Clin Orthop Surg.
2019 Jun;11(2):159-163. 10.4055/cios.2019.11.2.159.
Relationship between Body Mass Index and Complications during the First 45 Days after Primary Total Hip and Knee Replacement: A Single-Center Study from South America
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Osteoarticular Diseases, Centro Médico Imbanaco, Cali, Colombia. correandres@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2445049
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2019.11.2.159
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The goal of this study was to evaluate the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and early complications of total hip replacement (THR) and total knee replacement (TKR).
METHODS
This is a retrospective study of patients who underwent primary THR and TKR between January 2011 and December 2015. We included patients between 18 and 90 years of age with BMI less than 40 kg/m2 with a minimal postoperative follow-up time of 45 days. The primary outcomes were the presence of infection, mechanical complications (dislocation, fractures, arthrofibrosis, or neuropraxia), and thromboembolic events. Overweight and obesity were defined as a BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 and ≥ 30 kg/m2, respectively.
RESULTS
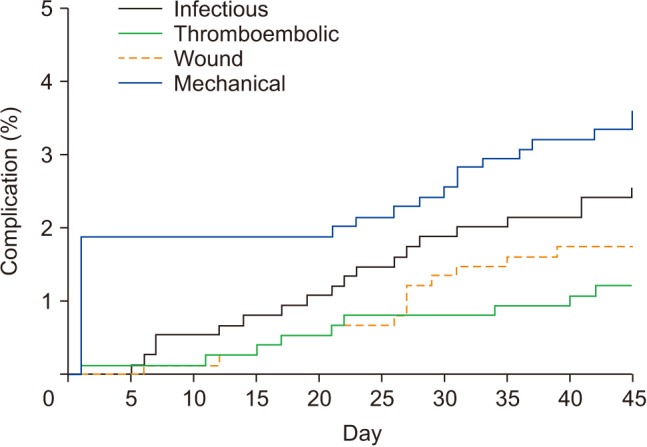
In total 750 patients were included (THR, 268; TKR, 482) with a mean age of 65.0 ± 12.4 years. The percentage of patients with normal weight, overweight, and obesity was 24.9% (n = 187), 41.7% (n = 313), and 33.4% (n = 250), respectively. The early complication rate was 8.9% (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.1% to 11.2%). Infection and mechanical complications were most prevalent. There was no statistically significant relationship between the incidence of complications and BMI (obesity vs. normal weight: hazard ratio [HR], 1.49; 95% CI, 0.72 to 3.06; p = 0.282); however, there was a tendency toward a greater risk of infectious complications in the patients with obesity (HR, 6.08; 95% CI, 0.75 to 49.16; p = 0.090). Patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) had more risk of infectious complications than those without DM (HR, 2.60; 95% CI, 1.00 to 6.79).
CONCLUSIONS
There was no statistical relationship between BMI and early complications of THR and TKR. Nonetheless, there was a tendency toward a higher risk of infection in patients with some degree of obesity.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Busato A, Roder C, Herren S, Eggli S. Influence of high BMI on functional outcome after total hip arthroplasty. Obes Surg. 2008; 18(5):595–600. PMID: 18369684.
Article2. Dowsey MM, Choong PF. Obese diabetic patients are at substantial risk for deep infection after primary TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467(6):1577–1581. PMID: 18841430.
Article3. Jain NB, Guller U, Pietrobon R, Bond TK, Higgins LD. Comorbidities increase complication rates in patients having arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (435):232–238.
Article4. Winiarsky R, Barth P, Lotke P. Total knee arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80(12):1770–1774. PMID: 9875934.
Article5. Suleiman LI, Ortega G, Ong'uti SK, et al. Does BMI affect perioperative complications following total knee and hip arthroplasty? J Surg Res. 2012; 174(1):7–11. PMID: 21816426.
Article6. Wang JL, Gadinsky NE, Yeager AM, Lyman SL, Westrich GH. The increased utilization of operating room time in patients with increased BMI during primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(4):680–683. PMID: 23142454.
Article7. Lubbeke A, Zingg M, Vu D, et al. Body mass and weight thresholds for increased prosthetic joint infection rates after primary total joint arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2016; 87(2):132–138. PMID: 26731633.8. Issa K, Harwin SF, Malkani AL, Bonutti PM, Scillia A, Mont MA. Bariatric orthopaedics: total hip arthroplasty in superobese patients (those with a BMI of ≥50 kg/m2). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98(3):180–185. PMID: 26842407.
Article9. Alvi HM, Mednick RE, Krishnan V, Kwasny MJ, Beal MD, Manning DW. The effect of BMI on 30 day outcomes following total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(7):1113–1117. PMID: 25683294.
Article10. Wallace G, Judge A, Prieto-Alhambra D, de Vries F, Arden NK, Cooper C. The effect of body mass index on the risk of post-operative complications during the 6 months following total hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22(7):918–927. PMID: 24836211.11. Moran M, Walmsley P, Gray A, Brenkel IJ. Does body mass index affect the early outcome of primary total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(7):866–869. PMID: 16230236.
Article12. Patel AD, Albrizio M. Relationship of body mass index to early complications in hip replacement surgery: study performed at Hinchingbrooke Hospital, Orthopaedic Directorate, Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire. Int Orthop. 2007; 31(4):439–443. PMID: 16960720.13. Jiganti JJ, Goldstein WM, Williams CS. A comparison of the perioperative morbidity in total joint arthroplasty in the obese and nonobese patient. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (289):175–179. PMID: 8472410.
Article14. Deshmukh RG, Hayes JH, Pinder IM. Does body weight influence outcome after total knee arthroplasty? A 1-year analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17(3):315–319. PMID: 11938508.
Article15. Perka C, Arnold U, Buttgereit F. Influencing factors on perioperative morbidity in knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (378):183–191.
Article16. Wagner ER, Kamath AF, Fruth KM, Harmsen WS, Berry DJ. Effect of body mass index on complications and reoperations after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016; 98(3):169–179. PMID: 26842406.
Article17. Haverkamp D, Klinkenbijl MN, Somford MP, Albers GH, van der Vis HM. Obesity in total hip arthroplasty: does it really matter? A meta-analysis. Acta Orthop. 2011; 82(4):417–422. PMID: 21657972.18. Felson DT. Weight and osteoarthritis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996; 63(3 Suppl):430S–432S. PMID: 8615335.
Article19. Namba RS, Paxton L, Fithian DC, Stone ML. Obesity and perioperative morbidity in total hip and total knee arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(7 Suppl 3):46–50. PMID: 16214002.
Article20. Selvan D, Donnelly T, McNicholas M. Management of complications of primary total knee replacement. Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27(6):355–363.21. Nutt JL, Papanikolaou K, Kellett CF. Complications of total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27(5):272–276.22. Liu W, Wahafu T, Cheng M, Cheng T, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The influence of obesity on primary total hip arthroplasty outcomes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101(3):289–296. PMID: 25817907.
Article23. Singh JA, Jensen MR, Harmsen SW, Lewallen DG. Are gender, comorbidity, and obesity risk factors for postoperative periprosthetic fractures after primary total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(1):126–131. PMID: 22552223.
Article24. Maradit Kremers H, Lewallen LW, Mabry TM, Berry DJ, Berbari EF, Osmon DR. Diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia, hemoglobin A1C and the risk of prosthetic joint infections in total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(3):439–443. PMID: 25458090.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Perioperative Anesthetic Management of Total Knee or Hip Replacement Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study
- Total Hip Replacement for Ankylosed and Deformed Hip
- Geometric Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Study on the Incidence of Pulmonary Embolism before and after Hip and Knee Replacement Arthroplasties
- Quality of Life after Total Knee and Total Hip Replacement