J Clin Neurol.
2018 Oct;14(4):577-579. 10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.577.
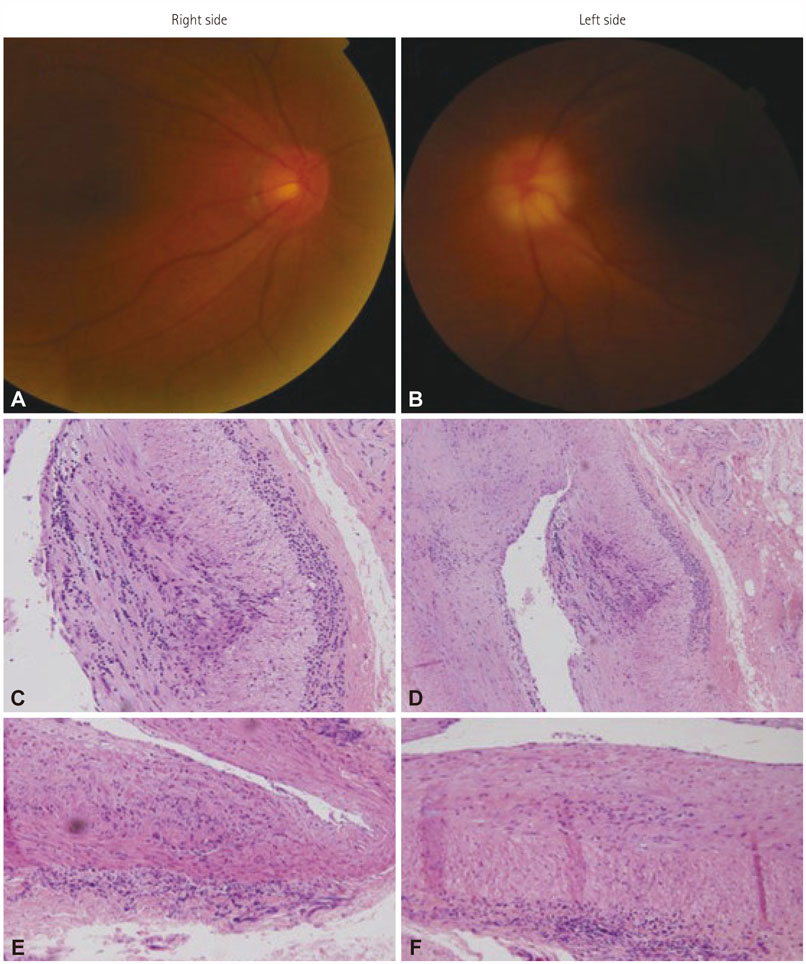
Giant Cell Arteritis Associated Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: Sudden Vision Loss on the Contralateral Side of Headache
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. koodaelim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2424189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2018.14.4.577
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant-Cell Arteritis in Korean Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis and Review of the Literature
Jae-Hwan Choi, Jong Hoon Shin, Jae Ho Jung
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(3):386-392. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.386.
Reference
-
1. Chacko JG, Chacko JA, Salter MW. Review of giant cell arteritis. Saudi J Ophthalmol. 2015; 29:48–52.
Article2. Chen JJ, Leavitt JA, Fang C, Crowson CS, Matteson EL, Warrington KJ. Evaluating the incidence of arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy and other causes of vision loss from giant cell arteritis. Ophthalmology. 2016; 123:1999–2003.
Article3. Gonzalez-Gay MA, Barros S, Lopez-Diaz MJ, Garcia-Porrua C, Sanchez-Andrade A, Llorca J. Giant cell arteritis: disease patterns of clinical presentation in a series of 240 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005; 84:269–276.
Article4. Hocevar A, Rotar Z, Jese R, Semrl SS, Pizem J, Hawlina M, et al. Do early diagnosis and glucocorticoid treatment decrease the risk of permanent visual loss and early relapses in giant cell arteritis: a prospective longitudinal study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3210.5. Danesh-Meyer HV, Savino PJ, Eagle RC Jr, Kubis KC, Sergott RC. Low diagnostic yield with second biopsies in suspected giant cell arteritis. J Neuroophthalmol. 2000; 20:213–215.
Article6. Breuer GS, Nesher G, Nesher R. Rate of discordant findings in bilateral temporal artery biopsy to diagnose giant cell arteritis. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:794–796.
Article7. Jonasson F, Cullen JF, Elton RA. Temporal arteritis. A 14-year epidemiological, clinical and prognostic study. Scott Med J. 1979; 24:111–117.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Subtype Giant Cell Arteritis Without Symptoms of Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Two Cases in Which Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Due to Giant Cell Arteritis Occurred Sequentially in Both Eyes
- Temporal Arteritis with Diagnostic Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Bilateral Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant Cell Arteritis in Korea
- Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Associated with Giant-Cell Arteritis in Korean Patients: A Retrospective Single-Center Analysis and Review of the Literature