickets around the world: an update. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2017; 37:84–98.
Article8. De Braekeleer M, Larochelle J. Population genetics of vitamin D-dependent rickets in northeastern Quebec. Ann Hum Genet. 1991; 55:283–90.
Article9. Wang JT, Lin CJ, Burridge SM, Fu GK, Labuda M, Portale AA. Genetics of vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency in 17 families. Am J Hum Genet. 1998; 63:1694–702.10. Kim CJ, Kaplan LE, Perwad F, Huang N, Sharma A, Choi Y, et al. Vitamin D 1alpha-hydroxylase gene mutations in patients with 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:3177–82.11. Cho JH, Kang E, Kim GH, Lee BH, Choi JH, Yoo HW. Long-term clinical outcome and the identification of homozygous CYP27B1 gene mutations in a patient with vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2016; 21:169–73.12. Durmaz E, Zou M, Al-Rijjal RA, Bircan I, Akçurin S, Meyer B, et al. Clinical and genetic analysis of patients with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1A. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2012; 77:363–9.13. Tahir S, Demirbilek H, Ozbek MN, Baran RT, Tanriverdi S, Hussain K. Genotype and phenotype characteristics in 22 patients with vitamin D-dependent rickets type I. Horm Res Paediatr. 2016; 85:309–17.14. Acar S, Demir K, Shi Y. Genetic causes of rickets. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017; 9(Suppl 2):88–105.15. Wang X, Zhang MY, Miller WL, Portale AA. Novel gene mutations in patients with 1alpha-hydroxylase deficiency that confer partial enzyme activity in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:2424–30.16. Giannakopoulos A, Efthymiadou A, Chrysis D. A case of vitamin-D-dependent rickets type 1A with normal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D caused by two novel mutations of the CYP27B1 gene. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017; 87:58–63.17. Alzahrani AS, Zou M, Baitei EY, Alshaikh OM, Al-Rijjal RA, Meyer BF, et al. A novel G102E mutation of CYP27B1 in a large family with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:4176–83.18. Edouard T, Alos N, Chabot G, Roughley P, Glorieux FH, Rauch F. Short- and long-term outcome of patients with pseudo-vitamin D deficiency rickets treated with calcitriol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96:82–9.19. Baştuğ F, Gündüz Z, Tülpar S, Poyrazoğlu H, Düşünsel R. Urolithiasis in infants: evaluation of risk factors. World J Urol. 2013; 31:1117–22.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term clinical outcome and the identification of homozygous CYP27B1 gene mutations in a patient with vitamin D hydroxylation-deficient rickets type 1A
- Vitamin D Dependent Rickets Type 1A Caused by CYP27B1 Mutation
- Vitamin D Deficiency Rickets
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy in a 2 Month-Old Infant: A Severe Form of Hypocalcemia With Vitamin D Deficient Rickets
- A Clinical Experience of Fractures in Rickets