Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Apr;43(2):234-238. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.234.
Correlation Between Vanishing White Matter Disease and Novel Heterozygous EIF2B3 Variants Using Next-Generation Sequencing: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Green Cross Genome, Yongin, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. jseok337@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2449007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.234
Abstract
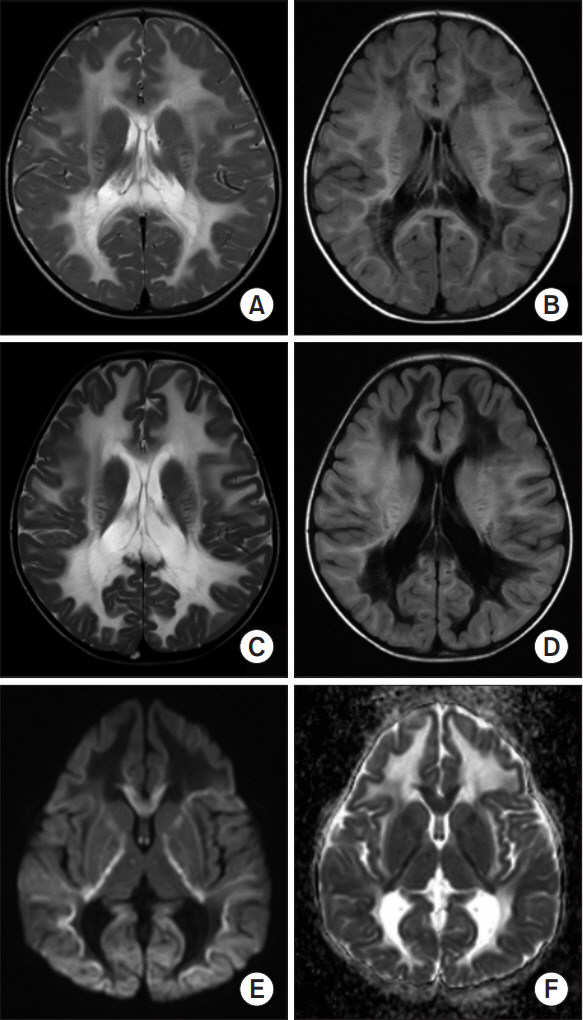
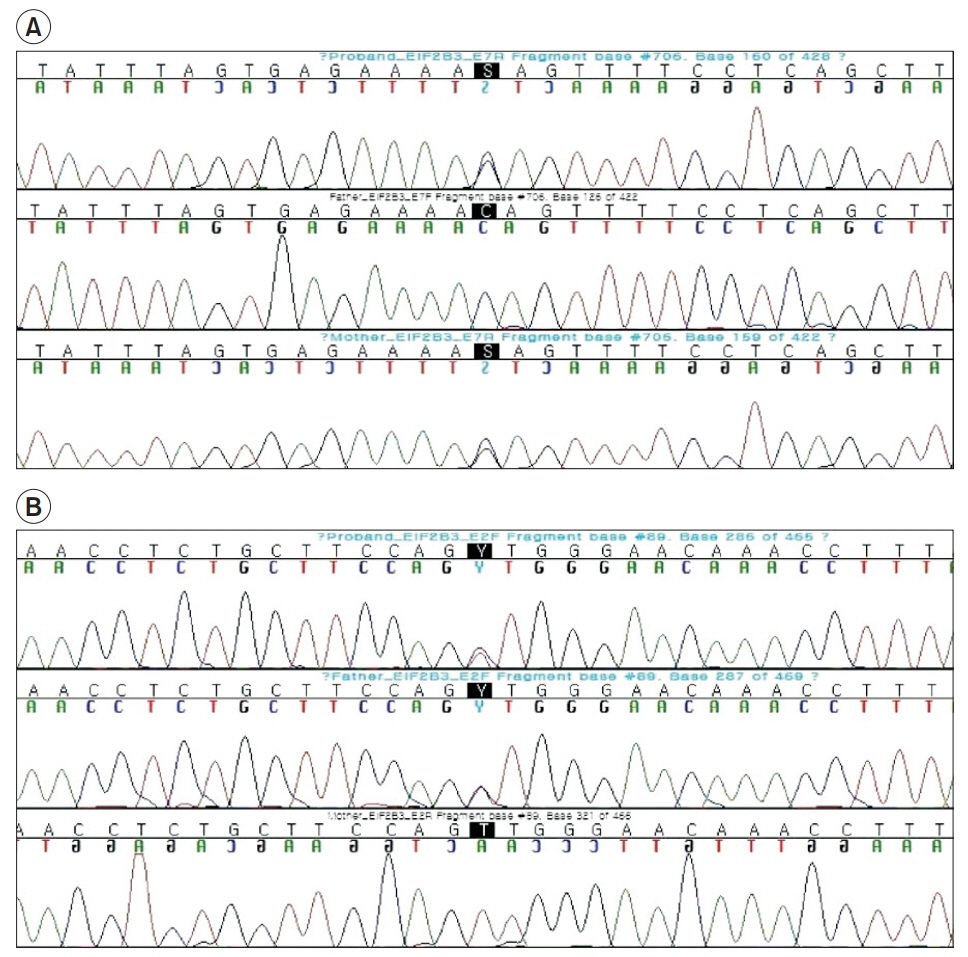
- Vanishing white matter (VWM) disease is an autosomal recessive disorder that affects the central nervous system of a patient, and is caused by the development of pathogenic mutations in any of the EIF2B1-5 genes. Any dysfunction of the EIF2B1-5 gene encoded eIF2B causes stress-provoked episodic rapid neurological deterioration in the patient, followed by a chronic progressive disease course. We present the case of a patient with an infantile-onset VWM with the pre-described specific clinical course, subsequent neurological aggravation induced by each viral infection, and the noted consequent progression into a comatose state. Although the initial brain magnetic resonance imaging did not reveal specific pathognomonic signs of VWM to distinguish it from other types of demyelinating leukodystrophy, the next-generation sequencing studies identified heterozygous missense variants in EIF2B3, including a novel variant in exon 7 (C706G), as well as a 0.008% frequency reported variant in exon 2 (T89C). Hence, the characteristic of unbiased genomic sequencing can clinically affect patient care and decisionmaking, especially in terms of the consideration of genetic disorders such as leukoencephalopathy in pediatric patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. van der Knaap MS, Pronk JC, Scheper GC. Vanishing white matter disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5:413–23.
Article2. van der Knaap MS, Leegwater PA, Konst AA, Visser A, Naidu S, Oudejans CB, et al. Mutations in each of the five subunits of translation initiation factor eIF2B can cause leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Ann Neurol. 2002; 51:264–70.
Article3. Fogli A, Schiffmann R, Hugendubler L, Combes P, Bertini E, Rodriguez D, et al. Decreased guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity in eIF2B-mutated patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004; 12:561–6.
Article4. Pronk JC, van Kollenburg B, Scheper GC, van der Knaap MS. Vanishing white matter disease: a review with focus on its genetics. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2006; 12:123–8.
Article5. Oh JY, Do HJ, Lee S, Jang JH, Cho EH, Jang DH. Identification of a heterozygous SPG11 mutation by clinical exome sequencing in a patient with hereditary spastic paraplegia: a case report. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40:1129–34.6. Ding XQ, Bley A, Ohlenbusch A, Kohlschutter A, Fiehler J, Zhu W, et al. Imaging evidence of early brain tissue degeneration in patients with vanishing white matter disease: a multimodal MR study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:926–32.
Article7. van der Lei HD, Steenweg ME, Bugiani M, Pouwels PJ, Vent IM, Barkhof F, et al. Restricted diffusion in vanishing white matter. Arch Neurol. 2012; 69:723–7.
Article8. Zhang H, Dai L, Chen N, Zang L, Leng X, Du L, et al. Fifteen novel EIF2B1-5 mutations identified in Chinese children with leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter and a long term follow-up. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0118001.9. La Piana R, Vanderver A, van der Knaap M, Roux L, Tampieri D, Brais B, et al. Adult-onset vanishing white matter disease due to a novel EIF2B3 mutation. Arch Neurol. 2012; 69:765–68.
Article10. Gowda VK, Srinivasan VM, Bhat M, Benakappa A. Case of Childhood ataxia with central nervous system hypomyelination with a novel mutation in EIF2B3 gene. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2017; 12:196–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Vanishing White Matter Disease Case with a Homozygous Point Mutation in the EIF2B2 Gene Assessed by the Whole-Exome Sequencing
- Application of Whole Exome Sequencing to Identify Disease-Causing Variants in Inherited Human Diseases
- A Korean Case of Neonatal Nemaline Myopathy Carrying KLHL40 Mutations Diagnosed Using Next Generation Sequencing
- Report of the Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service on Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis for Somatic Variants (2018–2020)
- A case of Galloway-Mowat syndrome with novel compound heterozygous variants in the WDR4 gene