Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Apr;43(2):163-177. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.163.
Duration of Treatment Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave on Spasticity and Subgroup-Analysis According to Number of Shocks and Application Site: A Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. rehabdoc@seoulmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2448999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.2.163
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate duration of the treatment effect of extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) on spasticity levels measured with Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) regardless of the patient group (stroke, multiple sclerosis, and cerebral palsy) and evaluate its spasticity-reducing effect depending on the number of shocks and site of application.
METHODS
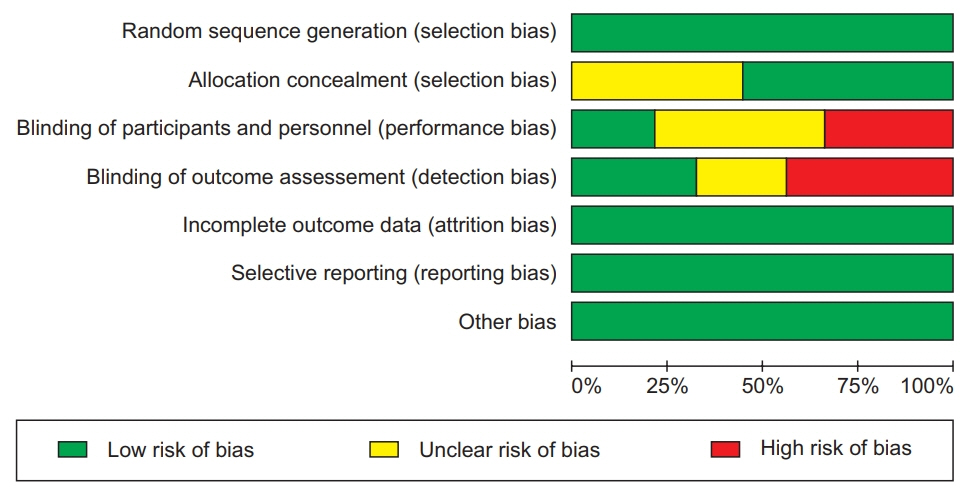
PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, and Scopus were searched from database inception to February 2018. Randomized controlled trials and cross-over trials were included. All participants had spasticity regardless of cause. ESWT was the main intervention and MAS score was the primary outcome. Among 122 screened articles, 9 trials met the inclusion criteria.
RESULTS
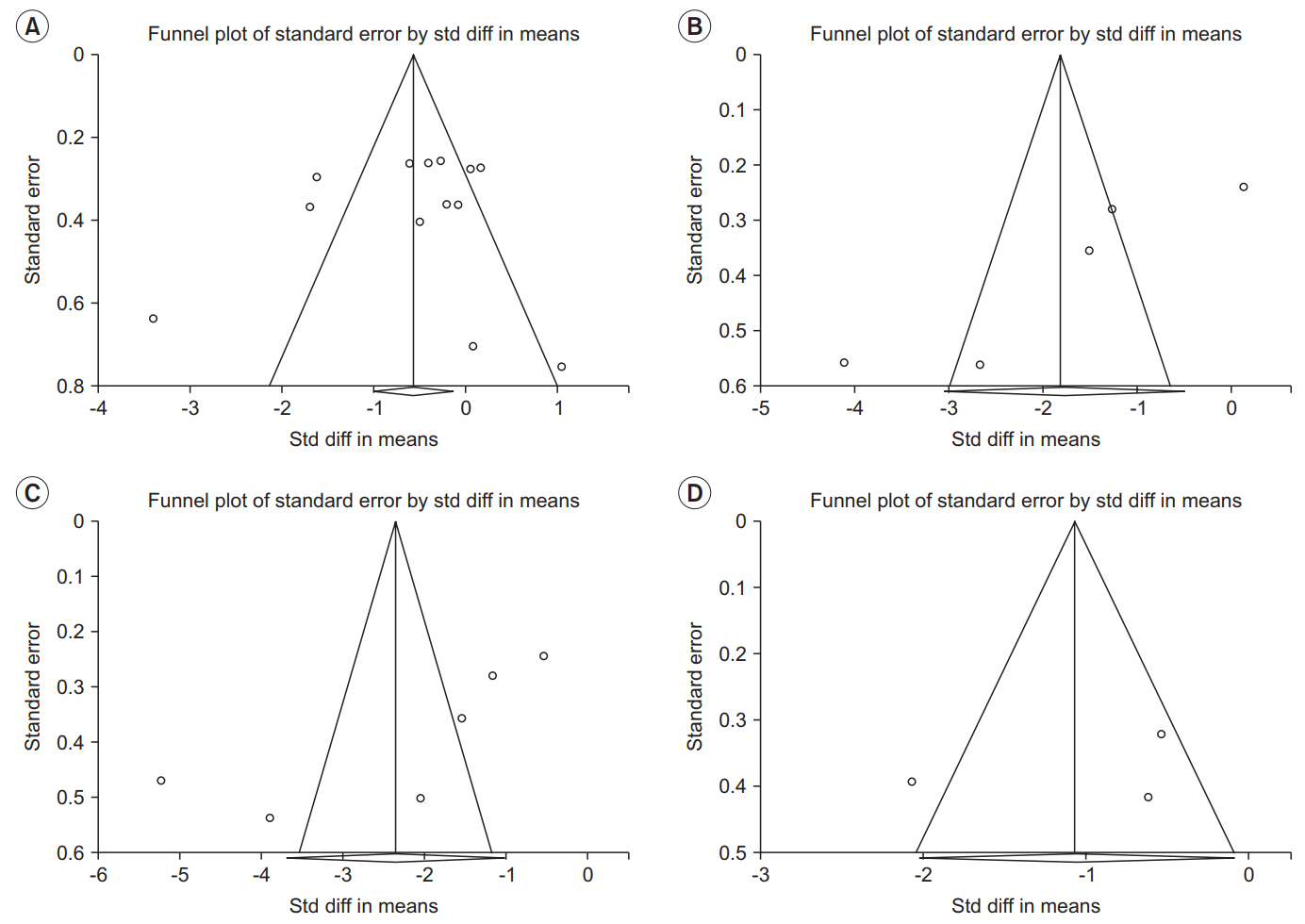
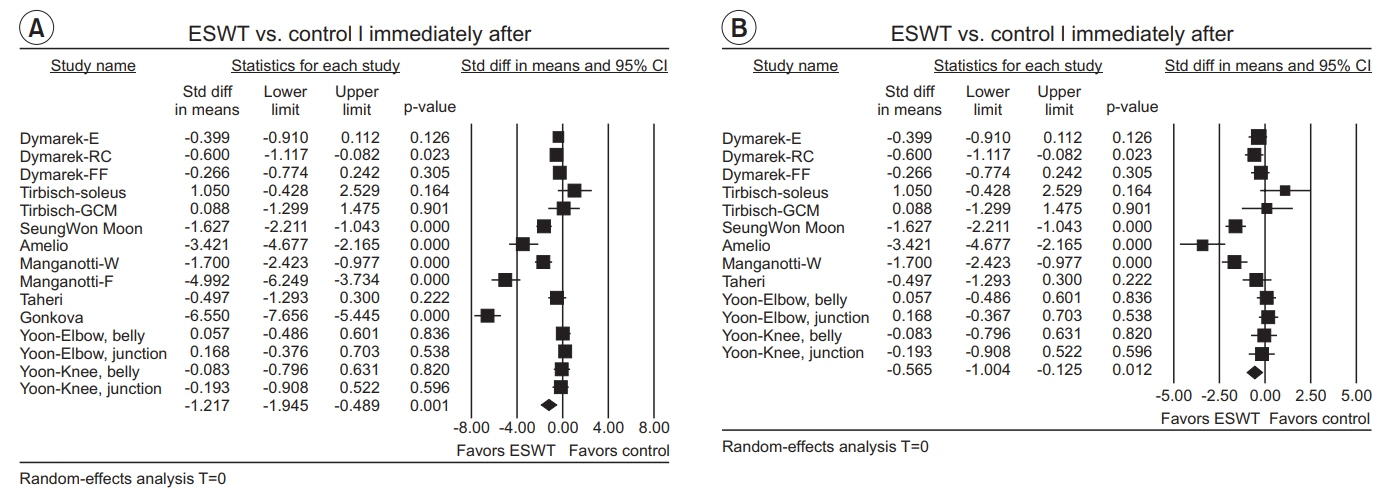
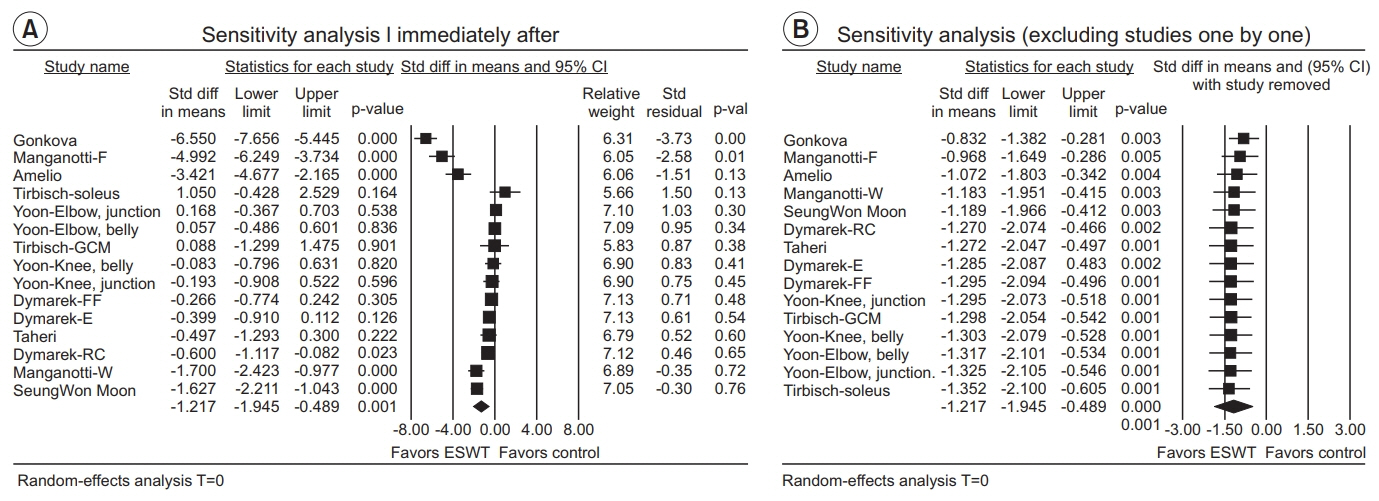
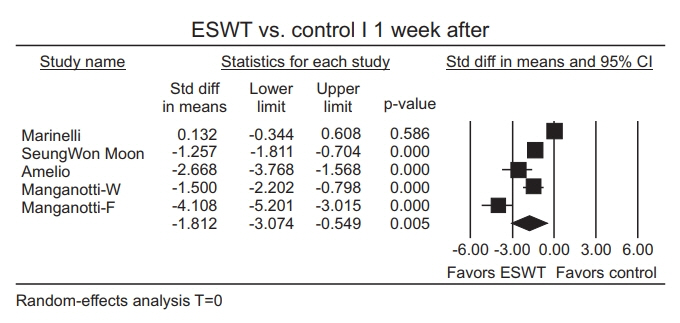
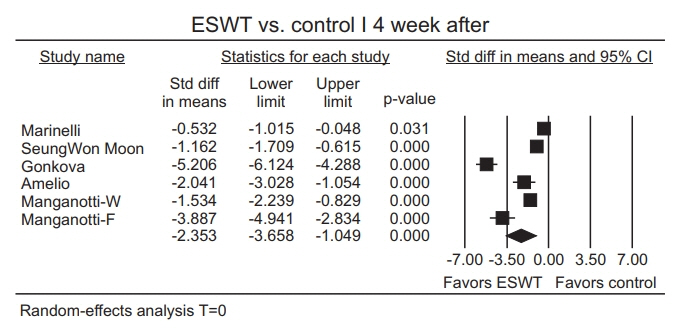
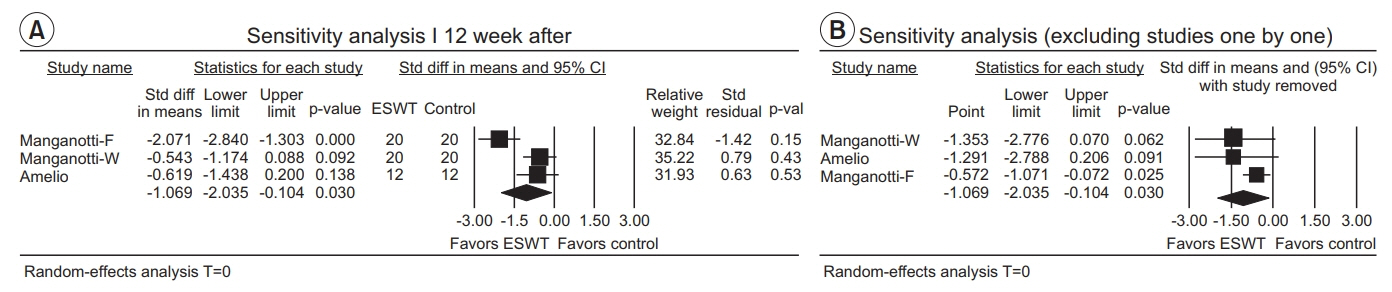
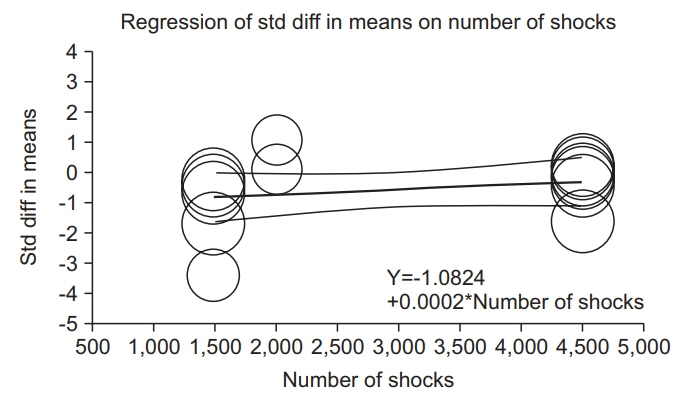
The estimate of effect size showed statistically significant MAS grade reduction immediately after treatment (standardized mean difference [SMD]=-0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], -1.00 to -0.13; p=0.012), 1 week after (SMD=-1.81; 95% CI, -3.07 to -0.55; p=0.005), 4 weeks after (SMD=-2.35; 95% CI, -3.66 to -1.05; p<0.001), and 12 weeks after (SMD=-1.07; 95% CI, -2.04 to -0.10; p=0.03). Meta-regression and subgroup analysis were performed for the "˜immediately after ESWT application' group. The prediction equation obtained from metaregression was -1.0824+0.0002* (number of shocks), which was not statistically significant. Difference in MAS grade reduction depending on site of application was not statistically significant either in subgroup analysis (knee and ankle joints vs. elbow, wrist, and finger joints).
CONCLUSION
ESWT effectively reduced spasticity levels measured with MAS regardless of patient group. Its effect maintained for 12 weeks. The number of shocks or site of application had no significant influence on the therapeutic effect of ESWT in reducing spasticity. Ongoing trials with ESWT are needed to address optimal parameters of shock wave to reduce spasticity regarding intensity, frequency, and numbers.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lance JW. Symposium synopsis. In : Feldman RG, Young RR, Koella WP, editors. Spasticity: disordered motor control. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers;1980. p. 485–4.2. Sheean G. The pathophysiology of spasticity. Eur J Neurol. 2002; 9 Suppl 1:3–9.
Article3. Tsai KH, Yeh CY, Chang HY, Chen JJ. Effects of a single session of prolonged muscle stretch on spastic muscle of stroke patients. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 2001; 25:76–81.4. Matsumoto S, Kawahira K, Etoh S, Ikeda S, Tanaka N. Short-term effects of thermotherapy for spasticity on tibial nerve F-waves in post-stroke patients. Int J Biometeorol. 2006; 50:243–50.
Article5. Levin MF, Hui-Chan C. Are H and stretch reflexes in hemiparesis reproducible and correlated with spasticity? J Neurol. 1993; 240:63–71.
Article6. Panizza M, Balbi P, Russo G, Nilsson J. H-reflex recovery curve and reciprocal inhibition of H-reflex of the upper limbs in patients with spasticity secondary to stroke. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1995; 74:357–63.
Article7. Morris S. Ashworth and Tardieu Scales: their clinical relevance for measuring spasticity in adult and paediatric neurological populations. Phys Ther Rev. 2002; 7:53–62.
Article8. Yan T, Hui-Chan CW, Li LS. Functional electrical stimulation improves motor recovery of the lower extremity and walking ability of subjects with first acute stroke: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Stroke. 2005; 36:80–5.9. Bohannon RW, Smith MB. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987; 67:206–7.
Article10. Chaussy C, Brendel W, Schmiedt E. Extracorporeally induced destruction of kidney stones by shock waves. Lancet. 1980; 2:1265–8.
Article11. Wang CJ. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7:11.
Article12. Manganotti P, Amelio E. Long-term effect of shock wave therapy on upper limb hypertonia in patients affected by stroke. Stroke. 2005; 36:1967–71.
Article13. Dymarek R, Taradaj J, Rosinczuk J. The effect of radial extracorporeal shock wave stimulation on upper limb spasticity in chronic stroke patients: a single-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016; 42:1862–75.
Article14. Gonkova MI, Ilieva EM, Ferriero G, Chavdarov I. Effect of radial shock wave therapy on muscle spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Int J Rehabil Res. 2013; 36:284–90.
Article15. Amelio E, Manganotti P. Effect of shock wave stimulation on hypertonic plantar flexor muscles in patients with cerebral palsy: a placebo-controlled study. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42:339–43.
Article16. Marinelli L, Mori L, Solaro C, Uccelli A, Pelosin E, Curra A, et al. Effect of radial shock wave therapy on pain and muscle hypertonia: a double-blind study in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2015; 21:622–9.
Article17. Lee JY, Kim SN, Lee IS, Jung H, Lee KS, Koh SE. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in patients after brain injury: a meta-analysis. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014; 26:1641–7.18. Guo P, Gao F, Zhao T, Sun W, Wang B, Li Z. Positive effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on spasticity in poststroke patients: a meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017; 26:2470–2476.
Article19. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009; 62:1006–12.
Article20. Higgins J, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Special topics in statistics. In : Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons;2008. p. 481–530.21. Higgins J, Altman DG. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In : Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons;2008. p. 184–242.22. Deeks JJ, Higgins J, Altman DG. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In : Higgins J, Green S, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons;2008. p. 243–96.23. Taheri P, Vahdatpour B, Mellat M, Ashtari F, Akbari M. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on lower limb spasticity in stroke patients. Arch Iran Med. 2017; 20:338–43.24. Yoon SH, Shin MK, Choi EJ, Kang HJ. Effective site for the application of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy on spasticity in chronic stroke: muscle belly or myotendinous junction. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017; 41:547–55.
Article25. Tirbisch L. Effects of radial shock wave therapy on sural triceps spasticity in hemiplegic patients in subacute phase: a controlled randomized trial. Kinésithérapie. 2015; 15:62–9.26. Moon SW, Kim JH, Jung MJ, Son S, Lee JH, Shin H, et al. The effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on lower limb spasticity in subacute stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:461–70.
Article27. Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Performance of the trim and fill method in the presence of publication bias and between-study heterogeneity. Stat Med. 2007; 26:4544–62.
Article28. Santamato A, Micello MF, Panza F, Fortunato F, Logroscino G, Picelli A, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of poststroke plantar-flexor muscles spasticity: a prospective open-label study. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014; 21 Suppl 1:S17–24.
Article29. Kim YW, Shin JC, Yoon JG, Kim YK, Lee SC. Usefulness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the spasticity of the subscapularis in patients with stroke: a pilot study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013; 126:4638–43.30. Sohn MK, Cho KH, Kim YJ, Hwang SL. Spasticity and electrophysiologic changes after extracorporeal shock wave therapy on gastrocnemius. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:599–604.
Article31. Kim JH, Kim JY, Choi CM, Lee JK, Kee HS, Jung KI, Yoon SR. The dose-related effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015; 39:616–23.
Article32. Zhang X, Yan X, Wang C, Tang T, Chai Y. The doseeffect relationship in extracorporeal shock wave therapy: the optimal parameter for extracorporeal shock wave therapy. J Surg Res. 2014; 186:484–92.
Article33. Wang CJ, Yang KD, Wang FS, Hsu CC, Chen HH. Shock wave treatment shows dose-dependent enhancement of bone mass and bone strength after fracture of the femur. Bone. 2004; 34:225–30.
Article34. Rompe JD, Kirkpatrick CJ, Kullmer K, Schwitalle M, Krischek O. Dose-related effects of shock waves on rabbit tendo Achillis: a sonographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:546–52.35. Sehgal N, McGuire JR. Beyond Ashworth: electrophysiologic quantification of spasticity. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1998; 9:949–79.
Article36. Eisen A, Odusote K. Amplitude of the F wave: a potential means of documenting spasticity. Neurology. 1979; 29(9 Pt 1):1306–9.
Article37. Hultborn H, Nielsen JB. H‐reflexes and F‐responses are not equally sensitive to changes in motoneuronal excitability. Muscle Nerve. 1995; 18:1471–4.
Article38. Bakheit AM, Maynard VA, Curnow J, Hudson N, Kodapala S. The relation between Ashworth scale scores and the excitability of the alpha motor neurones in patients with post-stroke muscle spasticity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003; 74:646–8.
Article39. Dymarek R, Ptaszkowski K, Słupska L, Halski T, Taradaj J, Rosinczuk J. Effects of extracorporeal shock wave on upper and lower limb spasticity in poststroke patients: a narrative review. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2016; 23:293–303.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithortripsy Experimentally Induced Cholelithiasis and Organs in the Dog
- Spasticity and Electrophysiologic Changes after Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Gastrocnemius
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy and Quantitative Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Rheologic Effect in the Patients with Post-stroke Upper Limb Spasticity: A Case Report
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Effective Site for the Application of Extracorporeal Shock-Wave Therapy on Spasticity in Chronic Stroke: Muscle Belly or Myotendinous Junction