Korean J Radiol.
2016 Jun;17(3):435-442. 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.435.
Maturation Disparity between Hand-Wrist Bones in a Chinese Sample of Normal Children: An Analysis Based on Automatic BoneXpert and Manual Greulich and Pyle Atlas Assessment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China. dingxiaoyi2013@qq.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Shanghai Children's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200040, China.
- KMID: 2451417
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.435
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the maturation disparity of hand-wrist bones using the BoneXpert system and Greulich and Pyle (GP) atlas in a sample of normal children from China.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Our study included 229 boys and 168 girls aged 2-14 years. The bones in the hand and wrist were divided into five groups: distal radius and ulna, metacarpals, proximal phalanges, middle phalanges and distal phalanges. Bone age (BA) was assessed separately using the automatic BoneXpert and GP atlas by two raters. Differences in the BA between the most advanced and retarded individual bones and bone groups were analyzed.
RESULTS
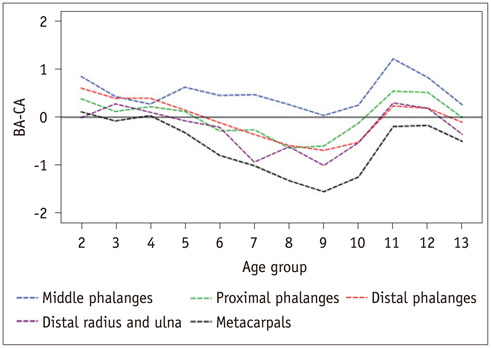
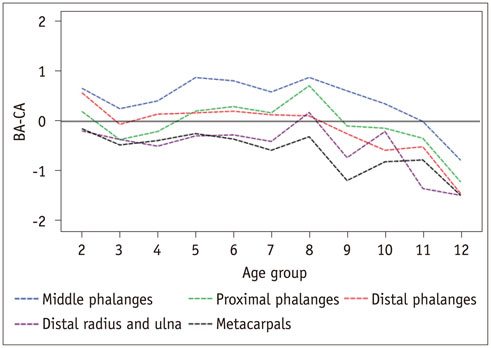
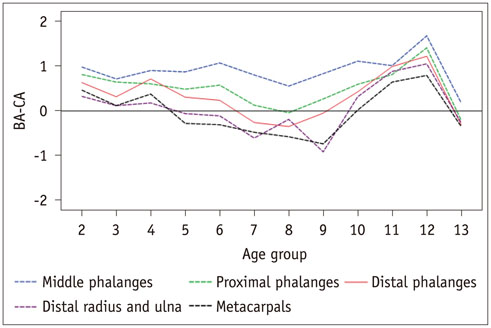
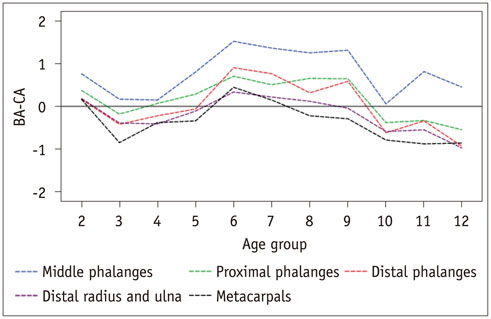
In 75.8% of children assessed with the BoneXpert and 59.4% of children assessed with the GP atlas, the BA difference between the most advanced and most retarded individual bones exceeded 2.0 years. The BA mean differences between the most advanced and most retarded individual bones were 2.58 and 2.25 years for the BoneXpert and GP atlas methods, respectively. Furthermore, for both methods, the middle phalanges were the most advanced group. The most retarded group was metacarpals for BoneXpert, while metacarpals and the distal radius and ulna were the most retarded groups according to the GP atlas. Overall, the BAs of the proximal and distal phalanges were closer to the chronological ages than those of the other bone groups.
CONCLUSION
Obvious and regular maturation disparities are common in normal children. Overall, the BAs of the proximal and distal phalanges are more useful for BA estimation than those of the other bone groups.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical validation of a deep-learning-based bone age software in healthy Korean children
Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Winnah Wu-In Lea, Zepa Yang, Eunjin Noh, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee, Suk-Joo Hong
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024;29(2):102-108. doi: 10.6065/apem.2346050.025.
Reference
-
1. Greulich WW, Pyle SI. Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist. 2nd ed. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press;1959.2. Kim JR, Lee YS, Yu J. Assessment of bone age in prepubertal healthy Korean children: comparison among the Korean standard bone age chart, Greulich-Pyle method, and Tanner-Whitehouse method. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:201–205.3. Ashizawa K, Kumakura C, Zhou X, Jin F, Cao J. RUS skeletal maturity of children in Beijing. Ann Hum Biol. 2005; 32:316–325.4. Zhang SY, Liu LJ, Wu ZL, Liu G, Ma ZG, Shen XZ, et al. Standards of TW3 skeletal maturity for Chinese children. Ann Hum Biol. 2008; 35:349–354.5. Hsieh CW, Liu TC, Wang JK, Jong TL, Tiu CM. Simplified radius, ulna, and short bone-age assessment procedure using grouped-Tanner-Whitehouse method. Pediatr Int. 2011; 53:567–575.6. Thangam P, Mahendiran TV, Thanushkodi K. Skeletal bone age assessment - research directions. J Eng Sci Technol Rev. 2012; 2:90–96.7. Thodberg HH. Clinical review: an automated method for determination of bone age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:2239–2244.8. Martin DD, Sato K, Sato M, Thodberg HH, Tanaka T. Validation of a new method for automated determination of bone age in Japanese children. Horm Res Paediatr. 2010; 73:398–404.9. Kaplowitz P, Srinivasan S, He J, McCarter R, Hayeri MR, Sze R. Comparison of bone age readings by pediatric endocrinologists and pediatric radiologists using two bone age atlases. Pediatr Radiol. 2011; 41:690–693.10. Zhang SY, Liu G, Ma CG, Han YS, Shen XZ, Xu RL, et al. Automated determination of bone age in a modern Chinese population. ISRN Radiol. 2013; 2013:874570.11. Thodberg HH, Sävendahl L. Validation and reference values of automated bone age determination for four ethnicities. Acad Radiol. 2010; 17:1425–1432.12. Vejvoda M, Grant DB. Discordant bone maturation of the hand in children with precocious puberty and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981; 70:903–905.13. Jiménez-Castellanos J, Carmona A, Catalina-Herrera CJ, Viñuales M. Skeletal maturation of wrist and hand ossification centers in normal Spanish boys and girls: a study using the Greulich-Pyle method. Acta Anat (Basel). 1996; 155:206–211.14. Lee MM. Maturation disparity between hand-wrist bones in Hong Kong Chinese children. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1971; 34:385–395.15. Carpenter CT, Lester EL. Skeletal age determination in young children: analysis of three regions of the hand/wrist film. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993; 13:76–79.16. Thodberg HH, Kreiborg S, Juul A, Pedersen KD. The BoneXpert method for automated determination of skeletal maturity. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2009; 28:52–66.17. van Rijn RR, Thodberg HH. Bone age assessment: automated techniques coming of age? Acta Radiol. 2013; 54:1024–1029.18. Erhart S, Lutz M, Arora R, Schmoelz W. Measurement of intraarticular wrist joint biomechanics with a force controlled system. Med Eng Phys. 2012; 34:900–905.19. de Bruin M, van de Giessen M, Vroemen JC, Veeger HE, Maas M, Strackee SD, et al. Geometrical adaptation in ulna and radius of cerebral palsy patients: measures and consequences. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2014; 29:451–457.20. Daly RM, Saxon L, Turner CH, Robling AG, Bass SL. The relationship between muscle size and bone geometry during growth and in response to exercise. Bone. 2004; 34:281–287.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Skeletal Development of Korean Children, Part IV: The Stature, Menarche and Skeletal Development
- Assessment of Bone Age: A comparison of the Greulich Pyle Method to the Tanner Whitehouse Method
- Comparison of Bone Ages in Early Puberty: Computerized Greulich-Pyle Based Bone Age vs. Sauvegrain Method
- A Study on the Skeletal Development of Korean Children, Part I: The Hand and Wrist
- Assessment of Bone Age During Pubertal Age