Lab Med Online.
2019 Jul;9(3):185-188. 10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.185.
Unique Red Blood Cell Morphology Detected in a Patient with Myelodysplastic Syndrome by Three-dimensional Refractive Index Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ssjang@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Tomocube Inc., Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2450846
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2019.9.3.185
Abstract
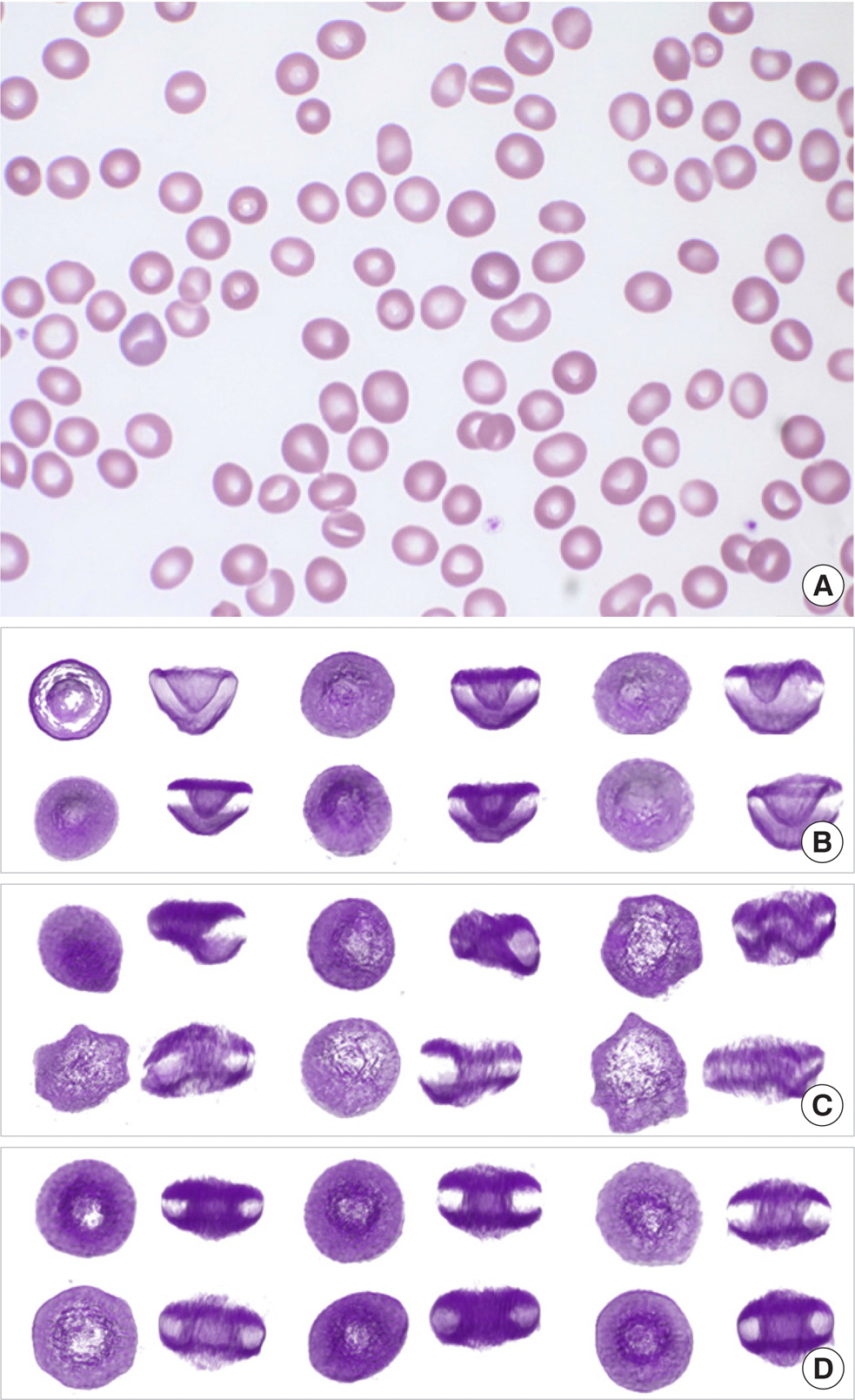
- The three-dimensional (3-D) shape of erythrocytes is strongly associated with various diseases. However, conventional optical imaging approaches with Wright's staining only provide information on two-dimensional morphology. Here, we employed optical diffraction tomography (ODT), a label-free 3-D quantitative phase imaging technique, and observed uniquely shaped red blood cells (RBCs) in the peripheral blood of a patient diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndrome. Peripheral blood samples were collected when the patient visited our hospital for his two out-patient follow-ups in May 2018. The 3-D tomograms of randomly chosen RBCs were reconstructed using a commercial ODT setup. From the reconstructed 3-D RBCs, 37.5% and 32.8% of RBCs demonstrated cup-like shapes at the first and the second out-patient follow-up, respectively. Even though this is a single case report, the finding is novel and can be a potential dyserythropoietic feature found in peripheral blood.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jaffe ES, Arber DA, et al. eds. Hematopathology. 2nd ed.Philadelphia PA: Elsevier;2006. p. 793–4.2. Kim Y, Shim H, Kim K, Park H, Jang S, Park Y. Profling individual human red blood cells using common-path diffraction optical tomography. Sci Rep. 2014; 4:6659.
Article3. Kim K, Kim KS, Park H, Ye JC, Park Y. Realtime visualization of 3-D dynamic microscopic objects using optical diffraction tomography. Opt Express. 2013; 21:32269–78.
Article4. Salsbury AJ and Clarke JA. New method for detecting changes in the surface appearance of human red blood cells. J Clin Pathol. 1967; 20:603–10.5. Shin S, Kim K, Yoon J, Park Y. Active illumination using a digital micro-mirror device for quantitative phase imaging. Opt Lett. 2015; 40:5407–10.
Article6. Kaushansky K, Lichtman MA, et al. eds. Williams hematology. 9th ed.New York: McGraw-Hill Education;2006. p. 468–74.7. Hoffman JF. Biconcave shape of human red-blood-cell ghosts relies on density differences between the rim and dimple of the ghost's plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113:14847–51.
Article8. Peng Z, Li X, Pivkin IV, Dao M, Karniadakis GE, Suresh S. Lipid bilayer and cytoskeletal interactions in a red blood cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110:13356–61.
Article9. Lee SY, Park HJ, Best-Popescu C, Jang S, Park YK. The effects of ethanol on the morphological and biochemical properties of individual human red blood cells. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0145327.
Article10. Lee S, Park H, Kim K, Sohn Y, Jang S, Park Y. Refractive index tomograms and dynamic membrane fuctuations of red blood cells from patients with diabetes mellitus. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:1039.
Article11. Lefèvre C, Bondu S, Le Goff S, Kosmider O, Fontenay M. Dyserythro-poiesis of myelodysplastic syndromes. Curr Opin Hematol. 2017; 24:191–7.
Article12. Germing U, Strupp C, Giagounidis A, Haas R, Gattermann N, Starke C, et al. Evaluation of dysplasia through detailed cytomorphology in 3156 patients from the Düsseldorf Registry on myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2012; 36:727–34.
Article13. Della Porta MG, Travaglino E, Boveri E, Ponzoni M, Malcovati L, Pa-paemmanuil E, et al. Minimal morphological criteria for defning bone marrow dysplasia: A basis for clinical implementation of WHO classifcation of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia. 2015; 29:66–75.14. Park YK, Depeursinge C, Popescu G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine. Nat Photonics. 2018; 12:578–89.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome combined with pure red cell aplasia
- A Case of Am
- Pregnancy complicated with myelodysplastic syndrome and severe preeclampsia: A case report
- Sweet's Syndrome with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Progressing to Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Erythroid Aplasia following Pure Red Cell Aplasia