J Bacteriol Virol.
2018 Dec;48(4):166-174. 10.4167/jbv.2018.48.4.166.
The Comparison of Clinical Characteristics in Three Types of Viral Acute Diarrhea in Infants and Toddlers and the Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus on Rotaviral Diarrhea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Hallym University Medical Center, Gyeonggi-do, Korea.
- 2College of Pharmacy, Duksung Women's University, Seoul, Korea. hsshin@duksung.ac.kr
- KMID: 2452069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2018.48.4.166
Abstract
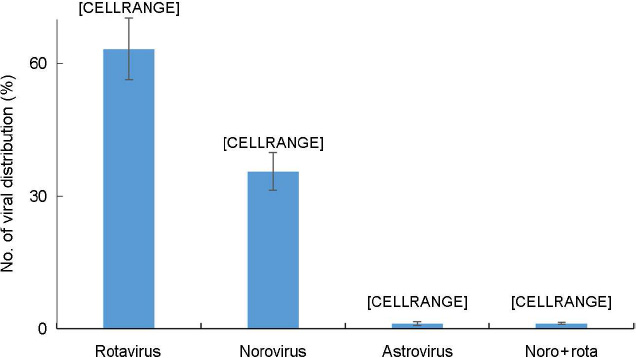
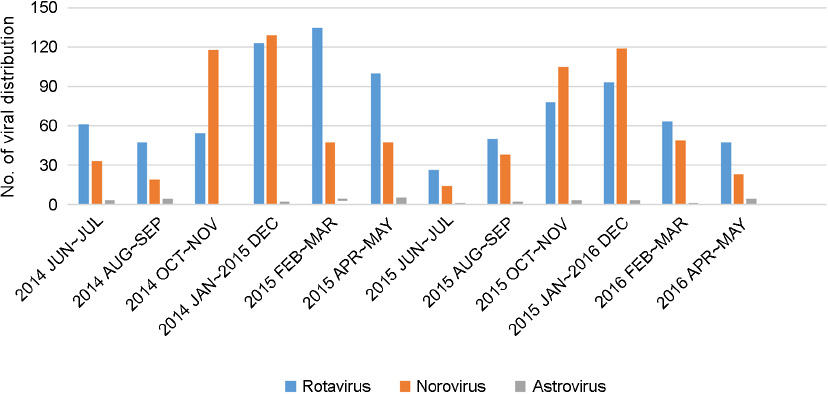
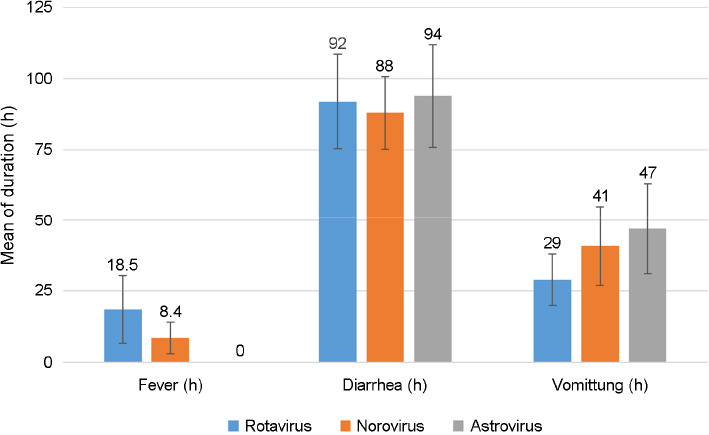
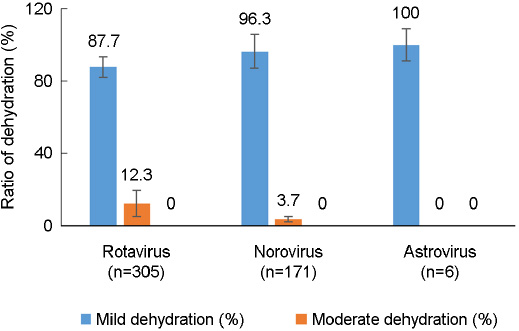
- The most common causes of acute viral diarrhea in infants and toddlers are rotavirus, astrovirus and norovirus. The purpose of this study was to evaluate epidemiological data of pathogens obtained from stool exams and compare them with the clinical course in pediatric patients with symptoms of viral acute diarrhea and to investigate the clinical efficacy of Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus) for acute diarrhea caused by rotavirus. Clinical data for three types of viral acute diarrhea were compared with the viral detection results by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Viruses were detected in 65.8% of subjects, with rotavirus being the most commonly reported in 63.3% of subjects. To examine the characteristics of each virus, a clinical epidemiological study was performed for 482 cases. Noroviral infection symptoms included vomiting and diarrhea in patients of all age groups. Dehydration in noroviral acute diarrheal patients was less common than in rotaviral acute diarrheal patients. The clinical efficacy of orally administered L. acidophilus in the treatment of acute viral diarrhea in infants and toddlers was also evaluated. L. acidophilus was a probiotic adjuvant in viral acute diarrhea in infants and toddlers.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vandenplas Y, Alturaiki MA, Al-Qabandi W, AlRefaee F, Bassil Z, Eid B, et al. Middle East consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of functional gastrointestinal disorders in <12 months old infants. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2016; 19:291–292.
Article2. Oh SA, Park SH, Ham HJ, Seung HJ, Jang JI, Suh SW, et al. Molecular characterization of norovirus and rotavirus in outbreak of acute gastroenteritis in Seoul. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:307–316.
Article3. Baek IH, Kim SA, Kim JH, Park HK, Kim W. A metaviromic analysis of viral communities in the feces of unexplained acute gastroenteritis. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:290–296.
Article4. Park SE, Kim KH, Kim JH, Shin SH, Oh SH, Lee HJ, et al. Rotavirus vaccine. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:803–810.5. Lin JS, Chiu YH, Lin NT, Chu CH, Huang KC, Liao KW, et al. Different effects of probiotic species/strains on infections in preschool children: a double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Vaccine. 2009; 27:1073–1079.
Article6. Hojsak I. Probiotics in children: what is the evidence? Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2017; 20:139–146.
Article7. Gutierrez-Castrellon P, Lopez-Velazquez G, Diaz-Garcia L, Jimenez-Gutierrez C, Mancilla-Ramirez J, Estevez-Jimenez J, et al. Diarrhea in preschool children and Lactobacillus reuteri : A randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2014; 133:e904–e909.8. Chmielewska A, Ruszczynski M, Szajewska H. Lactobacillus reuteri strain ATCC 55730 for the treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in children: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pediatria Wspolczesna. 2008; 10:32–36.9. Ham H, Oh S, Jo S, Choi S. Antigen distributions of rotavirus and adenovirus detected by Enzyme Immuno Assay (EIA) from acute gastroenteritis patients in Seoul. J Bacteriol Virol. 2014; 44:108–111.
Article10. Teran CG, Teran-Escalera CN, Villarroel P. Nitazoxanide vs. probiotics for the treatment of acute rotavirus diarrhea in children: A randomized, single-blind, controlled trial in Bolivian children. Int J Infect Dis. 2009; 13:518–523.
Article11. Lee JI, Park SH, Kim MS, Oh YH, Yu IS, Choi BH, et al. Surveillance of acute gastroenteritis in Seoul, Korea, during May 2004 and June 2007. J Bacteriol Virol. 2009; 39:363–371.
Article12. Hwang PJ, Kwak JH, Lee TJ, Jeong SJ. Clinical features of acute noroviral gastroenteritis in children: comparison with rotaviral gastroenteritis. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:453–457.
Article13. Im IJ, Lee MJ, Chung EH, Yu J, Chang YP, Park WS, et al. Etiology and clinical manifestation of acute gastroenteritis in children. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2006; 13:147–154.
Article14. Moon SK, Lee JI, Yoon HS, Ahn YM. Isolation rate of 4 type virus of acute gastroenteritis in full-term neonates during neonatal period. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:855–861.
Article15. Maulen-Radovan I, Gutierrez-Castrellón P, Hashem M, Neylan M, Baggs G, Zaldo R, et al. Safety and efficacy of a premixed, rice-based oral rehydration solution. J Peditr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004; 38:159–163.
Article16. Eom TH, Oh EY, Kim YH, Lee HS, Jang PS, Kim DU, et al. The therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in acute diarrhea in infants and toddlers. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:986–990.17. Han HJ, Han HJ, Lee HS, Lee IS, Yang HJ. Efficacy of Lactobacillus acidophilus in treatment of acute diarrhea in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004; 7:24–30.
Article18. Moon G, Myung SJ, Jeong JY, Yang SK, Cho YK, Lee SM, et al. Prophylactic effect of Lactobacillus GG in animal colitis and its effect on cytokine secretion and mucin gene expressions. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:234–245.19. Gutierrez-Castrellon P, Lopez-Velazquez G, Diaz-Garcia L, Jimenez-Gutierrez C, Mancilla-Ramirez J, Estevez-Jimenez J, et al. Diarrhea in preschool children and Lactobacillus reuteri : A randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2014; 133:904–909.20. Van Niel CW, Feudtner C, Garrsion MM, Christakis DA. Lactobacillus therapy for acute infectious diarrhea in children: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2002; 109:678–684.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Treatment of Acute Diarrhea in Children
- The Therapeutic Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in Acute Diarrhea in Infants and Toddlers
- Clinical features of acute noroviral gastroenteritis in children : comparison with rotaviral gastroenteritis
- Comparison of Clinical Manifestations of Rotaviral Gastroenteritis between Neonates and Infants
- Comparison of Clinical Features between Noroviral and Rotaviral Gastroenteritis