J Clin Neurol.
2019 Jan;15(1):108-115. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.1.108.
Tafamidis, a Noninvasive Therapy for Delaying Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China.
- 2Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China. huwen0320@sohu.com
- 3Department of Neurology, The People's Hospital of Liaoning Province, Shenyang, China.
- KMID: 2451153
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.1.108
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Tafamidis functions to delay the loss of function in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy (TTR-FAP), which is a rare inherited amyloidosis with progressive sensorimotor and autonomic polyneuropathy. This systematic literature review and meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of tafamidis in TTR-FAP patients, with the aim of improving the evidence-based medical evidence of this treatment option for TTP-FAP.
METHODS
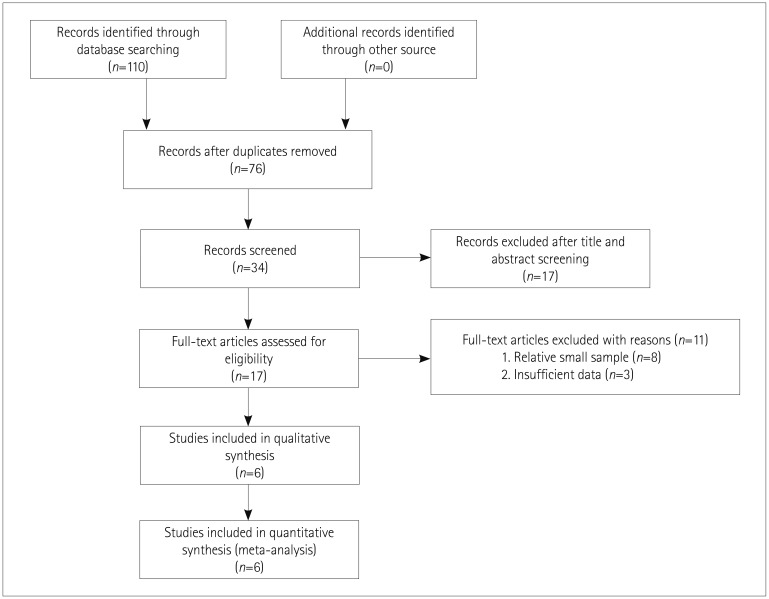
A systematic search of the English-language literature in five databases was performed through to May 31, 2018 by two reviewers who independently extracted data and assessed the risk of bias. We extracted efficacy and safety outcomes and performed a meta-analysis. Statistical tests were performed to check for heterogeneity and publication bias.
RESULTS
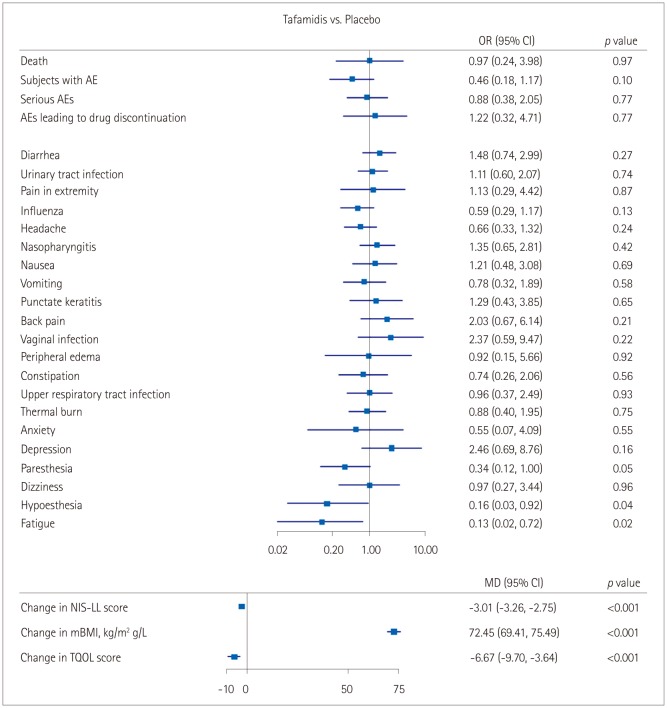
The meta-analysis identified six relevant studies. The tafamidis group showed smaller changes from baseline in the Neuropathy Impairment Score-Lower Limbs [mean difference (MD)=−3.01, 95% confidence interval (CI)=−3.26 to −2.75, p < 0.001] and the Norfolk Quality of Life-Diabetic Neuropathy total quality of life score (MD=−6.67, 95% CI=−9.70 to −3.64, p < 0.001), and a higher modified body mass index (MD=72.45, 95% CI=69.41 to 75.49, p < 0.001), with no significant difference in total adverse events [odds ratio (OR)=0.69, 95% CI=0.35 to 1.35, p=0.27]. The incidence of adverse events did not differ between tafamidis and placebo treatment except for fatigue (OR=0.13, 95% CI=0.02 to 0.72, p=0.02) and hypesthesia (OR=0.16, 95% CI=0.03 to 0.92, p=0.04).
CONCLUSIONS
This systematic review and meta-analysis has demonstrated that tafamidis delays neurologic progression and preserves a better nutritional status and the quality of life. The rates of adverse events did not differ between the patients in the tafamidis and placebo groups. Tafamidis might be a safer noninvasive option for patients with TTR-FAP.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schmidt HH, Waddington-Cruz M, Botteman MF, Carter JA, Chopra AS, Hopps M, et al. Estimating the global prevalence of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2018; 57:829–837. PMID: 29211930.
Article2. Hund E, Linke RP, Willig F, Grau A. Transthyretin-associated neuropathic amyloidosis. Pathogenesis and treatment. Neurology. 2001; 56:431–435. PMID: 11261421.
Article3. Benson MD. The hereditary amyloidoses. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2003; 17:909–927. PMID: 15123043.
Article4. Andersson R. Familial amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. A clinical study based on patients living in northern Sweden. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1976; 590:1–64. PMID: 1064291.5. Planté-Bordeneuve V, Lalu T, Misrahi M, Reilly MM, Adams D, Lacroix C, et al. Genotypic-phenotypic variations in a series of 65 patients with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology. 1998; 51:708–714. PMID: 9748014.
Article6. Monaco HL, Rizzi M, Coda A. Structure of a complex of two plasma proteins: transthyretin and retinol-binding protein. Science. 1995; 268:1039–1041. PMID: 7754382.
Article7. Connors LH, Lim A, Prokaeva T, Roskens VA, Costello CE. Tabulation of human transthyretin (TTR) variants, 2003. Amyloid. 2003; 10:160–184. PMID: 14640030.
Article8. Gertz MA, Benson MD, Dyck PJ, Grogan M, Coelho T, Cruz M, et al. Diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of transthyretin amyloidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015; 66:2451–2466. PMID: 26610878.9. Almeida MR, Alves IL, Terazaki H, Ando Y, Saraiva MJ. Comparative studies of two transthyretin variants with protective effects on familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: TTR R104H and TTR T119M. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000; 270:1024–1028. PMID: 10772944.
Article10. Koike H, Misu K, Sugiura M, Iijima M, Mori K, Yamamoto M, et al. Pathology of early- vs late-onset TTR Met30 familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Neurology. 2004; 63:129–138. PMID: 15249622.
Article11. Planté-Bordeneuve V, Said G. Familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Lancet Neurol. 2011; 10:1086–1097. PMID: 22094129.
Article12. Saraiva MJ. Transthyretin mutations in health and disease. Hum Mutat. 1995; 5:191–196. PMID: 7599630.13. Sekijima Y, Kelly JW, Ikeda S. Pathogenesis of and therapeutic strategies to ameliorate the transthyretin amyloidoses. Curr Pharm Des. 2008; 14:3219–3230. PMID: 19075702.
Article14. Ericzon BG, Wilczek HE, Larsson M, Wijayatunga P, Stangou A, Pena JR, et al. Liver transplantation for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis: after 20 years still the best therapeutic alternative? Transplantation. 2015; 99:1847–1854. PMID: 26308415.15. Okamoto S, Wixner J, Obayashi K, Ando Y, Ericzon BG, Friman S, et al. Liver transplantation for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: impact on Swedish patients' survival. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:1229–1235. PMID: 19790145.
Article16. Winkler M, Brinkmann C, Jost U, Oldhafer K, Ringe B, Pichlmayr R. Long-term side effects of cyclosporine-based immunosuppression in patients after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1994; 26:2679–2682. PMID: 7940839.17. Suhr OB, Larsson M, Ericzon BG, Wilczek HE. FAPWTR's investigators. Survival after transplantation in patients with mutations other than Val30Met: extracts from the FAP world transplant registry. Transplantation. 2016; 100:373–381. PMID: 26656838.18. Bulawa CE, Connelly S, Devit M, Wang L, Weigel C, Fleming JA, et al. Tafamidis, a potent and selective transthyretin kinetic stabilizer that inhibits the amyloid cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:9629–9634. PMID: 22645360.
Article19. Plante-Bordeneuve V. Update in the diagnosis and management of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Neurol. 2014; 261:1227–1233. PMID: 24888313.
Article20. Adams D, Cauquil C, Labeyrie C, Beaudonnet G, Algalarrondo V, Théaudin M. TTR kinetic stabilizers and TTR gene silencing: a new era in therapy for familial amyloidotic polyneuropathies. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016; 17:791–802. PMID: 26800456.
Article21. Tong C, Blanco M, Goddard WA 3rd, Seinfeld JH. Thermodynamic properties of multifunctional oxygenates in atmospheric aerosols from quantum mechanics and molecular dynamics: dicarboxylic acids. Environ Sci Technol. 2004; 38:3941–3949. PMID: 15298204.
Article22. Waddington Cruz M, Benson MD. A review of tafamidis for the treatment of transthyretin-related amyloidosis. Neurol Ther. 2015; 4:61–79. PMID: 26662359.
Article23. Kim DH, Zeldenrust SR, Low PA, Dyck PJ. Quantitative sensation and autonomic test abnormalities in transthyretin amyloidosis polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 2009; 40:363–370. PMID: 19618439.
Article24. Kolb NA, Smith AG, Singleton JR, Beck SL, Stoddard GJ, Brown S, et al. The association of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms and the risk of falling. JAMA Neurol. 2016; 73:860–866. PMID: 27183099.
Article25. Vinik EJ, Hayes RP, Oglesby A, Bastyr E, Barlow P, Ford-Molvik SL, et al. The development and validation of the Norfolk QOL-DN, a new measure of patients' perception of the effects of diabetes and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2005; 7:497–508. PMID: 15929681.
Article26. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:1–12. PMID: 8721797.
Article27. Keohane D, Schwartz J, Gundapaneni B, Stewart M, Amass L. Tafamidis delays disease progression in patients with early stage transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: additional supportive analyses from the pivotal trial. Amyloid. 2017; 24:30–36.
Article28. Gundapaneni BK, Sultan MB, Keohane DJ, Schwartz JH. Tafamidis delays neurological progression comparably across Val30Met and non-Val30Met genotypes in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Eur J Neurol. 2018; 25:464–468. PMID: 29115008.
Article29. Suhr OB, Conceição IM, Karayal ON, Mandel FS, Huertas PE, Ericzon BG. Post hoc analysis of nutritional status in patients with transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: impact of tafamidis. Neurol Ther. 2014; 3:101–112. PMID: 26000226.
Article30. Coelho T, Maia LF, da Silva AM, Cruz MW, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Suhr OB, et al. Long-term effects of tafamidis for the treatment of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. J Neurol. 2013; 260:2802–2814. PMID: 23974642.
Article31. Barroso FA, Judge DP, Ebede B, Li H, Stewart M, Amass L, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of tafamidis for the treatment of hereditary transthyretin amyloid polyneuropathy: results up to 6 years. Amyloid. 2017; 24:194–204. PMID: 28758793.
Article32. Coelho T, Maia LF, Martins da Silva A, Waddington Cruz M, Planté-Bordeneuve V, Lozeron P, et al. Tafamidis for transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology. 2012; 79:785–792. PMID: 22843282.
Article33. Maurer MS, Grogan DR, Judge DP, Mundayat R, Packman J, Lombardo I, et al. Tafamidis in transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy: effects on transthyretin stabilization and clinical outcomes. Circ Heart Fail. 2015; 8:519–526. PMID: 25872787.34. Maurer MS, Schwartz JH, Gundapaneni B, Elliott PM, Merlini G, Waddington-Cruz M, et al. Tafamidis treatment for patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:1007–1016. PMID: 30145929.
Article35. Berk JL, Suhr OB, Obici L, Sekijima Y, Zeldenrust SR, Yamashita T, et al. Repurposing diflunisal for familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013; 310:2658–2667. PMID: 24368466.36. Takahashi R, Ono K, Shibata S, Nakamura K, Komatsu J, Ikeda Y, et al. Efficacy of diflunisal on autonomic dysfunction of late-onset familial amyloid polyneuropathy (TTR Val30Met) in a Japanese endemic area. J Neurol Sci. 2014; 345:231–235. PMID: 25060417.
Article37. Sekijima Y, Tojo K, Morita H, Koyama J, Ikeda S. Safety and efficacy of long-term diflunisal administration in hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2015; 22:79–83. PMID: 26017328.
Article38. Sekijima Y, Dendle MA, Kelly JW. Orally administered diflunisal stabilizes transthyretin against dissociation required for amyloidogenesis. Amyloid. 2006; 13:236–249. PMID: 17107884.
Article39. Miller SR, Sekijima Y, Kelly JW. Native state stabilization by NSAIDs inhibits transthyretin amyloidogenesis from the most common familial disease variants. Lab Invest. 2004; 84:545–552. PMID: 14968122.
Article40. Benson MD, Waddington-Cruz M, Berk JL, Polydefkis M, Dyck PJ, Wang AK, et al. Inotersen treatment for patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:22–31. PMID: 29972757.41. Benson MD, Kluve-Beckerman B, Zeldenrust SR, Siesky AM, Bodenmiller DM, Showalter AD, et al. Targeted suppression of an amyloidogenic transthyretin with antisense oligonucleotides. Muscle Nerve. 2006; 33:609–618. PMID: 16421881.
Article42. Coelho T, Adams D, Silva A, Lozeron P, Hawkins PN, Mant T, et al. Safety and efficacy of RNAi therapy for transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:819–829. PMID: 23984729.
Article43. Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998; 391:806–811. PMID: 9486653.
Article44. Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001; 411:494–498. PMID: 11373684.
Article45. Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O'Riordan WD, Yang CC, Ueda M, Kristen AV, et al. Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:11–21. PMID: 29972753.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tafamidis for Cardiac Transthyretin Amyloidosis
- Tafamidis for a Transplant Patient with Transthyretin Amyloid Polyneuropathy
- Familial Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Variant Asp38Ala Presenting with Orthostatic Hypotension and Chronic Diarrhea
- Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis with Polyneuropathy
- Familial Amyloidotic Polyneuropathy With Transthyretin Gene Mutation