J Clin Neurol.
2019 Jul;15(3):386-392. 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.386.
Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant-Cell Arteritis in Korean Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Ophthalmology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 4Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jaeho.jung@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2451124
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.386
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to report the relative incidence of arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AAION) associated with giant-cell arteritis (GCA) in a single-center and evaluate the clinical features of AAION in Korean patients.
METHODS
The medical records of patients with presumed AION who visited our hospital from January 2013 to August 2018 were examined retrospectively. The patients were divided into two groups: AAION associated with GCA, and non AION (NAION). We additionally reviewed the literature and identified all cases of AAION in Korean and Caucasian patients. We evaluated the clinical data including the initial and final best-corrected visual acuities, fundus photographs, visual field tests, fluorescein angiography, and contrast-enhanced MRI, and compared the data with those for Caucasian patients in the literature.
RESULTS
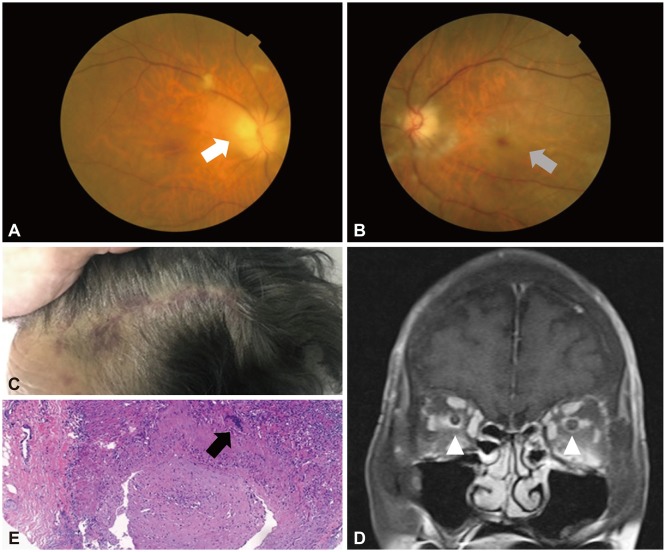
Of the 142 patients with presumed AION, 3 (2.1%) were diagnosed with AAION and 139 (97.9%) were diagnosed with NAION. Seven Korean patients with AAION associated with GCA were identified in our data and the literature review. We found no difference in any clinical features other than laterality: four of the seven Korean patients had bilateral involvement. Moreover, the optic nerve sheath was enhanced in two of our Korean patients.
CONCLUSIONS
AAION associated with GCA is a very rare condition compared to NAION in Korea. However, GCA should be considered in all cases of ischemic optic neuropathy because AAION is associated with poor visual outcome, and sometimes presents bilaterally.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Clinical characteristics and courses of Korean patients with giant cell arteritis: a multi-center retrospective study
Jee-In Lee, Jun Won Park, Youjin Jung, Kichul Shin, Se Rim Choi, Eun Ha Kang, Yun Jong Lee, Jong Jin Yoo, You-Jung Ha
J Rheum Dis. 2024;31(3):160-170. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0007.
Reference
-
1. Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant-cell arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 139:505–515. PMID: 13679329.
Article2. Rahman W, Rahman FZ. Giant cell (temporal) arteritis: an overview and update. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005; 50:415–428. PMID: 16139037.
Article3. Hayreh SS, Podhajsky PA, Zimmerman B. Occult giant cell arteritis: ocular manifestations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1998; 125:521–526. PMID: 9559738.
Article4. Hayreh SS. Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009; 28:34–62. PMID: 19063989.
Article5. Pereira LS, Yoon MK, Hwang TN, Hong JE, Ray K, Porco T, et al. Giant cell arteritis in Asians: a comparative study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:214–216. PMID: 20584707.
Article6. Kobayashi S, Yano T, Inaba Y, Hashimoto H, Matsumoto Y, Tamakoshi A, et al. Ocular involvements of Japanese patients with giant cell arteritis from the first nation-wide survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 49:867–868. PMID: 14673978.
Article7. Cha DM, Lee T, Choe G, Yang HK, Hwang JM. Silent giant cell arteritis in an elderly Korean woman. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2013; 27:224–227. PMID: 23730119.
Article8. Kang YS, Park SW, Lee HK, Choi YD, Heo H. Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with giant cell arteritis in an elderly Korean man. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2016; 30:239–241. PMID: 27247526.
Article9. Yoon HJ, Park SW, Lee HK, Choi YD, Heo H. Bilateral arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with giant cell arteritis in Korea. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2017; 31:466–467. PMID: 28994270.
Article10. Lee SM, Shin DH, Choi JH, Jung JH. A case of bilateral arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in Korean patient. Clin Neuroophthalmol. 2018; 8:9–12.11. Lee EJ, Woo KA, Koo DL. Giant cell arteritis associated arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: sudden vision loss on the contralateral side of headache. J Clin Neurol. 2018; 14:577–579. PMID: 30198237.
Article12. Miller NR. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: diagnosis and management. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1980; 56:643–654. PMID: 6932236.13. Miller NR, Arnold AC. Current concepts in the diagnosis, pathogenesis and management of nonarteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy. Eye (Lond). 2015; 29:65–79. PMID: 24993324.
Article14. Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Stevens MB, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1122–1128. PMID: 2202311.
Article15. Hayreh SS. Ischemic optic neuropathies-where are we now? Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251:1873–1884. PMID: 23821118.16. Gruener AM, Chang JR, Bosley TM, Al-Sadah ZM, Kum C, McCulley TJ. Relative frequencies of arteritic and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in an Arab population. J Neuroophthalmol. 2017; 37:382–385. PMID: 28099197.
Article17. Tatò F, Hoffmann U. Giant cell arteritis: a systemic vascular disease. Vasc Med. 2008; 13:127–140. PMID: 18593802.
Article18. Nuenninghoff DM, Hunder GG, Christianson TJ, McClelland RL, Matteson EL. Incidence and predictors of large-artery complication (aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, and/or large-artery stenosis) in patients with giant cell arteritis: a population-based study over 50 years. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:3522–3531. PMID: 14674004.
Article19. Currey J. Scalp necrosis in giant cell arteritis and review of the literature. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:814–816. PMID: 9255121.
Article20. Tsianakas A, Ehrchen JM, Presser D, Fischer T, Kruse-Loesler B, Luger TA, et al. Scalp necrosis in giant cell arteritis: case report and review of the relevance of this cutaneous sign of large-vessel vasculitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009; 61:701–706. PMID: 19577329.
Article21. Purvin V, Kawasaki A, Jacobson DM. Optic perineuritis: clinical and radiographic features. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001; 119:1299–1306. PMID: 11545635.23. Byon IS, Jung JH, Kim HY, Park SW, Lee JE. Optic perineuritis secondary to acute retinal necrosis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2013; 33:419–421. PMID: 24177430.
Article24. Morgenstern KE, Ellis BD, Schochet SS, Linberg JV. Bilateral optic nerve sheath enhancement from giant cell arteritis. J Rheumatol. 2003; 30:625–627. PMID: 12610827.25. Morotti A, Liberini P, Padovani A. Bilateral optic perineuritis as the presenting feature of giant cell arteritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:bcr2011007959.
Article26. Attaseth T, Vanikieti K, Poonyathalang A, Preechawat P, Jindahra P, Wattanatranon D. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy due to biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis in Thai patients. Clin Ophthalmol. 2015; 9:1071–1075. PMID: 26109841.
Article27. Liu TY, Miller NR. Giant cell arteritis presenting as unilateral anterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with bilateral optic nerve sheath enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging. J Neuroophthalmol. 2015; 35:360–363. PMID: 26087368.
Article28. Bengtsson BA, Malmvall BE. The epidemiology of giant cell arteritis including temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica. Incidences of different clinical presentations and eye complications. Arthritis Rheum. 1981; 24:899–904. PMID: 7259802.29. Graham E, Holland A, Avery A, Russell RW. Prognosis in giant-cell arteritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981; 282:269–271.
Article30. Aiello PD, Trautmann JC, McPhee TJ, Kunselman AR, Hunder GG. Visual prognosis in giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology. 1993; 100:550–555. PMID: 8479714.
Article31. Baldursson O, Steinsson K, Björnsson J, Lie JT. Giant cell arteritis in Iceland. An epidemiologic and histopathologic analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994; 37:1007–1012. PMID: 8024610.32. Liu GT, Glaser JS, Schatz NJ, Smith JL. Visual morbidity in giant cell arteritis. Clinical characteristics and prognosis for vision. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1779–1785. PMID: 7800356.33. Chen JJ, Leavitt JA, Fang C, Crowson CS, Matteson EL, Warrington KJ. Evaluating the incidence of arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy and other causes of vision loss from giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology. 2016; 123:1999–2003. PMID: 27297405.
Article34. Giambene B, Sodi A, Sofi F, Marcucci R, Fedi S, Abbate R, et al. Evaluation of traditional and emerging cardiovascular risk factors in patients with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy: a case-control study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009; 247:693–697. PMID: 19052769.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Subtype Giant Cell Arteritis Without Symptoms of Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Giant Cell Arteritis Associated Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: Sudden Vision Loss on the Contralateral Side of Headache
- Bilateral Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant Cell Arteritis in Korea
- Temporal Arteritis with Diagnostic Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Two Cases in Which Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Due to Giant Cell Arteritis Occurred Sequentially in Both Eyes