Ann Dermatol.
2019 Jun;31(3):355-356. 10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.355.
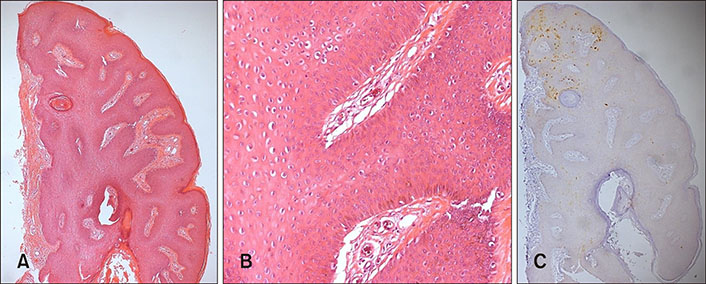
A Case of Suggested Pigmented Condyloma Acuminatum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. hjpark@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2444876
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2019.31.3.355
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park KC, Jung SY, Choi YM, Kim SH, Lee YS. Detection of genital human papilloma viruses using PCR. Ann Dermatol. 1991; 3:37–39.
Article2. Sano T, Oyama T, Kashiwabara K, Fukuda T, Nakajima T. Expression status of p16 protein is associated with human papillomavirus oncogenic potential in cervical and genital lesions. Am J Pathol. 1998; 153:1741–1748.
Article3. Shimizu A, Tamura A, Nakatani Y, Shimizu N, Hoshino H, Ishikawa O. Pigmented plaque-type condyloma acuminatum associated with human papillomavirus type 6. J Dermatol. 2012; 39:860–861.
Article4. Kazlouskaya V, Shustef E, Allam SH, Lal K, Elston D. Expression of p16 protein in lesional and perilesional condyloma acuminata and bowenoid papulosis: clinical significance and diagnostic implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013; 69:444–449.
Article5. Shimizu A, Kato M, Ishikawa O. Pigmented condyloma acuminatum. J Dermatol. 2014; 41:337–339.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Human Papillomavirus DNA in Genital and Laryngeal Papilloma Using the Polymerase Chain Reaction
- The Successful Treatment of Intraurethral Condyloma Acuminatum with Thiotepa: Report of a Case
- A Case of Condyloma Acuminatum of Pharynx
- A Case of unusual condyloma Acuminatum in an Immunosuppressed Patient
- Intraurethral Instillation of 5-fluorouracil with Suprapubic Cystostomy for Intraurethral Condyloma Acuminatum