J Adv Prosthodont.
2019 Apr;11(2):105-111. 10.4047/jap.2019.11.2.105.
Sealing capability and marginal fit of titanium versus zirconia abutments with different connection designs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, University of Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey. nazmiye.sonmez@istanbul.edu.tr
- 2Department of Medical Microbiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Istanbul, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2444144
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2019.11.2.105
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Limited data is available regarding the differences for possible microleakage problems and fitting accuracy of zirconia versus titanium abutments with various connection designs. The purpose of this in vitro study was to investigate the effect of connection design and abutment material on the sealing capability and fitting accuracy of abutments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
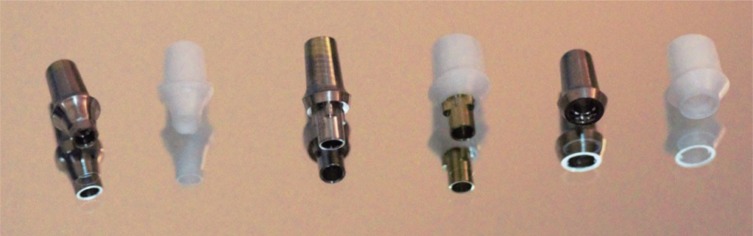
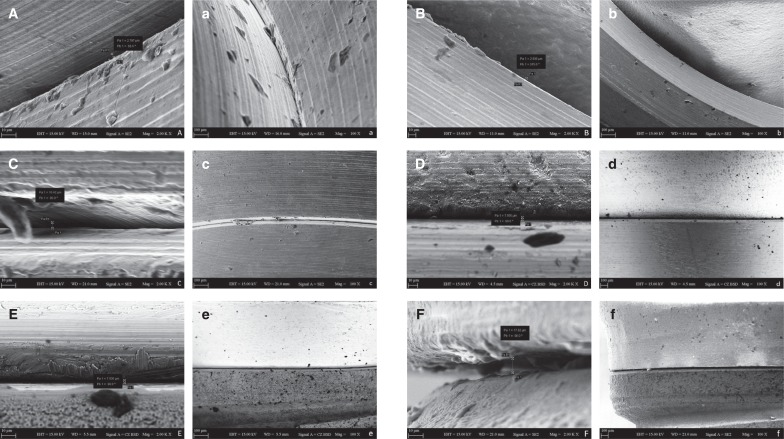
A total of 42 abutments with different connection designs [internal conical (IC), internal tri-channel (IT), and external hexagonal (EH)] and abutment materials [titanium (Ti) and zirconia (Zr)] were evaluated. The inner parts of implants were inoculated with 0.7 µL of polymicrobial culture (P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, T. denticola and F. nucleatum) and connected with their respective abutments under sterile conditions. The penetration of bacteria into the surrounding media was assessed by the visual evaluation of turbidity at each time point and the number of colony forming units (CFUs) was counted. The marginal gap at the implant- abutment interface (IAI) was measured by scanning electron microscope. The data sets were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis followed by Mann-Whitney U tests with the Bonferroni-Holm correction (α=.05).
RESULTS
Statistically significant difference was found among the groups based on the results of leaked colonies (P<.05). The EH-Ti group characterized by an external hexagonal connection were less resistant to bacterial leakage than the groups EH-Zr, IT-Zr, IT-Ti, IC-Zr, and IC-Ti (P<.05). The marginal misfit (in µm) of the groups were in the range of 2.7-4.0 (IC-Zr), 1.8-5.3 (IC-Ti), 6.5-17.1 (IT-Zr), 5.4-12.0 (IT-Ti), 16.8-22.7 (EH-Zr), and 10.3-15.4 (EH-Ti).
CONCLUSION
The sealing capability and marginal fit of abutments were affected by the type of abutment material and connection design.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gracis S, Michalakis K, Vigolo P, Vult von Steyern P, Zwahlen M, Sailer I. Internal vs external connections for abutments/reconstructions: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23:202–216. PMID: 23062143.
Article2. Shim HW, Yang BE. Long-term cumulative survival and mechanical complications of single-tooth Ankylos Implants: focus on the abutment neck fractures. J Adv Prosthodont. 2015; 7:423–430. PMID: 26813443.
Article3. Binon PP. Implants and components: entering the new millennium. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15:76–94. PMID: 10697942.4. Koutouzis T, Neiva R, Nonhoff J, Lundgren T. Placement of implants with platform-switched Morse taper connections with the implant-abutment interface at different levels in relation to the alveolar crest: a short-term (1-year) randomized prospective controlled clinical trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013; 28:1553–1563. PMID: 24278924.
Article5. Siadat H, Beyabanaki E, Mousavi N, Alikhasi M. Comparison of fit accuracy and torque maintenance of zirconia and titanium abutments for internal tri-channel and external-hex implant connections. J Adv Prosthodont. 2017; 9:271–277. PMID: 28874994.
Article6. Moon SJ, Kim HJ, Son MK, Chung CH. Sinking and fit of abutment of locking taper implant system. J Adv Prosthodont. 2009; 1:97–101. PMID: 21165262.
Article7. Lee JH, Kim DG, Park CJ, Cho LR. Axial displacements in external and internal implant-abutment connection. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014; 25:e83–e89. PMID: 23088616.
Article8. Goodacre CJ, Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Clinical complications of osseointegrated implants. J Prosthet Dent. 1999; 81:537–552. PMID: 10220658.
Article9. Nakamura K, Kanno T, Milleding P, Ortengren U. Zirconia as a dental implant abutment material: a systematic review. Int J Prosthodont. 2010; 23:299–309. PMID: 20617217.10. Teixeira W, Ribeiro RF, Sato S, Pedrazzi V. Microleakage into and from two-stage implants: an in vitro comparative study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011; 26:56–62. PMID: 21365038.11. Mishra SK, Chowdhary R, Kumari S. Microleakage at the different implant abutment interface: A systematic review. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017; 11:ZE10–ZE15. PMID: 28764310.
Article12. Al-Jadaa A, Attin T, Peltomäki T, Schmidlin PR. Comparison of three in vitro implant leakage testing methods. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015; 26:e1–e7.13. Harder S, Dimaczek B, Açil Y, Terheyden H, Freitag-Wolf S, Kern M. Molecular leakage at implant-abutment connection--in vitro investigation of tightness of internal conical implant-abutment connections against endotoxin penetration. Clin Oral Investig. 2010; 14:427–432.
Article14. Nascimento C, Ikeda LN, Pita MS, Pedroso e Silva RC, Pedrazzi V, Albuquerque RF, Ribeiro RF. Marginal fit and microbial leakage along the implant-abutment interface of fixed partial prostheses: An in vitro analysis using Checkerboard DNA-DNA hybridization. J Prosthet Dent. 2015; 114:831–838. PMID: 26359546.15. Abdelhamed MI, Galley JD, Bailey MT, Johnston WM, Holloway J, McGlumphy E, Leblebicioglu B. A Comparison of Zirconia and Titanium Abutments for Microleakage. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2015; 17:e643–e651. PMID: 25726941.
Article16. Nascimento CD, Pita MS, Fernandes FHNC, Pedrazzi V, de Albuquerque RF Junior, Ribeiro RF. Bacterial adhesion on the titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014; 25:337–343. PMID: 23316996.
Article17. Nascimento CD, Pita MS, Fernandes FHNC, Pedrazzi V, de Albuquerque RF Junior, Ribeiro RF. Bacterial adhesion on the titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014; 25:337–343. PMID: 23316996.
Article18. Smith NA, Turkyilmaz I. Evaluation of the sealing capability of implants to titanium and zirconia abutments against Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia, and Fusobacterium nucleatum under different screw torque values. J Prosthet Dent. 2014; 112:561–567. PMID: 24656409.
Article19. Black DL, Turkyilmaz I, Lien W, Chong CH. Evaluation of the sealing capability of the internal conical connections of implants with titanium and zirconia abutments. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2017; 18:915–922. PMID: 28989130.20. Baixe S, Fauxpoint G, Arntz Y, Etienne O. Microgap between zirconia abutments and titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:455–460. PMID: 20556243.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of marginal and internal fit of zirconia abutments with titanium abutments in internal hexagonal implants
- Comparison of fit accuracy and torque maintenance of zirconia and titanium abutments for internal tri-channel and external-hex implant connections
- The effect of a titanium socket with a zirconia abutment on screw loosening after thermocycling in an internally connected implant: a preliminary study
- Marginal and internal fit of all ceramic crown using the replica technique and the triple-scan protocol
- Zirconia Abutment Fracture in the Anterior Region: Case Series