J Korean Med Assoc.
2019 May;62(5):283-292. 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.5.283.
Child injury death statistics from 2006 to 2016 in the Republic of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Vital Statistics Division, Statistics Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 3Department of Parasitology and Institute of Medical Education, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. shuh@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2445793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2019.62.5.283
Abstract
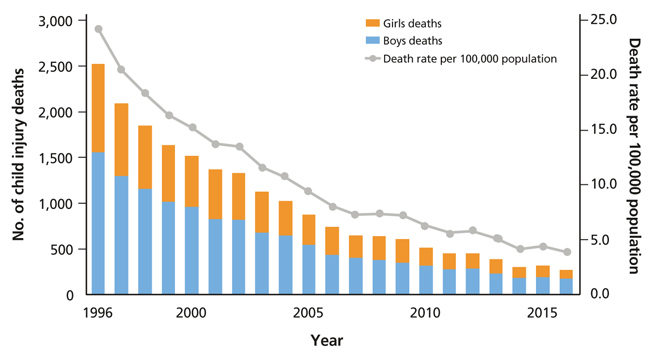
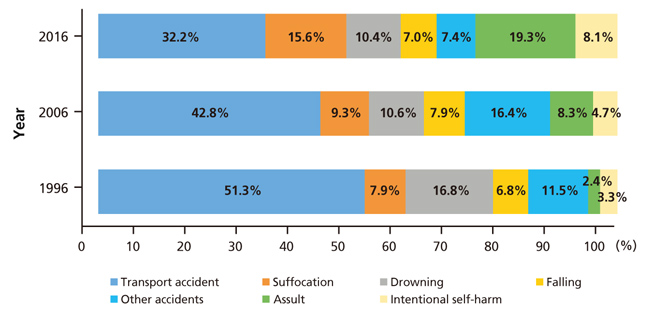
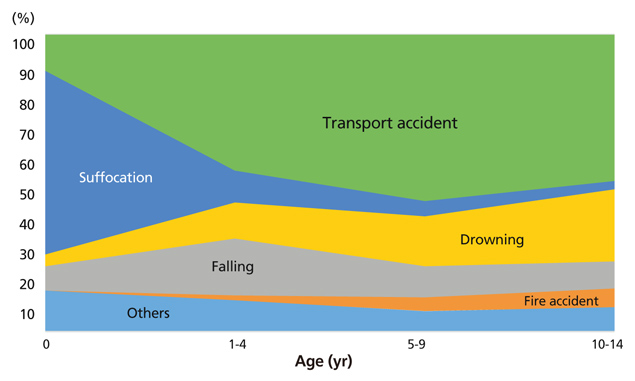
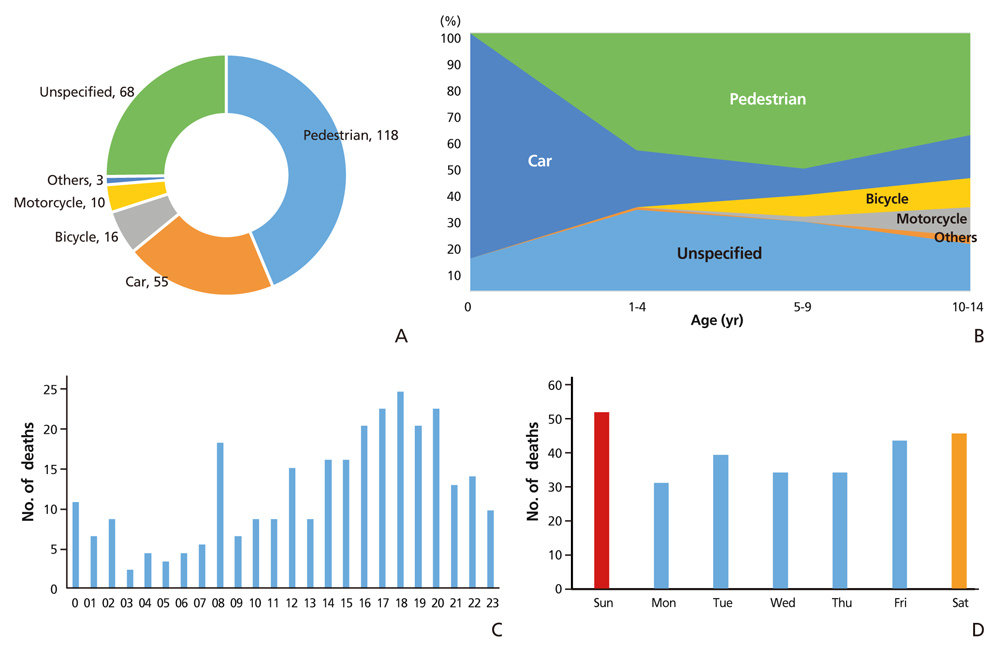
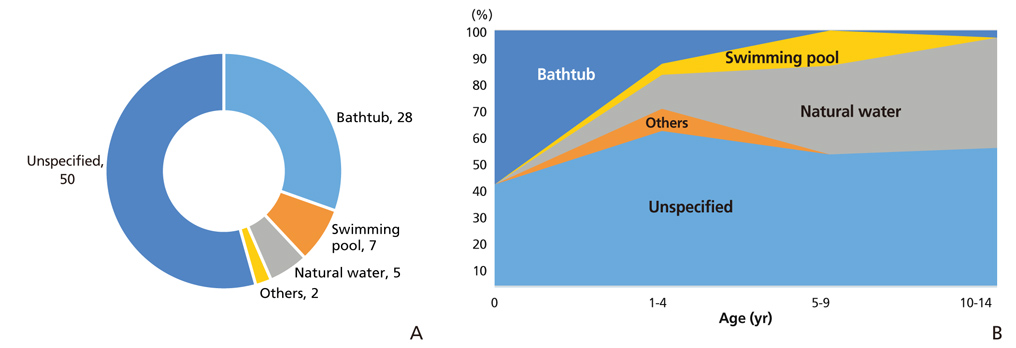
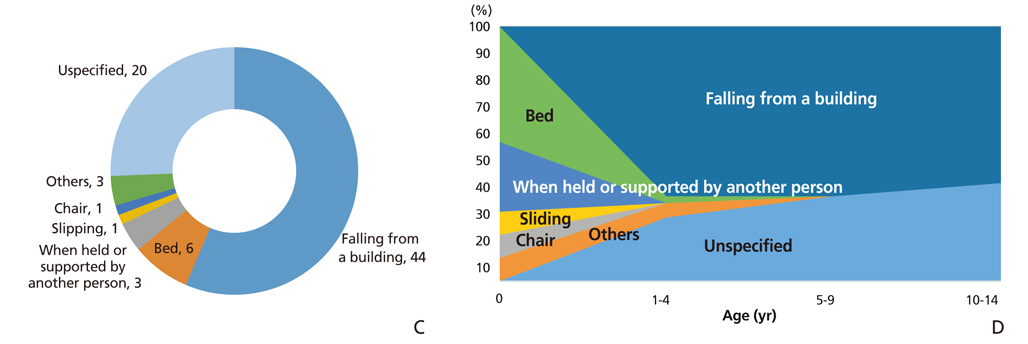
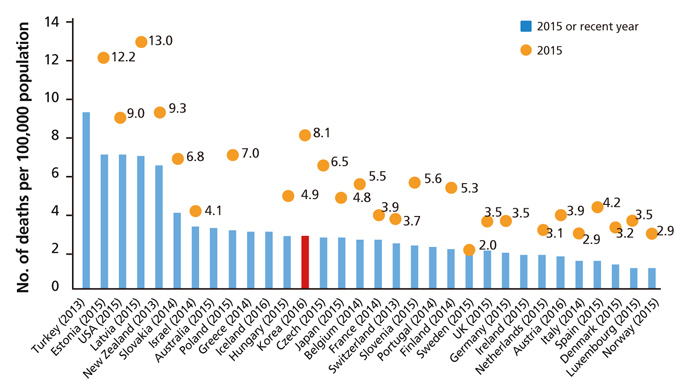
- This study aimed to analyze changing trends in child injury deaths from 2006 to 2016 and to provide basic data for initiatives to help prevent child injury deaths through improvements in social systems and education. Specific causes of death were analyzed using micro-data of the death statistics of Korea from 2006 to 2016, which were made available by Statistics Korea. Types and place of death were classified according to the KCD-7 (Korean Standard Classification of Diseases and Causes of Death). The data were compared to those of other Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development countries. Changing trends were presented. The number of child deaths by injury was 270 in 2016. The death rate was 8.1 per 100,000 population in 2006, while it was 3.9 in 2016. The death rate of boys was 1.7 times greater than that of girls. Unintentional injury deaths comprised 72.6% of all child injury deaths in 2016, while intentional injury deaths comprised 27.4%. The first leading cause of unintentional injury deaths in infants (less than 1-year-old) was suffocation, while that of children aged 1 to 14 years was transport accidents. The second leading cause of death in infants was transport accidents, that of children aged 1 to 4 was falling, and that of children aged 5 to 14 was drowning. Pedestrian accidents comprised 43.7% of the transport accidents from 2014 to 2016. To prevent child injury deaths by both unintentional and intentional causes, nation-wide policy measures and more specific interventions according to cause are required.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Statistics Korea Vital Statistics Division. Shin HY, Lee JY, Kim JE, Lee S, Youn H, Kim H, Lee J, Park MS, Huh S. Cause-of-death statistics in 2016 in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2018; 61:573.
Article2. Jung JH, Kim DK, Jang HY, Kwak YH. Epidemiology and regional distribution of pediatric unintentional emergency injury in Korea from 2010 to 2011. J Korean Med Sci. 2015; 30:1625–1630.
Article3. Woo JH, Yang HJ, Lim YS, Cho JS, Kim JJ, Park WB, Jang JH, Lee G. Predictive indicators for the severity of pediatric trauma and the prevention of injuries according to the general characteristics and pre-hospital factors of severe pediatric trauma patients. J Trauma Inj. 2014; 27:43–49.4. Jung KY, Jung JH. Epidemiology of childhood injury in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:208–213.
Article5. Kim KH. Child injury prevention: home injuries and bicycle injuries. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008; 51:230–233.
Article6. Sleet DA. The global challenge of child injury prevention. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018; 09. 04. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15091921. [Epub].
Article7. Borse NN, Gilchrist J, Dellinger AM, Rudd RA, Ballesteros MF, Sleet DA. CDC childhood injury report: patterns of unintentional injuries among 0-19 year olds in the United States, 2000-2006 [Internet]. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2008. cited 2019 Apr 5. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/safechild/images/CDC-ChildhoodInjury.pdf.8. UNICEF. A league table of child deaths by injury in rich nations. Florence: UNICEF;2001.9. Kong SG. Current use of safety restraint systems and front seats in Korean children based on the 2008-2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Pediatr. 2018; 61:381–386.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Trend of Mortality Rate and Injury Burden of Transport Accidents, Suicides, and Falls
- Cause-of-death statistics in 2016 in the Republic of Korea
- Cause-of-death statistics in the Republic of Korea, 2014
- Causes of Child Mortality (1 to 4 Years of Age) From 1983 to 2012 in the Republic of Korea: National Vital Data
- Cause-of-death statistics in 2018 in the Republic of Korea