Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2019 May;36(2):152-154. 10.12701/yujm.2019.00066.
Surgical treatment of esotropia and unilateral ptosis in a patient with Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. eyekwj@ynu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2449329
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00066
Abstract
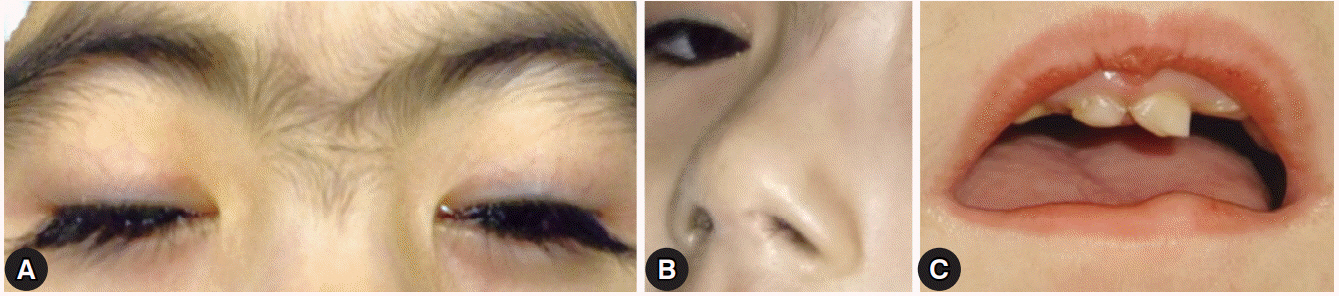
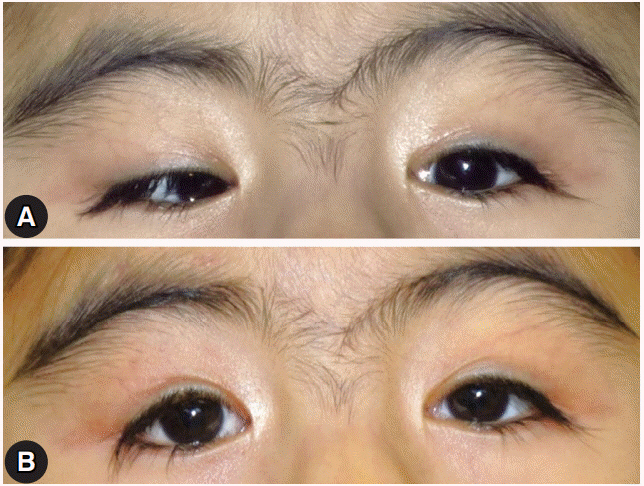
- Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) is a rare multisystemic disorder that is characterized by mental retardation, prenatal and postnatal growth retardation, limb anomalies, and distinctive facial features, which include arched eyebrows that often meet in the middle (synophrys), long eyelashes, low-set ears, small and widely spaced teeth, and a small and upturned nose. Ophthalmic manifestations include long eyelashes, nasolacrimal duct obstruction, myopia, ptosis, and strabismus. There has been no report of surgical treatment for esotropia and unilateral ptosis in patients with CdLS in Korea. I report a patient with CdLS who underwent surgical treatment for esotropia and unilateral ptosis with a good surgical outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Levin AV, Seidman DJ, Nelson LB, Jackson LG. Ophthalmologic findings in the Cornelia de Lange syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1990; 27:94–102.
Article2. Boyle MI, Jespersgaard C, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Bisgaard AM, Tümer Z. Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Clin Genet. 2015; 88:1–12.
Article3. Kline AD, Krantz ID, Sommer A, Kliewer M, Jackson LG, Fitz-Patrick DR, et al. Cornelia de Lange syndrome: clinical review, diagnostic and scoring systems, and anticipatory guidance. Am J Med Genet A. 2007; 143A:1287–96.
Article4. Kim IT, Park JW, Choi WC. A Korean case of Cornelia de Lange syndrome. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2005; 19:153–5.
Article5. Nallasamy S, Kherani F, Yaeger D, McCallum J, Kaur M, Devoto M, et al. Ophthalmologic findings in Cornelia de Lange syndrome: a genotype-phenotype correlation study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2006; 124:552–7.
Article6. Park KH, Lee ST, Ki CS, Byun SY. Cornelia de Lange Syndrome with NIPBL gene mutation: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1821–3.
Article7. Wygnanski-Jaffe T, Shin J, Perruzza E, Abdolell M, Jackson LG, Levin AV. Ophthalmologic findings in the Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. J AAPOS. 2005; 9:407–15.
Article8. Stacey AW, Sparagna C, Borri M, Rizzo S, Hadjistilianou T. A 6-year-old boy with Cornelia de Lange syndrome and Coats disease: case report and review of the literature. J AAPOS. 2015; 19:474–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Legg-Perthes Disease Associated with Cornelia de Lange Syndrome: A Case Report
- Dental Findings in Cornelia De Lange Syndrome
- A Korean Case of Cornelia de Lange Syndrome
- Two cases of Cornelia de Lange syndrome
- Anesthesiologic considerations in a pediatric patient with cornelia de lange syndrome: A case report