J Rhinol.
2019 May;26(1):38-42. 10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.38.
Two Cases of Septal Perforation Repair using Posterior Margin Based Hinge Flap
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. goma0320@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2449027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2019.26.1.38
Abstract
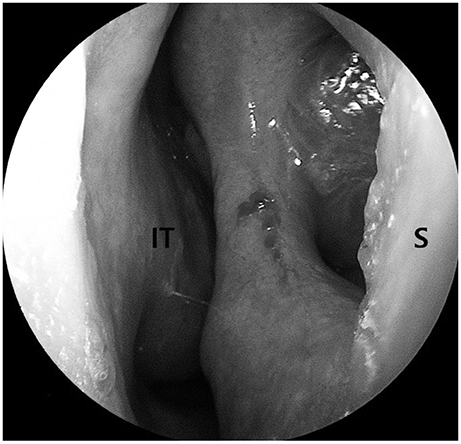
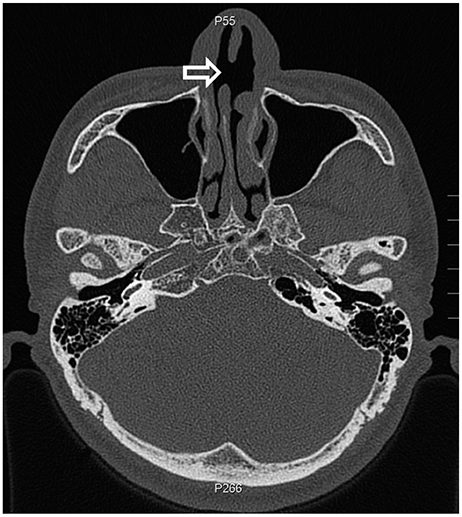
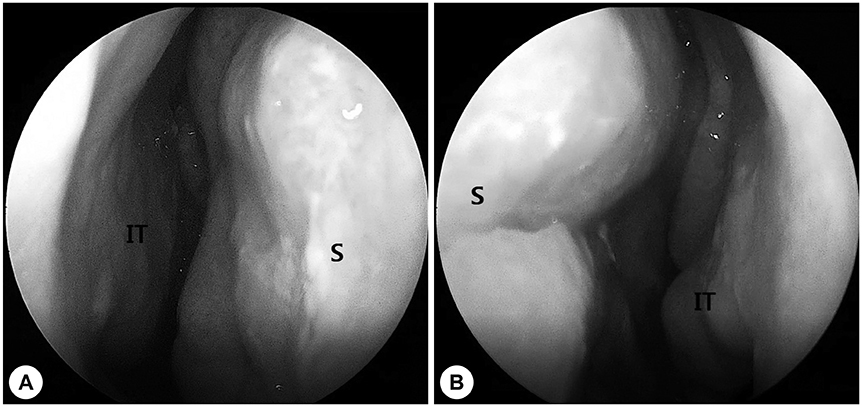
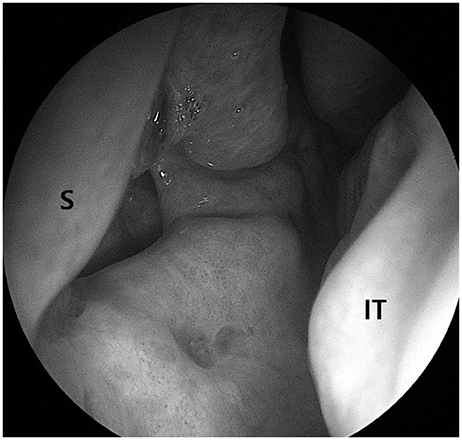
- Nasal septal perforation is a defect of cartilage, bone, or mucosa of the nasal septum. Nasal septal perforation has several potential causes such as previous septal surgeries, trauma, malignancy, inflammation, or drugs. According to previous studies, successful surgical outcome is affected by the size and location of the perforation. Although many surgical techniques have been reported, there is no standardized nor consistent surgical method for repairing nasal septal perforation. This report suggests a new surgical technique of repairing septal perforation using a posterior perforation-margin-based hinge flap.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Giacomini PG, Ferraro S, Di Girolamo S, Ottaviani F. Large nasal septal perforation repair by closed endoscopically assisted approach. Ann Plast Surg. 2011; 66:633–636.
Article2. Jin HR, Won TB. Septoplasty; Current Concept and Technique. J Rhinol. 2008; 15:13–29.3. Kim YD. Septoplasty and Turbinoplasty; Current Concept and Technique. J Rhinol. 2012; 19:19–28.4. Taskin U, Yigit O, Sisman SA. Septal perforation repairing with combination of mucosal flaps and auricular interpositional grafts in revision patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 145:828–832.
Article5. Chen FH, Rui X, Deng J, Wen YH, Xu G, Shi JB. Endoscopic sandwich technique for moderate nasal septal perforations. Laryngoscope. 2012; 122:2367–2372.
Article6. Kim SW, Rhee CS. Nasal septal perforation repair: predictive factors and systematic review of the literature. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012; 20:58–65.7. Ribeiro JS, da Silva GS. Technical advances in the correction of septal perforation associated with closed rhinoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007; 9:321–327.
Article8. Andre RF, Lohuis PJ, Vuyk HD. Nasal septum perforation repair using differently designed, bilateral intranasal flaps, with nonopposing suture lines. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006; 59:829–834.
Article9. Park JH, Kim D, Jin HR. Nasal septal perforation repair using intranasal rotation and advancement flaps. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013; 27:e42–e47.
Article10. Taylor RJ, Sherris DA. Prosthetics for nasal perforations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; 152:803–810.11. Goh AY, Hussain SS. Different surgical treatments for nasal septal perforation and their outcomes. J Laryngol Otol. 2007; 121:419–426.
Article12. Pedroza F, Patrocinio LG, Arevalo O. A review of 25-year experience of nasal septal perforation repair. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007; 9:12–18.
Article13. Kuriloff DB. Nasal septal perforations and nasal obstruction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1989; 22:333–350.
Article14. Romo T 3rd, Sclafani AP, Falk AN, Toffel PH. A graduated approach to the repair of nasal septal perforations. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 103:66–75.
Article15. Belmont JR. An approach to large nasoseptal perforations and attendant deformity. Arch Otolaryngol. 1985; 111:450–455.
Article16. Kridel RW. Considerations in the etiology, treatment, and repair of septal perforations. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2004; 12:435–450.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Septal Perforation Repair with Middle Turbinate Flap
- Prevention Technique Using Inferior Turbinate Mucosal Flap for Septal Perforation after Septoplasty
- Reconstruction of Full Thickness Ala Defect with Nasolabial Fold and Septal Mucosal Hinge Flap
- Repair of Nasal Septal Perforation Using Silastic Sheet
- Repair of Nasal Septal Perforation Using Polycaprolactone Plate and Temporalis Fascia Graft